Abstract
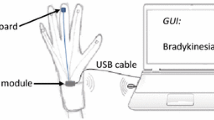
The purpose of this study is to develop a more convenient system for measurement of hand rotation, and to validate the system by correlation of performance indices derived from the system with the bradykinesia score of hand rotation movement during on-medication state. Forty patients with Parkinson’s disease and 14 age-matched control subjects participated in this study. The measurement system was developed using a ceramic gyroscope that is significantly smaller and lighter than those in the literature. The sensor signal was bandpass filtered and action tremor was eliminated by additional lowpass filtering (fc=5Hz) with automated tremor discrimination. Four performance indices (RMS velocity and RMS angle, peak power and total power) were derived from the angular velocity signal. Correlations of performance indices with clinical scores and difference of performance indices among subject groups were investigated. Correlations of all performance indices were far better with bradykinesia score of hand rotation (best r=−.78) than with the other categorized subscores of UPDRS (bradykinesia subscore, axial symptom subscore, and total motor score; best r=−.64). Elimination of action tremor resulted in improvement in correlations of RMS velocity and total power with bradykinesia score for hand rotation (r=−.84 from −.81). Differences between low scores were greater in total power and differences between high scores were greater in RMS velocity, suggesting that use of more than one PI would be beneficial for diagnosis of a wide range of patients. The convenient sensor system, action tremor elimination, and performance indices suggested in this study are expected to be useful in clinical situations.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Patrick, S. K., Denington, A. A., Gauthier, M. J., Gillard, D. M. and Prochazka, A., “Quantification of the Updrs Rigidity Scale,” IEEE Trans. Neural Syst. Rehabil. Eng., Vol. 9, No. 1, pp. 31–41, 2001.
Lyons, K. E., Pahwa, R., Troster, A. I. and Koller, W. C., “A Comparison of Parkinson’s Disease Symptoms and Self-Reported Functioning and Well Being,” Parkinsonism Relat. Disord., Vol. 3, No. 4, pp. 207–209, 1997.
Machado, A., Rezai, A. R., Kopell, B. H., Gross, R. E., Sharan, A. D. and Benabid, A. L., “Deep Brain Stimulation for Parkinson’s Disease: Surgical Technique and Perioperative Management,” Mov. Disord., Vol. 21, Suppl. 14, pp. S247–258, 2006.
Koop, M. M., Shivitz, N. and Bronte-Stewart, H., “Quantitative Measures of Fine Motor, Limb, and Postural Bradykinesia in Very Early Stage, Untreated Parkinson’s Disease,” Mov. Disord., Vol. 23, No. 9, pp. 1262–1268, 2008.
Koop, M. M., Andrzejewski, A., Hill, B. C., Heit, G. and Bronte-Stewart, H. M., “Improvement in a Quantitative Measure of Bradykinesia after Microelectrode Recording in Patients with Parkinson’s Disease During Deep Brain Stimulation Surgery,” Mov. Disord., Vol. 21, No. 5, pp. 673–678, 2006.
Louie, S., Koop, M. M., Frenklach, A. and Bronte-Stewart, H., “Quantitative Lateralized Measures of Bradykinesia at Different Stages of Parkinson’s Disease: The Role of the Less Affected Side,” Mov. Disord., Vol. 24, No. 13, pp. 1991–1997, 2009.
Motus Bioengineering Inc., “Technical Note No. 32: System Components,” www. Motusbioengineering.com
Koh, S. B., Kwon, D. Y., Seo, W. K., Kim, J. H., Lee, S. H., Oh, K., Kim, B. J. and Park, K. W., “Dissociation of Cardinal Motor Signs in Parkinson’s Disease Patients,” Eur. Neurol., Vol. 63, No. 5, pp. 307–310, 2010.
Toth, C., Rajput, M. and Rajput, A. H., “Anomalies of Asymmetry of Clinical Signs in Parkinsonism,” Mov. Disord., Vol. 19, No. 2, pp. 151–157, 2004.
Fahn, S., Marsden, C. D., Calne, D. B. and Goldstein, M., “Recent developments in Parkinson’s diesase,” MacMillan Healthcare Information, Vol. 2, pp. 153–163, 1987.
Van Someren, E. J., Pticek, M. D., Speelman, J. D., Schuurman, P. R., Esselink, R. and Swaab, D. F., “New Actigraph for Long-Term Tremor Recording,” Mov. Disord., Vol. 21, No. 8, pp. 1136–1143, 2006.
Movement Disorder Society Task Force on Rating Scales for Parkinson’s Disease, “The Unified Parkinson’s Disease Rating Scale (Updrs): Status and Recommendations,” Mov. Disord., Vol. 18, No. 7, pp. 738–750, 2003.
http://www.quantitativeskills.com/sisa/statistics/corrhlp.htm
Chae, J., Yang, G., Park, B. K. and Labatia, I., “Delay in Initiation and Termination of Muscle Contraction, Motor Impairment, and Physical Disability in Upper Limb Hemiparesis,” Muscle Nerve., Vol. 25, No. 4, pp. 568–575, 2002.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Jun, JH., Kim, JW., Kwon, Y. et al. Quantification of limb bradykinesia in patients with Parkinson’s disease using a gyrosensor — Improvement and validation. Int. J. Precis. Eng. Manuf. 12, 557–563 (2011). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12541-011-0070-3
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12541-011-0070-3