Abstract
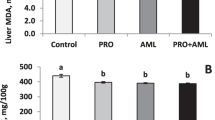
The aim of this study was to evaluate the efficacy of autochthonous Pichia kudriavzevii as a novel bioadsorbent for aflatoxin B1 (AFB1). The selection of this yeast was based on the AFB1 adsorption capacity previously demonstrated in vitro (Magnoli et al. 2016). One-day-old Cobb broilers (n = 160) were randomly assigned to four dietary treatments (T1: basal diet (B); T2: B + 0.1% yeast; T3: B + AFB1, 100 μg/kg; T4: B + 0.1% yeast + AFB1, 100 μg/kg). Performance parameters (average daily weight gain body, average daily consumption, feed conversion ratio, carcass weight, and dead weight), biochemical parameters (albumin, globulin, and albumin/globulin), liver pathological changes, and AFB1 residual levels in the liver and excreta were evaluated. Significant differences (P < 0.05) in performance parameters were observed among treatments and controls: T3 group showed the lowest average daily body weight gain value while in T4 group, the value of this parameter increased significantly (P < 0.05). T3 and T4 groups showed the lowest and highest values for average daily feed consumption, respectively. The feed conversion ratio (FC) showed no significant differences among treatments. T3 group showed the lowest dead weight and carcass weight compared with T1 group. The biochemical parameters showed no significant differences among treatments. T3 group showed macroscopic and microscopic liver changes compared to the control. Aflatoxin B1 levels (μg/g) were detected in broiler livers and showed significant differences among treatments (P < 0.05). In conclusion, native P. kudriavzevii incorporation (0.1%) in broiler diets containing AFB1 was shown to be effective in ameliorating the adverse effects of AFB1 on production.


Similar content being viewed by others
References
Afzal M, Saleem Z (2004) Effects of addition of a mycotoxin detoxifier in poultry feed containing different levels of aflatoxins on the performance of broilers. Asian-Australian J Anim Sci 17:990–994
Aravind KL, Patil VS, Devegowda G, Umakantha B, Ganpule SP (2003) Efficacy of esterified glucomannan to counteract mycotoxicosis in naturally-contaminated feed on performance, serum biochemical and haematological parameters in broilers. Poult Sci 82:570–576
Armando MR, Dogi CA, Pizzolitto RP, Escobar F, Peirano MS, Salvano MA, Sabini LI, Combina M (2011) Saccharomyces cerevisiae strains from animal environmental with aflatoxin B1 binding ability and antipathogenic bacteria influence in vitro. World Mycotoxin J 4:59–68
Armando MR, Pizzolitto RP, Dogi CA, Cristofolini A, Merkis C, Poloni VL, Dalcero AM, Cavaglieri LR (2012a) Adsorption of ochratoxin A and zearalenone by potential probiotic Saccharomyces cerevisiae strains and its relation with cell wall thickness. J Appl Microbiol 113(2):256–264
Armando MR, Dogi CA, Rosa C, Dalcero AM, Cavaglieri LR (2012b) Saccharomyces cerevisiae strains reduce Aspergillus parasiticus growth and aflatoxin B1 production at different interacting environmental conditions. Food Addit Contam Part A Chem Anal Control Expo Risk Assess 29(9):1443–1449
Association of Official Agricultural Chemists (AOAC) (1994) Official methods of analysis 979.22 14th ed. see column chromatographic procedure. Gaithersburg
Association of Official Agricultural Chemists (AOAC) (1995) Official methods of analysis, 16th edn. 990.33 AOAC Int., Gaithersburg
Association of Official Agricultural Chemists (AOAC) (2000) Official Methods Sampling of Aflatoxins, Preparation of sample 977.16 17th ed. Washington, DC
Azizpour A, Moghadam N (2015) Effects of yeast glucomannan and sodium bentonite on the toxicity of aflatoxin in broilers Brazilian Journal of Poultry Science ISSN 1516-635X Oct - Dec 2015 / Special Issue. Nutrition - Poultry feeding additives / 007–014
Baptista AS, Horii Y, Calori-Domingues MA, Da Gloria EM, Salgado JM, Vizioli MR (2004) The capacity of manno-oligosaccharides, thermolysed yeast and active yeast to attenuate aflatoxicosis. World J Microbiol Biotechnol 20:474–481
