Abstract
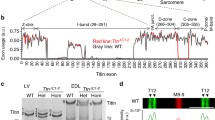
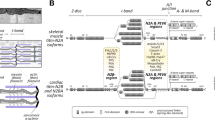
The giant multi-functional striated muscle protein titin is the third most abundant muscle protein after myosin and actin. Titin plays a pivotal role in myocardial passive stiffness, structural integrity and stress-initiated signaling pathways. The complete sequence of the human titin gene contains three isoform-specific mutually exclusive exons [termed novel exons (novex)] coding for the I-band sequence, named novex-1 (exon 45), novex-2 (exon 46) and novex-3 (exon 48). Transcripts containing either the novex-1 or novex-2 exons code for the novex-1 and novex-2 titin isoforms. The novex-3 transcript contains a stop codon and polyA tail signal, resulting in an unusually small (∼700 kDa) isoform, referred to as novex-3 titin. This ‘tiny titin’ isoform extends from the Z-disc (N-terminus) to novex-3 (C-terminus) and is expressed in all striated muscles. Biochemical analysis of novex-3 titin in cardiomyocytes shows that obscurin, a vertebrate muscle protein, binds to novex-3 titin. The novex-3/obscurin complex localizes to the Z-disc region and may regulate calcium, and SH3- and GTPase-associated myofibrillar signaling pathways. Therefore, novex-3 titin could be involved in stress-initiated sarcomeric restructuring.

Similar content being viewed by others
References
Ackermann MA, Shriver M, Perry NA, Hu LY, Kontrogianni-Konstantopoulos A (2014) Obscurins: Goliaths and Davids take over non-muscle tissues. PLoS One 9:e88162
Arber S, Halder G, Caroni P (1994) Muscle LIM protein, a novel essential regulator of myogenesis, promotes myogenic differentiation. Cell 79:221–231
Bang ML, Centner T, Fornoff F, Geach AJ, Gotthardt M, McNabb M, Witt CC, Labeit D, Gregorio CC, Granzier H, Labeit S (2001) The complete gene sequence of titin, expression of an unusual approximately 700-kDa titin isoform, and its interaction with obscurin identify a novel Z-line to I-band linking system. Circ Res 89:1065–1072
Brown DD, Davis AC, Conlon FL (2006) Xtn3 is a developmentally expressed cardiac and skeletal muscle- specific novex-3 titin isoform. Gene Expr Patterns 6:913–918
Ceyhan-Birsoy O, Agrawal PB, Hidalgo C, Schmitz-Abe K, DeChene ET, Swanson LC, Soemedi R, Vasli N, Iannaccone ST, Shieh PB, Shur N, Dennison JM, Lawlor MW, Laporte J, Markianos K, Fairbrother WG, Granzier H, Beggs AH (2013) Recessive truncating titin gene, TTN, mutations presenting as centronuclear myopathy. Neurology 81:1205–1214
Chauveau C, Rowell J, Ferreiro A (2014) A rising titan: TTN review and mutation update. Hum Mutat 35:1046–1059
Freiburg A, Trombitas K, Hell W, Cazorla O, Fougerousse F, Centner T, Kolmerer B, Witt C, Beckmann JS, Gregorio CC, Granzier H, Labeit S (2000) Series of exon-skipping events in the elastic spring region of titin as the structural basis for myofibrillar elastic diversity. Circ Res 86:1114–1121
Furst DO, Osborn M, Nave R, Weber K (1988) The organization of titin filaments in the half-sarcomere revealed by monoclonal antibodies in immunoelectron microscopy: a map of ten nonrepetitive epitopes starting at the Z line extends close to the M line. J Cell Biol 106:1563–1572
Gerull B, Gramlich M, Atherton J, McNabb M, Trombitas K, Sasse-Klaassen S, Seidman JG, Seidman C, Granzier H, Labeit S, Frenneaux M, Thierfelder L (2002) Mutations of TTN, encoding the giant muscle filament titin, cause familial dilated cardiomyopathy. Nat Genet 30:201–204
Granzier HL, Irving TC (1995) Passive tension in cardiac muscle: contribution of collagen, titin, microtubules, and intermediate filaments. Biophys J 68:1027–1044
Granzier HL, Labeit S (2004) The giant protein titin: a major player in myocardial mechanics, signaling, and disease. Circ Res 94:284–295
