Abstract
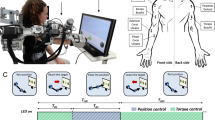
The objective of this study is to design a meal assistance system operated by electromyogram (EMG) signals. The system consists of four parts, EMG data acquisition, onset analysis, control circuit and operation of meal assistance robot. An algorithm based on EMG power with adaptive threshold is proposed for onset analysis, and applied to the operation of robot via control circuit. The performance of EMG-control system is tested in rate of success and comfort by both subjective and objective indices. The results show EMG signals acquired from active muscles in a human body can be used as control signals for the apparatus, by the proposed onset detection algorithm with adaptive threshold. The high rate of success and comfort of meal assistance system operated by EMG signals guarantee its use for patients with disabled upper limbs.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
K. Nishiwaki and K. Yano, “Variable impedance control of meal assistance robot using potential method,” Proc. of IEEE/RSJ International Conference on Intelligent Robots and Systems, Nice, France, pp. 3242–3247, September 2008.
M. Nakamura and T. Zhang, “Neural networkbased hybrid human-in-the-loop control for meal assistance orthosis,” IEEE Trans. Neural Syst. Rehabil Eng., vol. 14, no. 1, pp. 64–75, March 2006.
T. Sakaki, “An effective design method for welfare robot and its application to the design of mealassistance robot,” Proc. of the 17th IEEE International Symposium on Robot and Human Interactive Communication, Munich, Germany, pp. 309–314, August 2008.
M. Topping, “An overview of the development of Handy 1, a rehabilitation robot to assist the severely disabled,” Journal of Intelligent and Robotic Systems, vol. 34, no. 3, pp. 253–263, July 2002.
W. H. Morewood, “The Model 5 Winsford Feeder,” United States Patents US 4,277,213 and #5,037,261, 1981.
S. Ishii, S. Tanaka, and F. Hiramatsu, “Meal assistance robot for severely handicapped people,” Proc. of IEEE Int. Conf. Robotics Automation, Nagoya, Japan, vol. 2, pp. 1308–1313, May 1995.
M. C. Su, S. Y. Su, and G. D. Chen, “A low cost vision-based human-computer interface for people with sever disabilities,” Biomedical Engineering-Applications, Basis, & Communication, vol. 17, no. 6, pp. 10–18, December 2005.
S. Goto, M. Nakamura, and T. Sugi, “Development of meal assistance orthosis for disabled persons using EOG signal and dish image,” International Journal of Advanced Mechatronic Systems, vol. 1, no. 2, pp. 107–115, 2008.
C. Cipriani, F. Zaccone, S. Micera, and M. C. Carrozza, “On the shared control of an EMGcontrolled prosthetic hand: analysis of userprosthesis interaction,” IEEE Trans. on Robotics, vol. 24, no. 1, pp. 170–184, February 2008.
R. J. Cordo and L. M. Nashner, “Properties of postural adjustments associated with rapid arm movements,” J. Neurophysiol, vol. 47, no. 2, pp. 287–308, February 1982.
J. R. Carey, J. D. Allison, and M. O. Mundale, “Electromyographic study of muscular overflow during precision hand grip,” Phys. Ther, vol. 63, pp. 505–511, April 1983.
S. Kuroiwa, A. Yamaguchi, K. Ishii, S. Matsumoto, S. Ishii, and K. Sato, “Development of the meal assistance robot,” Proc. 17th RESJA Annual Conf, Okayama, Japan, pp. 443–446, August 2002.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Recommended by Editorial Board member Duk-Sun Shim under the direction of Editor Young-Hoon Joo. This work is supported by National Nature Science Foundation of China 60543005, 60674089; and Shanghai Leading Academic Discipline Project, B504.
Xiu Zhang received her B.S. degree in Electrical Engineering from University of Shanghai for Science and Technology in 2005, and now is a Ph.D. candidate in Pattern Recognition and Intelligent System at East China University of Science and Technology. Her research interests include neuro-physiological signal processing and control.
Xingyu Wang received his Ph.D. degree in Engineering from East China University of Science and Technology in 1984 and is presently a Professor at East China University of Science and Technology. He has worked on control theory and its application, especially biomedical engineering.
Bei Wang received her Ph.D. degree in Engineering from Saga University in 2009. She is also an assistant researcher at East China University of Science and Technology from 2003. She has worked on biomedical signal analysis and application.
Takenao Sugi received his Ph.D. degree in Engineering from Saga University in 1999 and is presently an Associated Professor at Saga University. He has worked on automatic EEG interpretation and Brain Motor function analysis.
Masatoshi Nakamura received his Ph.D. degree in Engineering from Kyushu University in 1974 and was a Professor at Saga University. He has worked on control theory and its application in biomedical engineering, robotics and power system control.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Zhang, X., Wang, X., Wang, B. et al. Meal assistance system operated by electromyogram (EMG) signals: Movement onset detection with adaptive threshold. Int. J. Control Autom. Syst. 8, 392–397 (2010). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12555-010-0226-4
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12555-010-0226-4