Abstract
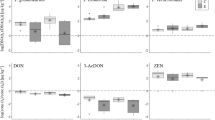
Conservation tillage combined with crop-residue mulching is increasingly important to meet soil protection targets. Concurrently, the health risk of soil-borne pathogenic fungi like Fusarium species, which produce deoxynivalenol (DON) as their major mycotoxin, is increasing. The detritivorous earthworm species Lumbricus terrestris takes part in the efficient degradation of Fusarium-infected and DON-contaminated wheat straw. Against this background, a laboratory study was conducted to quantify by means of ELISA technique the uptake of DON and its possible absorption and accumulation in tissue by L. terrestris in the short-term (5 weeks) and long-term (11 weeks). The DON concentrations in L. terrestris of the Fusarium-infected treatment were significantly different in the order of gut tissue > body wall > gut content at both dates with a decline in the long-term. The DON concentrations in the tissues decreased by an order of magnitude of weeks to months.

Similar content being viewed by others
References
Bonkowski S, Griffiths BS, Ritz K (2000) Food preference of earthworms for soil fungi. Pedobiologia (Jena) 44:666–676. doi:10.1078/S0031-4056(04)70080-3
Bünemann EK, Schwenke GD, van Zwieten L (2006) Impact of agricultural inputs on soil organisms—a review. Aust J Soil Res 44:379–406. doi:10.1071/SR05125
Brown GG (1995) How do earthworms affect microfloral and faunal community diversity? Plant Soil 170:209–231. doi:10.1007/BF02183068
Cote LM, Dahlem AM, Yoshizawa T, Swanson SP, Buck WB (1986) Excretion of deoxynivalenol and its metabolite in milk, urine, and faeces of lactating dairy cows. J Dairy Sci 69:2416–2423
Curry JP, Schmidt O (2007) The feeding ecology of earthworms—a review. Pedobiologia (Jena) 50:463–477. doi:10.1016/j.pedobi.2006.09.001
Dänicke S, Valenta H, Döll S (2004) On the toxicokinetics and the metabolism of deoxynivalenol (DON) in the pig. Arch Anim Nutr 58:169–180. doi:10.1080/00039420410001667548
Döll S, Dänicke S (2004) In vivo detoxification of Fusarium toxins. Arch Anim Nutr 58:419–441. doi:10.1080/00039420400020066
Edwards CA, Fletcher KE (1988) Interactions between earthworms and microorganisms in organic-matter breakdown. Agric Ecosyst Environ 24:235–247. doi:10.1016/0167-8809(88)90069-2
Flegel M, Schrader S (2000) Importance of food quality on selected enzyme activities in earthworm casts (Dendrobaena octaedra, Lumbricidae). Soil Biol Biochem 32:1191–1196. doi:10.1016/S0038-0717(00)00035-3
Heise J, Höltge S, Schrader S, Kreuzig R (2006) Chemical and biological characterization of non-extractable sulfonamide residues in soil. Chemosphere 65:2352–2357. doi:10.1016/j.chemosphere.2006.04.084
Holland JM (2004) The environmental consequences of adopting conservation tillage in Europe: reviewing the evidence. Agric Ecosyst Environ 103:1–25. doi:10.1016/j.agee.2003.12.018
Huhta V, Wright DH, Coleman DC (1989) Characteristics of defaunated soil I. A comparison of three techniques applied to two different forest soils. Pedobiologia (Jena) 33:417–426
IUSS Working Group WRB (2007) World Reference Base for Soil Resources 2006, first update 2007. World Soil Resources Reports No. 103. FAO, Rome
Langmaack M (1999) Earthworm communities in arable land influenced by tillage, compaction, and soil. Z Okologie Naturschutz 8:11–21
Lee KE (1985) Earthworms—their ecology and relationships with soils and land use. Academic Press, Sydney
Maraun M, Martens H, Migge S, Theenhaus A, Scheu S (2003) Adding to ‘the enigma of soil animal biodiversity’: fungal feeders and saprophagous soil invertebrates prefer similar food substrates. Eur J Soil Biol 39:85–95. doi:10.1016/S1164-5563(03)00006-2