Granzier H, Radke M, Royal J, Wu Y, Irving TC, Gotthardt M, Labeit S (2007) Functional genomics of chicken, mouse, and human titin supports splice diversity as an important mechanism for regulating biomechanics of striated muscle. Am J Physiol Regul Integr Comp Physiol 293:R557–R567
Greaser ML, Krzesinski PR, Warren CM, Kirkpatrick B, Campbell KS, Moss RL (2005) Developmental changes in rat cardiac titin/connectin: transitions in normal animals and in mutants with a delayed pattern of isoform transition. J Muscle Res Cell Motil 26:325–332
Gregorio CC, Trombitás K, Centner T, Kolmerer B, Stier G, Kunkel K, Suzuki K, Obermayr F, Herrmann B, Granzier H, Sorimachi S, Labeit S (1998) The NH2 terminus of titin spans the Z-disc: its interaction with a novel 19-kD ligand (T-cap) is required for sarcomeric integrity. J Cell Biol 143:1013–1027
Guo W, Schafer S, Greaser ML, Radke MH, Liss M, Govindarajan T, Maatz H, Schulz H, Li S, Parrish AM, Dauksaite V, Vakeel P, Klaassen S, Gerull B, Thierfelder L, Regitz-Zagrosek V, Hacker TA, Saupe KW, Dec GW, Ellinor PT, MacRae CA, Spallek B, Fischer R, Perrot A, Özcelik C, Saar K, Hubner N, Gotthardt M (2012) RBM20, a gene for hereditary cardiomyopathy, regulates titin splicing. Nat Med 18:766–773
Herman DS, Lam L, Taylor MR, Wang L, Teekakirikul P, Christodoulou D, Conner L, Depalma SR, Mcdonough B, Sparks E, Teodorescu DL, Cirino AL, Banner NR, Pennell DJ, Graw S, Merlo M, di Lenarda A, Sinagra G, Bos JM, Ackerman MJ, Mitchell RN, Murry CE, Lakdawala NK, Ho CY, Barton PJ, Cook SA, Mestroni L, Seidman JG, Seidman CE (2012) Truncations of titin causing dilated cardiomyopathy. N Engl J Med 366:619–628
Hinze F, Dieterich C, Radke MH, Granzier H, Gotthardt M (2016) Reducing RBM20 activity improves diastolic dysfunction and cardiac atrophy. J Mol Med 94:1349–1358
Hoshijima M (2006) Mechanical stress-strain sensors embedded in cardiac cytoskeleton: Z disk, titin, and associated structures. Am J Physiol Heart Circ Physiol 290:H1313–H1325
Kontrogianni-Konstantopoulos A, Bloch RJ (2003) The hydrophilic domain of small ankyrin-1 interacts with the two N-terminal immunoglobulin domains of titin. J Biol Chem 278:3985–3991
Kruger M, Linke WA (2011) The giant protein titin: a regulatory node that integrates myocyte signaling pathways. J Biol Chem 286:9905–9912
Kruger M, Kohl T, Linke WA (2006) Developmental changes in passive stiffness and myofilament Ca2+-sensitivity due to titin and troponin-I isoform switching are not critically triggered by birth. Am J Physiol Heart Circ Physiol 291:H496–H506
Labeit S, Kolmerer B (1995) Titins, giant proteins in charge of muscle ultrastructure and elasticity. Science 270:293–296
Lahmers S, Wu Y, Call DR, Labeit S, Granzier H (2004) Developmental control of titin isoform expression and passive stiffness in fetal and neonatal myocardium. Circ Res 94:505–513
LeWinter MM, Granzier HL (2013) Titin is a major human disease gene. Circulation 127:938–944
Linke WA (2008) Sense and stretchability: the role of titin and titin-associated proteins in myocardial stress-sensing and mechanical dysfunction. Cardiovasc Res 77:637–648
Liversage AD, Holmes D, Knight PJ, Tskhovrebova L, Trinick J (2001) Titin and the sarcomere symmetry paradox. J Mol Biol 305:401–409
Makarenko I, Opitz CA, Leake MC, Neagoe C, Kulke M, Gwathmey JK, del Monte F, Hajjar RJ, Linke WA (2004) Passive stiffness changes caused by upregulation of compliant titin isoforms in human dilated cardiomyopathy hearts. Circ Res 95:708–716
Methawasin M, Hutchinson KR, Lee EJ, Smith JE 3rd, Saripalli C, Hidalgo CG, Ottenheijm CA, Granzier H (2014) Experimentally increasing titin compliance in a novel mouse model attenuates the Frank-Starling mechanism but has a beneficial effect on diastole. Circulation 129:1924–1936
Methawasin M, Strom JG, Slater RE, Fernandez V, Saripalli C, Granzier H (2016) Experimentally increasing the compliance of titin through RNA binding motif-20 (RBM20) inhibition improves diastolic function in a mouse model of heart failure with preserved ejection fraction. Circulation 134:1085–1099