Basmacıoglu H, Oguz H, Ergul M, Col R, Birdane YO (2005) Effect of dietary esterified glucomannan on performance, serum biochemistry and haematology in broilers exposed to aflatoxin Czech. J Anim Sci 50(1):31–39
Bhat R, Rai RV, Karim A (2010) Mycotoxins in food and feed: present status and future concerns. Comprehensive Rev Food Sci Food Saf 9:57–81
Bilgic HN, Yesildere T (1992) Renal lesions on experimental aflatoxicosis in chickens. I U Vet Fak Derg 18:102–108
Bintvihok A (2002) New insights to controlling mycotoxin danger in ducks. Anim Feed Sci Tech 6:28–29
Bintvihok A, Kositcharoenkul S (2006) Effect of dietary calcium propionate on performance, hepatic enzyme activities and aflatoxin residues in broilers fed a diet containing low levels of aflatoxin B1. Toxicon 47:41–46
Bovo F, Franco LT, Kobashigawa E, Rottinghaus GE, Ledoux DR, Oliveira CAF (2015) Efficacy of beer fermentation residue containing Saccharomyces cerevisiae cells for ameliorating aflatoxicosis in broilers. Poult Sci 94(5):934–942
CAST (2003) Mycotoxins: risks in plant, animal, and human systems. Richard JL, Payne GA, editor. Ames, IA: Council for Agricultural Science and Technology (CAST) Council for Agricultural Science and Technology (CAST) Task Force Report No. 139
Celik K, Denli M, Erturk M, Ozturkcan O, Doran F (2001) Evaluation of dry yeast (SCE) in the feed to reduce AFB1 residues and toxicity to japonica quails. J Appl Anim Res 20:245–250
Chiacchiera SM, Magnoli CE, Astorga P, Miazzo R, Combina M, Dalcero AM, Kikot E, Basaldella E (2000) Use of synthetic zeolites to adsorb different mycotoxins, prevention of mycotoxicoses. Actualidad Fisicoquímica Organica 12:218–236
Daković A, Matijasevic S, George E, Rottinghaus D, Ledoux R (2008) Aflatoxin B1 adsorption by natural and copper modified montmorillonite. Colloids Surf B: Biointerfaces 66:20–25
Denli M, Okan F (2006) Efficacy of different adsorbents in reducing the toxic effects of aflatoxin B1 in broiler diets. South African J Anim Sci 36:222–228
Denli M, Okan F, Doran F (2004) Effect of conjugated linoleic acid (CLA) on the performance and serum variables of broiler chickens intoxicated with aflatoxin B1. South African J Anim Sci 34:97–103
Diaz GJ; Murcia HW, Cepeda SM (2010) Cytochrome P450 enzymes involved in the metabolism of aflatoxin B1 in chickens and quail. Poult Sci 89,11:2461-2469, ISSN 0032-5791
Dixon J, Kannewischer BI, Tenorio Arvide MG, Barrientos Velazquez AL (2007) Aflatoxin sequestration in animal feeds by quality-labeled smectite clays: an introductory plan. Appl Clay Sci 40:201–208
Dos Anjos FR, Ledoux DR, Rottinghaus GE, Chimonyo M (2015) Efficacy of adsorbents (bentonite and diatomaceous earth) and turmeric (Curcuma longa) in alleviating the toxic effects of aflatoxin in chicks. Brit Poult Sci 56(4):459–469
El-Nezami H, Kankaanpaa P, Salminen S, Ahokas J (1998) Ability of dairy strains of lactic acid bacteria to bind a common food carcinogen, aflatoxin B1. Food Chem Toxicol 36:321–326
El-Nezami H, Mykkanen H, Kankaakpaä P, Salminen S, Ahokas J (2000) Ability of Lactobacillus and Propionibacterium strains to remove aflatoxin B, from the chicken duodenum. J Food Protect 63:549–552
Fraga ME, Curvello F, Gatti MJ, Cavaglieri LR, Dalcero AM, Da Rocha Rosa CA (2007) Potential aflatoxin and ochratoxin A production by Aspergillus species in poultry feed processing. Vet Res Commun 31:343–353
Freimund S, Sauter M, Rys P (2003) Efficient adsorption of the mycotoxins zearalenone and T-2 toxin on a modified yeast glucan. J Environ Sci Heal B 38(3):243–255
González Pereyra ML, Dogi C, Torres Lisa A, Wittouck P, Ortíz M, Bagnis G, Yaciuk R, Poloni L, Torres A, Dalcero AM, Cavaglieri LR (2014) Genotoxicity and cytotoxicity evaluation of probiotic Saccharomyces cerevisiae RC016: a 60-day subchronic oral toxicity study in rats. J Appl Microbiol 117(3):824–833
