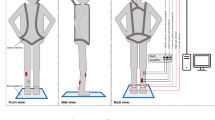
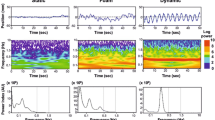
Abstract
The purpose of this study was to analyze the effects of vibration of the tibialis anterior and Achilles tendons during one-legged and two-legged stance in young and elderly individuals. Sway in the center of pressure (COP) and plantar pressure was observed in four vibration conditions, which included single vibration, combined vibration and non-vibration applied to the tibialis anterior and/or Achilles tendons of the supporting leg. For single vibration, whole-body tilts were directed backward and forward according to the location of the vibration. In combined vibration, very small amplitude body shifts were observed. Using combined vibration of the tibialis anterior and Achilles tendons, the decrease in the COP sway may improve the ability to balance during one-legged stance in elderly individuals. In particular, the decrease in COP sway may improve the ability to balance during one-legged stance by combined vibration in elderly subjects. These findings are important for the use of somatosensory information processing to regulate postural adjustments in the elderly
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Hausdorff, J. M., Nelson, M. E., Kaliton, D., Layne, J. E., Bernstein, M. J., Nuernberger, A. and Singh, M. A., “Etiology and modification of gait instability in older adults: a randomized controlled trial of exercise,” Journal of Appl. Physiol., Vol. 90, No. 6, pp. 2117–2129, 2001.
Onambele, G. L., Narici, M. V. and Maganaris, C. N., “Calf muscle-tendon properties and postural balance in old age,” J. Applied Physiology, Vol. 100, No. 6, pp. 2048–2056, 2006.
Carpenter, M. G., Adkin, A. L., Brawley, L. R. and Frank, J. S., “Postural, physiological and psychological reactions to challenging balance: does age make a difference?” Age and Ageing, Vol. 35, No. 3, pp. 298–303, 2006.
Quoniam, C., Hay, L., Roll, J. P. and Harlay, F., “Age effects on reflex and postural responses to propriomuscular inputs generated by tendon vibration,” Journal of Gerontology, Vol. 50, No. 3, pp. B155–B165, 1995.
Mak, M. K. and Ng, P. L., “Mediolateral sway in single-leg stance is the best discriminator of balance performance for Tai- Chi practitioners,” Archives of Physical Medicine and Rehabilitation, Vol. 84, No. 5, pp. 683–686, 2003.
Roll, J. P. and Roll, R., “Kinaesthetic and motor effects of extraocular muscle vibration in man. In: Reagan JKO, Levy-Shoen A (Ed.), Eye movements: from physiology to cognition,” Elsevier, North Holland, pp. 57–68, 1987.
Jonsson, E., Seiger, A. and Hirschfeld, H., “One-leg stance in healthy young and elderly adults: a measure of postural steadiness,” Clinical Biomechanics, Vol. 19, No. 7, pp. 688–694, 2004.
Horak, F. B. and MacPherson, J. M., “Postural orientation and equilibrium, in: J. Shepard, L. Rowell (Eds.), Handbook of Physiology: Section 12, Exercise: Regulation and Integration of Multiple Systems,” Oxford University Press, New York, pp. 255–292, 1996.
Gill, J., Allum, J. H. J., Carpenter, M. G., Held-Ziokowska, M., Adkin, A. L., Honegger, F. and Pierchala, K., “Trunk Sway Measures of Postural Stability During Clinical Balance Tests: Effect of Age,” Journal of Gerontology, Vol. 56, No. 7, pp. M438–M447, 2001.
Vershueren, S. M. P., Swinnen, S. P., Desloovere, K. and Duysens, J., “Effects of tendon vibration on the spatiotemporal characteristics of human locomotion,” Experimental Brain Research, Vol. 143, No. 2, pp. 231–239, 2002.
Ivanenko, Y. P., Grasso, R. and Lacquaniti, F., “Effect of gaze on postural responses to neck proprioceptive and vestibular stimulation in humans,” Journal of Physiology, Vol. 519, No. 1, pp. 301–314, 1999.
Eklund, G., “Further studies of vibration-induced effects on balance,” Upsala Journal of Medical Sciences, Vol. 78, No. 1, pp. 65–72, 1973.
DuPasquier, R. A., Blanc, Y., Sinnereich, M., Landis, T., Burkhard, P. and Vingerhoets, F. J. G., “The effect of aging on postural stability: a cross sectional and longitudinal study,” Neurophysiologie clinique, Vol. 33, No. 5, pp. 213–218, 2003.
Kavounoudias, A., Roll, R. and Roll, J. P., “Specific whole-body shifts induced by frequency-modulated vibrations of human plantar soles,” Neuroscience Letters, Vol. 266, No. 3, pp. 181–184, 1999.
Polonyova, A. and Hlavacka, F., “Human postural responses to different frequency vibrations of lower leg muscles,” Physiological Research, Vol. 50, No. 4, pp. 405–410, 2001.
Kavounoudias, A., Roll, R. and Roll, J. P., “Specific whole-body shifts induced by frequency-modulated vibrations of human plantar soles,” Neuroscience letters, Vol. 266, No. 3, pp. 181–184, 1999.
Hoogvliet, P., Duyl, W. A., Bakker, J. V., Mulder, P. G. H. and Stam, H. J., “A model for the relation between the displacement of the ankle and the center of pressure in the frontal plane, during one-leg stance,” Gait Posture, Vol. 6, No. 1, pp. 39–49, 1997.
Kenneth, J. C., Lisa, S. S. and Marcus, P. B., “Comparison of an in-shoe pressure measure device to a force plate: concurrent validity of center of pressure measurement,” Gait Posture, Vol. 12, No. 2, pp. 128–133, 2000.
