Abstract
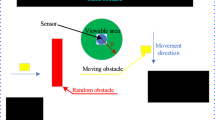
Path planning is required for a vehicle with the mission which includes the avoidance of certain areas. There are various kinds of algorithms for path planning. Typical algorithms are Voronoi diagram, visibility graph, potential field and trajectory optimization. These algorithms often need post-processing technique to satisfy the vehicles’ constraints such as turning angle and minimum moving distance. The proposed method does not need post-processing steps and always provides the fast and stable solution. It also gives a unique solution, while rapidly exploring random tree algorithms do not guarantee same solution. We use the local search and the global search at the same time in order to get a more appropriate path. We validate the proposed method by simulations and the results show that the method is fast and effective for path planning.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
O. M. Hammouri and M. M. Matalgah, “Voronoi path planning technique for recovering communication in UAVs,” Proc. of the 2008 IEEE/ACS International Conf. on Computer Systems and Applications, pp. 403–406, 2008.
M. C. Novy, D. R. Jacques, and M. Pachter, “Air vehicle optimal trajectories between two radars,” Proc. of American Control Conf., vol. 1, pp. 785–790, 2002.
M. Neus and S. Maouche, “Motion planning using the modified visibility graph,” Proc. of the IEEE International Conf. on Systems, Man and Cybernetics, vol. 4, pp. 12–15, 1999.
H. P. Huang and S. Y. Chung, “Dynamic visibility graph for path planning,” Proc. of IEEE/RSJ International Conf. on Intelligent Robots and Systems, Sendai, Japan, 2004.
H. J. S. Feder and J. J. E. Slotine, “Real-time path planning using harmonic potentials in dynamic environments,” Proc. of IEEE International Conf. on Robotics and Automation, pp. 874–881, vol. 1, 1997.
P. T. Kabamba, S. M. Meerkov, and F. H. Zeitz III, “Optimal path planning for unmanned combat aerial vehicles to defeat radar tracking,” Journal of Guidance, Control, and Dynamics, vol. 29, no. 2, pp. 279–288, 2006. [click]
J. J. Ruz, O. Arevalo, J. M. de la Cruz, and G. Pajares, “Using MILP for UAVs trajectory optimization under radar detection risk,” Proc. of 11th IEEE International Conf. on Emerging Technologies and Factory Automation, pp. 1–4, 2006.
K. Yang “Anytime Synchronized-Biased-Greedy Rapidlyexploring Random Tree Path Planning in Two Dimensional Complex Environments,” International Journal of Control, Automation, and Systems, vol. 9, no. 4, pp. 750–758, 2011. [click]
A. S. Lopez, R. Zapata, and M. O. Lama, “Sampling-based motion planning: a survey,” Computaciony Sistemas, vol. 12, no. 1, pp. 5–24, 2008.
B. Park, J. Choi, and W Chung, “Sampling-Based Retraction Method for Improving the Quality of Mobile Robot Path Planning,” International Journal of Control, Automation, and Systems, vol. 10, no. 5, pp. 982–991, 2012. [click]
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Recommended by Associate Editor Kang-Hyun Jo under the direction of Editor Fuchun Sun.
Won-Young Shin received his M.S. degree in Industrial Engineering from POSTECH University, Korea, in 2003. He is currently a senior researcher in Agency for Defense Development in Korea. His research interests include a mission planning, weapon modeling & simulation, combinatorial optimization.
Jong-Jin Shin received his M.S. degree in Mechanical Engineering from Stanford University, U.S.A., in 2003. He is currently a senior researcher in Agency for Defense Development in Korea. His research interests include a mission planning and target/background modeling & simulation.
Byung-Ju Kim received his M.S. and Ph.D. degrees in Electrical Engineering from Kyungpook National University, Korea, in 1999 and in 2007, respectively. He is currently a senior researcher in Agency for Defense Development in Korea. His research interests include a mission planning and target/background modeling & simulation.
Kwang-Rae Jeong received his M.S. degree in Electrical & Electronic Engineering from Yonsei University, Korea, in 2010. He is currently a researcher in Agency for Defense Development in Korea. His research interests include a mission planning and weapon modeling & simulation.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Shin, WY., Shin, JJ., Kim, BJ. et al. Line segment selection method for fast path planning. Int. J. Control Autom. Syst. 15, 1322–1331 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12555-015-0261-2
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12555-015-0261-2