Gutleba AC, Caloni F, Girauda F, Cortinovis C, Pizzo F, Hoffmanna L, Bohna T, Pasquali M (2015) Detection of multiple mycotoxin occurrences in soy animal feed by traditional mycological identification combined with molecular species identification. Toxicol Rep 2:275–279
Hashmi I, Pahsa TN, Jabbar MA, Arkam M, Hashmi AS (2006) Study of adsorption potential of yeast sludge against AF in broiler chicks. J Anim Pl Sci 16:12–14
Juan-juan L, De-cheng S, Xiao-ou S (2010) Binding capacity for AFB1 by different adsorbents. Agri Sci China 9:449–456
Kemal C, Muzaffer D, Türker S, (2003) Reduction of toxic effects of aflatoxin B1 by using baker yeast (Saccharomyces cerevisiae) in growing broiler chicks diets. R Bras Zootec 32:615-619
Khadem AA, Sharifi SD, Barati M, Borji M (2012) Evaluation of the effectiveness of yeast, zeolite and active charcoal as aflatoxin absorbents in broiler diets. Global Vet 8:426–432
Kumar TAC, Balachandran C (2014) Pathological effect of citrinin and aflatoxin in broiler chicken. Int J Life Sci Pharma Res 4:1–15
Kurtzman CP, Robnett CJ (2003) Phylogenetic relationships among yeasts of the Saccharomyces complex determined from multigene sequence analyses. FEMS Yeast Res 3:417–432
Lamelas K, Mair G, Beczkowski G (2010) Evolución del sector Avícola año 2009, perspectiva 2010. Boletín avícola 58:1–26 Ministerio de Agricultura, Ganadería, Pesca y Alimentación. Accessed Nov. http://www.minagri.gob.ar
Leeson S, Dias GJ, Summers JD (1995) Tricothecenes. In: Poultry Metabolic Disorders. Guelph, Ontario, Canada, 190–226
Lozano MC, Diaz GJ (2006) Microsomal and cytosolic biotransformation of aflatoxin B1 in four poultry species. Br Poult Sci 47:734–741
Magnoli AP, Monge MP, Miazzo RD, Cavaglieri LR, Magnoli CE, Merkis CI, Cristofolini AL, Dalcero AM, Chiacchiera SM (2011a) Effect of low levels of aflatoxin B1 on performance, biochemical parameters, and aflatoxin B1 in broiler liver tissues in the presence of monensin and sodium bentonite. Poult Sci 90:48–58
Magnoli AP, Texeira M, Rosa CAR, Miazzo RD, Cavaglieri LR, Magnoli CE (2011b) Sodium bentonite and monensin under chronic aflatoxicosis in broiler chickens. Poult Sci 90:352–357
Magnoli AP, Alonso VA, Cavaglieri LR, Dalcero AM, Chiacchiera SM (2013) Effect of monogastric and ruminant gastrointestinal conditions on in vitro aflatoxin B1 adsorption ability by a montmorillonite. Food Addit Contam Part A 30:743–749
Magnoli AP, Copia P, Monge MP, Magnoli CE, Dalcero AM, Chiacchiera SM (2014) Negligible effects of tryptophan on the aflatoxin adsorption of sodium bentonite. Food Addit Contam Part A 31(12):2063–2070
Magnoli AP, Rodriguez MC, Poloni VL, Rojo MC, Combina M, Chiacchiera SM, Dalcero AM, Cavaglieri LR (2016) Novel yeast isolated from broilers’ feedstuff, gut and faeces as aflatoxin B1 adsorbents. J Appl Microbiol ISSN 1364–5072
Manafi M, Hedayati M, Yari M (2014) Aflatoxicosis and herbal detoxification: the effectiveness of thyme essence on performance parameters and antibody titers of commercial broilers fed aflatoxin B1. Res Zool 4(2):43–50
Miazzo R, Rosa RCA, Carvalho De Queiroz EC, Magnoli C, Chiacchiera SM, Palacio G, Saenz M, Kikot A, Basaldella E, Dalcero A (2000) Efficacy of synthetic zeolite to reduce the toxicity of aflatoxin in broiler chicks. Poult Sci 79:1–6
Miazzo R, Peralta MF, Magnoli C, Salvano M, Ferrero S, Chiacchiera SM, Carvalho ECQ, Rosa CA, Dalcero A (2005) Efficacy of sodium bentonite as a detoxifier of broiler feed contaminated with aflatoxin and fumonisin. Poult Sci 84:1–8
Monge MP, Dalcero AM, Magnoli CE, Chiacchiera SM (2013) Natural co-occurrence of fungi and mycotoxins in poultry feeds from Entre Ríos, Argentina. Food Addit Contam Part B: Surveillance 6:168–174
Motawe HFA, Abdel Salam AF, El Meleigy KHM (2014) Reducing the toxicity of aflatoxin in broiler chickens’ diet by using probiotic and yeast. Int J Poult Sci 13(7):397–407
Nacional Research Council, (NRC). (1994) Nutrient requirements of chickens. En: Nutrient requirements of poultry. 8th rev. ed. National Academy Press, Washington DC 11–15