Piao, Y. J., Kim, K., Yu, M., Kwon, T. K., Kim, D. W. and Kim, N. G., “Analysis on Training Effects of Postural Control for Elderly Adults,” Int. J. Precis. Eng. Manuf., Vol. 10, No. 3, pp. 133–139, 2009.
Frzovic, D., Morris, M. E. and Vowels, L., “Clinical tests of standing balance: performance of persons with multiple sclerosis,” Archives of Physical Medicine and Rehabilitation, Vol. 81, No. 2, pp. 215–221, 2000.
Berg, K., Wood-Dauphinnee, S., Williams, J. I. and Gayton, D., “Measuring balance in the elderly: Preliminary development of an instrument,” Physiotherapy Canada, Vol. 41, No. 6, pp. 304–311, 1989.
Bohannon, R. W. and Leary, K. M., “Standing balance and function over the course of acute rehabilitation,” Archives of Physical Medicine and Rehabilitation, Vol. 76, No. 11, pp. 994–996, 1995.
Ivanenko, Y. P., Grasso, R. and Lacpuaniti, F., “Influence of leg muscle vibration on human walking,” The Journal of Neurophysiology, Vol. 84, No. 4, pp. 1737–1747, 2000.
Bove, M., Nardone, A. and Schieppati, M., “Effects of leg muscle tendon vibration on group Ia and group II reflex responses to stance perturbation in humans,” The Journal of Physiology, Vol. 550, No. 2, pp. 617–630, 2003.
Cardinale, M. and Lim, J., “Electromyography activity of vastus lateralis muscle during whole-body vibrations of different frequencies,” Journal of Strength & Conditioning Research, Vol. 17, No. 3, pp. 621–624, 2003.
Luo, J., McNamara, B. and Moran, K., “The use of vibration training to enhance muscle strength and power,” Sports Medicine, Vol. 35, No. 1, pp. 23–41, 2005.
Fransson, P. A., Kristinsdottir, E. K., Hafström, A., Magnusson, M. and Johansson, R., “Balance control and adaptation during vibratory perturbations in middle-aged and elderly humans,” European Journal of Applied Physiology, Vol. 91, No. 5–6, pp. 595–603, 2004.
Horak, F. B., Shupert, C. L. and Mirka, A., “Components of postural dyscontrol in the elderly: a review,” Nurobiology of Aging, Vol. 10, No. 6, pp. 727–738, 1989.
Choy, N. L., Brauer, S. and Nitz, J., “Changes in Postural Stability women aged 20-80 years,” Journal of Gerontology, Vol. 58, No. 6, pp. 525–530, 2003.
Woollacott, M. H., “Age-related changes in posture and movement,” Journal of Gerontology, Vol. 48, Special Issue, pp. 56–60, 1993.
Smetanin, B. N., Popov, K. Ye. and Shlikov, V. Yu., “Postural responses to vibrostimulation of the neck muscle proprioceptors in man,” Neurophysiology, Vol. 25, No. 2, pp. 101–108, 1993.
Gurfinkel, V. S., Ivanenko, Y. P., Levick, Y. S. and Babakova, I. A., “Kinesthetic reference for human orthograde posture,” Neuroscience, Vol. 68, No. 1, pp. 229–243, 1995.
Richardson, J. K., Ashton-Miller, J. A., Lee, S. G. and Jacobs, M. K., “Moderate peripheral neuropathy impairs weight transfer and unipedal balance in the elderly,” Archives of Physical Medicine and Rehabilitation, Vol. 77, No. 11, pp. 1152–1156, 1996.
Vuillerme, N., Danion, F., Forestier, N. and Nougier, V., “Postural sway under muscle vibration and muscle fatigue in humans,” Neuroscience Letters, Vol. 333, No. 2, pp. 131–135, 2002.
Tanaka, T., Hashinoto, M., Nakata, T., Ito, T., Ino, S. and Ifulube, T., “Analysis of toe pressure under the foot while dynamic standing on one foot in healthy subjects,” Journal of Orthopaedic & Sports Physical Therapy, Vol. 23, No. 3, pp. 188–193, 1996.
Tanaka, T., Seiji, N., Ino, S., Ifukube, T. and Nakata, M., “Objective method to determine the contribution of the great toe to standing balance and preliminary observation of age-related effects,” IEEE Transactions on Rehabilitation Engineering, Vol. 4, No. 2, pp. 84–90, 1996.
Ceyte, H., Cian, C., Zory, R., Barraud, P. A., Roux, A. and Guerraz, M., “Effect of Achilles tendon vibration on postural orientation,” Neuroscience Letters, Vol. 416, No. 1, pp. 71–75, 2007.
Nurse, M. A. and Nigg, B. M., “Quantifying a relationship between ractile and vibration sensitivity of the human foot with plantar pressure distributions during gait,” Clinical Biomechanics, Vol. 14, No. 9, pp. 667–672, 1999.
Tanaka, T., Takeda, H., Izumi, T., Ino, S. and Ifukube, T., “Effect on the location of the centre of gravity and the foot pressure contribution to standing balance associated with ageing,” Ergonomics, Vol. 42, No. 7, pp. 997–1010, 1999.
Roll, J. P. and Gilhodes, J. C., “Proprioceptive sensory codes mediating movement trajectory perception: human hand vibration-induced drawing illusion,” Canadian Journal of Physiology and Pharmacology, Vol. 73, No. 2, pp. 295–304, 1995.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Yu, M., Piao, YJ., Kim, SH. et al. Effects of tendon vibration during one-legged and two-legged stance in elderly individuals. Int. J. Precis. Eng. Manuf. 11, 969–977 (2010). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12541-010-0117-x
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12541-010-0117-x