Miller MK, Bang ML, Witt CC, Labeit D, Trombitas C, Watanabe K, Granzier H, McElhinny AS, Gregorio CC, Labeit S (2003) The muscle ankyrin repeat proteins: CARP, ankrd2/Arpp and DARP as a family of titin filament-based stress response molecules. J Mol Biol 333:951–964
Musa H, Meek S, Gautel M, Peddie D, Smith AJ, Peckham M (2006) Targeted homozygous deletion of M-band titin in cardiomyocytes prevents sarcomere formation. J Cell Sci 119:4322–4331
Nagueh SF, Shah G, Wu Y, Torre-Amione G, King NM, Lahmers S, Witt CC, Becker K, Labeit S, Granzier HL (2004) Altered titin expression, myocardial stiffness, and left ventricular function in patients with dilated cardiomyopathy. Circulation 110:155–162
Neagoe C, Kulke M, del Monte F, Gwathmey JK, de Tombe PP, Hajjar RJ, Linke WA (2002) Titin isoform switch in ischemic human heart disease. Circulation 106:1333–1341
Opitz CA, Leake MC, Makarenko I, Benes V, Linke WA (2004) Developmentally regulated switching of titin size alters myofibrillar stiffness in the perinatal heart. Circ Res 94:967–975
Prado LG, Makarenko I, Andresen C, Krüger M, Opitz CA, Linke WA (2005) Isoform diversity of giant proteins in relation to passive and active contractile properties of rabbit skeletal muscles. J Gen Physiol 126:461–480
Roberts AM, Ware JS, Herman DS, Schafer S, Baksi J, Bick AG, Buchan RJ, Walsh R, John S, Wilkinson S, Mazzarotto F, Felkin LE, Gong S, Macarthur JA, Cunningham F, Flannick J, Gabriel SB, Altshuler DM, Macdonald PS, Heinig M, Keogh AM, Hayward CS, Banner NR, Pennell DJ, O’Regan DP, San TR, de Marvao A, Dawes TJ, Gulati A, Birks EJ, Yacoub MH, Radke M, Gotthardt M, Wilson JG, O’Donnell CJ, Prasad SK, Barton PJ, Fatkin D, Hubner N, Seidman JG, Seidman CE, Cook SA (2015) Integrated allelic, transcriptional, and phenomic dissection of the cardiac effects of titin truncations in health and disease. Sci Transl Med 7:270ra6
Trombitás K, Redkar A, Centner T, Wu Y, Labeit S, Granzier H (2000) Extensibility of isoforms of cardiac titin: variation in contour length of molecular subsegments provides a basis for cellular passive stiffness diversity. Biophys J 79:3226–3234
Tskhovrebova L, Trinick J (2004) Properties of titin immunoglobulin and fibronectin-3 domains. J Biol Chem 279:46351–46354
Witt SH, Granzier H, Witt CC, Labeit S (2005) MURF-1 and MURF-2 target a specific subset of myofibrillar proteins redundantly: towards understanding MURF-dependent muscle ubiquitination. J Mol Biol 350:713–722
Young P, Ehler E, Gautel M (2001) Obscurin, a giant sarcomeric Rho guanine nucleotide exchange factor protein involved in sarcomere assembly. J Cell Biol 154:123–136
Zou Y, Evans S, Chen J, Kuo HC, Harvey RP, Chien KR (1997) CARP, a cardiac ankyrin repeat protein, is downstream in the Nkx2–5 homeobox gene pathway. Development 124:793–804
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Funding
This study was funded by National Institutes of Health grant HL062881 (HG), HL118524 (HG) and Interdisciplinary Training in Cardiovascular Research T32 HL007249 (DK).
Conflict of interest
Dalma Kellermayer declares that she has no conflicts of interest. John E. Smith declares that he has no conflicts of interest. Henk Granzier declares that he has no conflicts of interest.
Ethical approval
This article does not contain any studies with human participants or animals performed by any of the authors.
Additional information
This article is part of a Special Issue on ‘Titin and its Binding Proteins in Striated Muscles’ edited by Amy Li and Cristobal G. dos Remedios.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Kellermayer, D., Smith, J.E. & Granzier, H. Novex-3, the tiny titin of muscle. Biophys Rev 9, 201–206 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12551-017-0261-y
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12551-017-0261-y