Nemati Z, Janmohammadi H, Taghizadeh A, Maleki H, Nejad Mogaddam GH, Arzanlou M (2014a) Occurrence of aflatoxins in poultry feed and feed ingredients from north western Iran. Eur J Zool Res 3:56–60
Nemati Z, Janmohammadi H, Taghizadeh A, Moghaddam GH, Maleki Nejad H (2014b) Effect of bentonite supplementation to the contaminated diets with aflatoxin B1 on broiler performance. presented at the 6th Iranian congress on animal science, Tabriz
Nemati Z, Karimi A, Besharati M (2015) Impact of aflatoxin contaminnated feed and yeast cell wall suplementation on immune system in broiler chickens Intl Conf. International Conference on Innovations in Chemical and Agricultural Engineering (ICICAE’2015) Feb. 8–9, 2015 Kuala Lumpur
Oğuz H (2011) A review from experimental trials on detoxification of aflatoxin in poultry feed. Eurasian J Vet Sci 27:1–12
Oğuz H, Kececi T, Birdane YO, Onder F, Kurtoglu V (2000a) Effect of clinoptilolite on serum biochemical and haematological characters of broiler chickens during experimental aflatoxicosis. Res Vet Sci 69:89–93
Oğuz H, Kurtoglu V, Coskun B (2000b) Preventive efficacy of clinoptilolite in broiler during chronic aflatoxin (50 and 100 ppb) exposure. Res Vet Sci 69:197–201
Oğuz H, Hadimli HH, Kurtoglu V, Erganiş O (2003) Evaluation of humoral immunity of broilers during chronic aflatoxin (50 and 100 ppb) and clinoptilolite exposure. Rev Med Vet B Aires 154:483–486
Oliveira GR, Ribeiro JM, Fraga ME, Cavaglieri LR, Direito GM, Keller KM, Dalcero AM, Rosa CA (2006) Mycobiota in poultry feeds and natural occurrence of aflatoxins, fumonisins and zearalenone in the Rio de Janeiro State, Brazil. Mycopathologia 162:355–362
Onwurah FB, Okejim J, Amaefula KU (2013) Effect of yeast as water additive in the management of litter in the production starter broiler. Asian J Nat Appl Sci 2:127–130
Ortatatli M, Oğuz H (2001) Ameliorative effects of dietary clinoptilolite on pathological changes in broiler chickens during aflatoxicosis. Res Vet Sci 71:59–66
Ortatatli M, Oğuz H, Hatipoglu F, Karaman M (2005) Evaluation of pathological changes in broilers during chronic afla toxin (50 and 100 ppb) and clinoptilolite exposure. Res Vet Sci 78:61–68
Pizzolitto RP, Armando MR, Salvano MA, Dalcero AM, Rosa CA (2013) Evaluation of Saccharomyces cerevisiae as an antiaflatoxicogenic agent in broiler feedstuffs. Poult Sci 92:1655–1663
Raju MVLN, Devegowda G (2000) Influence of esterified-glucomannan on performance and organ morphology, serum biochemistry and haematology in broilers exposed to individual and combined mycotoxicosis (aflatoxin, ochratoxin and T-2 toxin). Brit Poult Sci 41:640–650
Rosa CAR, Miazzo R, Magnoli C, Salvano M, Chiacchiera SM, Ferrero S, Saenz M, Carvalho EC, Dalcero A (2001) Evaluation of the efficacy of bentonite from the south of Argentina to ameliorate the toxic effects of aflatoxin in broilers. Poult Sci 80:139–144
Rosa AP, Uttpatel R, Santurio JM, Sher A, Duarte V, Santos CB (2012) Performance of broilers derived from breeder hens fed with diets containing aflatoxins and esterified glucomannan as adsorbent. Braz J Anim Sci 41:347–352
Roto SM, Rubinelli PM, Ricke SC (2015) An introduction to the avian gut microbiota and the effects of yeast based prebiotic-type compounds as potential feed additives. Frontiers in Vet Sci 2:28
Santin E, Paulillo AC, Maiorka A, Satiko L, Macari M, Fischer Da Silva AV (2003) Evaluation of the efficacy of Saccharomyces cerevisiae cell wall to ameliorate the toxic effects of aflatoxin in broilers. Int J Poult Sci 2:341–344
Santin E, Paulillo AC, Nakagui LSO, Alessi AC, Maiorka A (2006) Evaluation of yeast cell wall on the performance of broiles fed diets with or without mycotoxins. Rev Bras Cienc Avic 8:221–225
Savlík M, Poláčkcová L, Szotáková B, Lamka J, Velík J, Skálová L (2007) Activities of biotransformation enzymes in pheasant (Phasianus colchicus) and their modulation by in vivo administration of mebendazole and ubendazole. Res Vet Sci 83:20–26