Meier U (2001) Growth stages of mono- and dicotyledonous plants. BBCH Monograph, 2nd edn. Federal Biological Research Centre for Agriculture and Forestry, Braunschweig
Moody SA, Briones MJI, Piearce TG, Dighton J (1995) Selective consumption of decomposing wheat straw by earthworms. Soil Biol Biochem 27:1209–1213. doi:10.1016/0038-0717(95)00024-9
Moody SA, Piearce TG, Dighton J (1996) Fate of some fungal spores associated with wheat straw decomposition on passage through the guts of Lumbricus terrestris and Aporrectodea longa. Soil Biol Biochem 28:533–537. doi:10.1016/0038-0717(95)00172-7
Nahmani J, Hodson ME, Black S (2007) A review of studies performed to assess metal uptake by earthworms. Environ Pollut 145:402–424. doi:10.1016/j.envpol.2006.04.009
Oldenburg E, Brunotte J, Weinert J (2007) Strategies to reduce DON contamination of wheat with different soil tillage and variety systems. Mycotoxin Res 23:73–77. doi:10.1007/BF02946029
Oldenburg E, Kramer S, Schrader S, Weinert J (2008) Impact of the earthworm Lumbricus terrestris on the degradation of Fusarium-infected and desoxynivalenol-contaminated wheat straw. Soil Biol Biochem 40:3049–3053. doi:10.1016/j.soilbio.2008.09.004
Pereyra SA, Dill-Macky R, Sims AL (2004) Survival and inoculum production of Gibberella zeae in wheat residue. Plant Dis 88:724–730. doi:10.1094/PDIS.2004.88.7.724
Pestka JJ (2007) Deoxynivalenol: Toxicity, mechanisms and animal health risks. Anim Feed Sci Technol 137:283–298. doi:10.1016/j.anifeedsci.2007.06.006
Prelusky DB, Trenholm HL, Lawrence GA, Scott PM (1984) Nontransmission of deoxynivalenol (vomitoxin) to milk following oral administration to dairy cows. J Environ Sci Health B 19:593–609. doi:10.1080/03601238409372453
Sabater-Vilar M, Malekinejad H, Selman MHJ, van der Doelen MAM, Fink-Gremmels J (2007) In vitro assessment of adsorbents aiming to prevent deoxynivalenol and zearalenone mycotoxicosis. Mycopathologia 163:81–90. doi:10.1007/s11046-007-0093-6
Schrader S, Münchenberg T, Baumgarte S, Tebbe CC (2008) Earthworms of different functional groups affect the fate of the Bt-toxin Cry1Ab from transgenic maize in soil. Eur J Soil Biol 44:283–289. doi:10.1016/j.ejsobi.2008.04.003
Shuster WD, Edwards CA (2003) Interactions between tillage and earthworms in agroecosystems. In: El Titi A (ed) Soil tillage in agroecosystems. Advances in agroecology, vol 9. CRC Press, Boca Raton, pp 229–260
Sims RW, Gerard BM (1985) Earthworms: keys and notes for the identification of the species. Synopses of the British Fauna. Backhuys, London, pp 171
Wagacha JM, Muthomi JW (2007) Fusarium culmorum: infection process, mechanisms of mycotoxin production and their role in pathogenesis in wheat. Crop Prot 26:877–885. doi:10.1016/j.cropro.2006.09.003
Wang XB, Cai DX, Hoogmoed WB, Oenema O, Perdok UD (2006) Potential effect of conservation tillage on sustainable land use: a review of global long-term studies. Pedosphere 16:587–595. doi:10.1016/S1002-0160(06)60092-1
Acknowledgements
We thank Dr. Joachim Brunotte for helpful advice with the experimental conception of this study and for providing the soil applied in the microcosms. The excellent technical assistance of Sabine El Sayed, Stefanie Schlißke, Bettina Schnauß, Sabine Peickert and Petra Romanczuk-Schulz is gratefully acknowledged.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Schrader, S., Kramer, S., Oldenburg, E. et al. Uptake of deoxynivalenol by earthworms from Fusarium-infected wheat straw. Mycotox Res 25, 53–58 (2009). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12550-009-0007-1
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12550-009-0007-1