Abstract
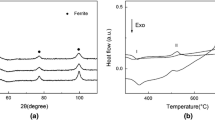
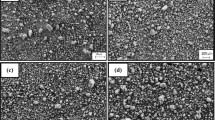
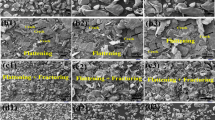
Microstructural changes and corrosion behavior of pure magnesium for different milling times were investigated. The samples with a finer grain size showed poor corrosion resistance because of unstable or metastable protective film formation after immersion in 0.8 wt% NaCl solution. The corrosion resistance did not improve despite the strong (0002) texture of the sample prepared by spark plasma sintering at 500 °C for 0.3 Ks and milling for 2 h. By studying the microstructural changes and texture development, we concluded that the deformation-dependent grain size is the dominant factor controlling the corrosion properties of mechanically milled magnesium. Increased grain boundary densities lead to an enhancement of the overall surface reactivity and, consequently, the corrosion rate.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
M. M. Avedesian and H. Baker, Mg and Mg alloys-ASM Speciality Handbook ASM International. 1 st ed., p.91, ASM International, Ohio (1999).
J. R. Davis, J. D. Destefani, T. B. Zorc, G. M. Crankovic, and A. W. Ronke, Metals Handbook 9 th ed., p.253, ASM international, Ohio (1988).
V. M. Segal, Mater. Sci. Eng. A, 197 157 (1995).
A. Ma, J. Jiang, N. Saito, I. Shigematsu, Y. Yuan, D. Yang, and Y. Nishida, Mater. Sci. Eng. A, 513–514 122 (2009).
E. Prados, V. Sordi, and M. Ferrante, Mater. Sci. Eng. A, 503, 68 (2007).
V. V. Stolyarov, Y. T. Zhu, and T. C. Lowe, Mater. Sci. Eng. A, 303, 82 (2001).
W. J. Kim, K. E. Lee, and S. H. Choi, Mater. Sci. Eng. A, 506, 71 (2009).
H. T. Jeong, T. K. Ha, and W. J. Kim, Korean J. Met. Mater. 43, 860 (2005).
S. J. Yoo and W. J. Kim, Korean J. Met. Mater. 49, 104 (2011).
H. J. Fecht, E. Hellstern, Z. Fu, and W. L. Johnson, Metall. Trans. A, 21, 2333 (1990).
J. Eckert, J. C. Holzer, C. E. Krill, and W. L. Johnson, J. Mater. Res. 7, 1751 (1992).
C. J. Younmgdahl, P. G. Sanders, J. A. Eastman, and J. R. Weertman, Scr. Mater. 37, 809 (1997).
G. W. Nieman and J. R. Weertman, J. Mater. Res. 6, 1012 (1991).
R. Z. Valiev and T. G. Langdon, Prog. Mater. Sci. 51, 881 (2006).
A. Shahryari, J. A. Szpunar, and S. Omanovic, Corros. Sci. 51, 677 (2009).
M. Azzi, S. Faghihi, M. Tabrizian, and J. A. Szpunar, The 15 th Int. Conf. on Texture of Materials, (eds. A.D. Rollett), p.117, The American Ceramic Society, Pitsburgh, PA., USA (2008).
J. Kruger, J. Electrochem. Soc. 106, 847 (1959).
B. W. Davis and P. J. Moran, Corros. Sci. 42, 2187 (2000).
A. Blyanov, J. Kutnyakova, N. A. Amirkhanova, V. V. Stolyarov, R. Z. Valiev, X. Z. Liao, Y. H. Zhao, Y. B. Jiang, H. F. Xu, T. C. Lowe, and Y. T. Zhu, Scr. Mater. 51, 225 (2004).
H. S. Kim, S. J. Yoo, J. W. Ahn, D. H. Kim, and W. J. Kim, Mater. Sci. Eng. A, 528, 8479 (2011).
N. Pebere, C. Riera, and F. Dabosi, Electrochim. Acta, 35, 555 (1990).
C. CaO, Electrochim. Acta, 35, 837 (1990).
S. B. Hocevar, S. Daniele, C. Bragato, and B. Ogorevc, Electrochim. Acta, 53, 555 (2007).
E. Kus, Z. Lee, S. Nutt, and F. Mansfeld, Corrosion, 62, 152 (2006).
M. K. Chung, Y. S. Choi, J. G. Kim, Y. M. Kim, and J. C. Lee, Mater. Sci. Eng. A, 366, 282 (2004).
E. Sikora, X. J. Wei, and B. A. Shaw, Corrosion, 60, 387 (2004).
T. C. Tsai and T. H. Chuang, Mater. Sci. Eng. A, 225, 135 (1997).
K. D. Ralston, N. Birbilis, and C. H. J. Davies, Scr. Mater. 63, 1201 (2010).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Kim, K.R., Ahn, J.W., Kim, GH. et al. Corrosion behavior of magnesium powder fabricated by high-energy ball milling and spark plasma sintering. Met. Mater. Int. 20, 1095–1101 (2014). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12540-014-6023-5
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12540-014-6023-5