Schatzmayr G, Florian Z, Täubel M, Schatzmayr D, Klimitsch A, Loibner AP, Binder EM (2006) Microbiologicals for deactivating mycotoxins. Mol Nutr Food Res 50(6):543–551
Sørensen LK, Elbæk TH (2005) Determination of mycotoxins in bovine milk by liquid chromatography tandem mass spectrometry. J Chromatogr B Analyt Technol Biomed Life Sci 820:183–196
Sur E, Celik I (2003) Effects of aflatoxin B1 on the development of the bursa of Fabricius and blood lymphocyte acid phosphatase of the chicken. Br Poult Sci 44:558–566
Tavčar-Kalcher G, Vrtač K, Pestevšek U, Vengust A (2007) Validation of the procedure for the determination of aflatoxin B1in animal liver using immunoaffinity columns and liquid chromatography with post-column derivatisation and fluorescence detection. Food Contr 18:333–337
Tessari ENC, Oliveria CAF, Cardoso ALSP, Ledoux DR, Rottinghaus GE (2006) Effects of aflatoxin B1 and fumonisin B1 on body weight, antibody titres and histology of broiler chicks. Brit Poult Sci 47:357–364
Trucksess MW, Stack ME, Nesheim S, Albert R, Romer T (1994) Multifunctional column coupled with liquid chromatography for determination of aflatoxins B1, B2, G1 and G2 in corn, almonds. Brazil nuts, peanuts, and pistachio nuts: collaborative study. J AOAC Int 77:1512–1521
U.E. (2006) Reglamento 401/2006 de la Comisión, de 23 de febrero de 2006, por el que se establecen los métodos de muestreo y de análisis para el control oficial del contenido de micotoxinas en los productos alimenticios. Diario Oficial de la Unión Europea L70 de 09/03/2006, pp.12–34
Vanhoutte I, Audenaert K, De Gelder L (2016) Biodegradation of Mycotoxins: Tales from Known and Unexplored Worlds. Front Microbiol 7:561.doi: 10.3389/fmicb.2016.00561
Wiener Laboratory (2000) Calorimetric method for determination of total protein, albumin and serum transaminase. Wiener Laboratory, Rosario
Yiannikouris A, Poughon L, Cameleyre X, Dussap CG, Francüois J, Bertin G, Jouany JP (2003) A novel technique to evaluate interactions between Saccharomyces cerevisiae cell wall and mycotoxins: application to zearalenone. Biotechnol Lett 25:783–789
Yiannikouris A, François J, Poughon L, Dussap CG, Bertin G, Jeminet G, Jouany JP (2004) Alkali-extraction of b-D-glucans from Saccharomyces cerevisiae cell wall and study of their adsorptive properties toward zearalenone. J Agr Food Chem 52:3666–3673
Zain ME (2011) Impact of mycotoxins on humans and animals. J Saudi Chem Soc 15:129–144
Acknowledgments
The authors are grateful to the SECyT (Secretaría de Ciencia y Técnica, Universidad Nacional de Río Cuarto) and Consejo Nacional de Investigaciones Científicas y Técnicas, Argentina (CONICET), which supported this study through grants. L.R.C and S.M.C held positions at CONICET. We thank Dra. Ana Maria Dalcero for the collaboration and contribution in this work.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Funding
This study was funded by Secretaría de Ciencia y Técnica, Universidad Nacional de Río Cuarto SECyT; Consejo Nacional de Investigación Científica y Técnica, Argentina (CONICET); and Agencia Nacional de Promoción Científica y Tecnológica (Fondo para la Investigación Científica y Tecnológica, FONCyT).
Conflict of interest
None of the authors has any financial or personal relationships that could inappropriately influence or bias the content of the paper.
Declarations
Availability of data and material: databases and all relevant raw data are freely available to any scientist wishing to use them.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Magnoli, A., Rodriguez, M., González Pereyra, M. et al. Use of yeast (Pichia kudriavzevii) as a novel feed additive to ameliorate the effects of aflatoxin B1 on broiler chicken performance. Mycotoxin Res 33, 273–283 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12550-017-0285-y
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12550-017-0285-y