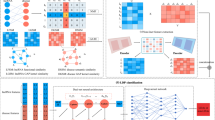
Abstract
LncRNAs play a part in numerous momentous processes of biology such as disease diagnoses, preventions and treatments. The associations between various diseases and lncRNAs are one of the crucial approaches to learn the role and status of lncRNAs in human diseases. With the researches on lncRNA and diseases, multiple methods based on neural network have been employed to predict these associations. However, the deep and complicated characteristic representations of lncRNA-disease associations were failed to be extracted, and the discriminative contributions of the interactions, correlations, and similarities among miRNAs diseases, and lncRNAs for the correlation predictions were ignored. In this paper, based on the multibiology premise of lncRNAs, miRNAs, and diseases, a dual attention network was proposed to predict the model of lncRNA-disease associations for miRNAs, the disease characteristic matrix, and lncRNAs. Through two attention modules, we enable the model to learn the nonlinear, more complex and useful features of lncRNA, miRNA, and disease characteristic matrix. For the feature embedding matrix composed of lncRNA-disease, the connection between lncRNA-disease feature embedding matrix and lncRNA, miRNA, and disease characteristic matrix was enhanced through deconvolution and feature fusion layer. Compared with several latest methods, the method proposed in this paper can produce better performance. Researches on the cases of osteosarcoma, lung cancer, and gastric cancer have confirmed the effective recognition of potential lncRNA-disease associations.







Similar content being viewed by others
References
Taft RJ, Pang KC, Mercer TR, Dinger M, Mattick JS (2010) Non-coding RNAs: regulators of disease. J Pathol 220(2):126–139. https://doi.org/10.1002/path.2638
Zeng M, Lu C, Zhang F, Li Y, Wu FX, Li Y, Li M (2020) SDLDA: lncRNA-disease association prediction based on singular value decomposition and deep learning. Methods 179:73–80. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ymeth.2020.05.002
Mercer TR, Mattick JS (2013) Structure and function of long noncoding RNAs in epigenetic regulation. Nat Struct Mol Biol 20(3):300–307. https://doi.org/10.1038/nsmb.2480
Zhang T, Wang M, Xi J, Li A (2020) LPGNMF: predicting long non-coding RNA and protein interaction using graph regularized nonnegative matrix factorization. IEEE/ACM Trans Comput Biol Bioinf 17(1):189–197. https://doi.org/10.1109/TCBB.2018.2861009
Bressin A, Schultesasse R, Figini D, Urdaneta EC, Beckmann BM, Marsico A (2019) TriPepSVM: de novo prediction of RNA-binding proteins based on short amino acid motifs. Nucleic Acids Res 47(9):4406–4417. https://doi.org/10.1093/nar/gkz203
Heller D, Krestel R, Ohler U, Vingron M, Marsico A (2017) SSHMM: extracting intuitive sequence-structure motifs from high-throughput RNA-binding protein data. Nucleic Acids Res 45(19):11004–11018. https://doi.org/10.1093/nar/gkx756
Gaur A, Jewell DA, Liang Y, Ridzon D, Moore JH, Chen C, Ambros VR, Israel MA (2007) Characterization of microRNA expression levels and their biological correlates in human cancer cell lines. Can Res 67(6):2456–2468. https://doi.org/10.1093/bioinformatics/btq241
Hrdlickova B, De Almeida RC, Borek Z, Withoff S (2014) Genetic variation in the non-coding genome: involvement of micro-RNAs and long non-coding RNAs in disease. Biochim Biophys Acta 1842(10):1910–1922. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.bbadis.2014.03.011
Piro RM, Marsico A (2019) Network-based methods and other approaches for predicting LncRNA functions and disease associations. Methods Mol Biol (Clifton, NJ). https://doi.org/10.1007/978-1-4939-8982-9_12
Fu L, Peng Q (2017) A deep ensemble model to predict miRNA-disease association. Sci Rep 7(1):14482–14482. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41598-017-15235-6
Mamoshina P, Vieira A, Putin E, Zhavoronkov A (2016) Applications of deep learning in biomedicine. Mol Pharm 13(5):1445–1454. https://doi.org/10.1021/acs.molpharmaceut.5b00982
Chen X, Yan CC, Luo C, Ji W, Zhang Y, Dai Q (2015) Constructing lncRNA functional similarity network based on lncRNA-disease associations and disease semantic similarity. Sci Rep 5(1):11338–11338. https://doi.org/10.1038/srep11338
Ping P, Wang L, Kuang L, Ye S, Iqbal MFB, Pei T (2018) A novel method for lncRNA-disease association prediction based on an lncRNA-disease association network. IEEE/ACM Trans Comput Biol Bioinform. https://doi.org/10.1109/TCBB.2018.2827373
Xuan P, Sheng N, Zhang T, Liu Y, Guo Y (2019) CNNDLP: a method based on convolutional autoencoder and convolutional neural network with adjacent edge attention for predicting lncrna-disease associations. Int J Mol ENCES 20(17):4260. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms20174260
Ping Xuan, Yihua Dong, Yahong Guo, Tiangang Zhang, Yong Liu (2018) Dual convolutional neural network based method for predicting disease-related miRNAs. Int J Mol Sci. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms19123732
Ping P, Wang L, Kuang L, Ye S, Iqbal MFB, Pei T (2019) A novel method for lncRNA-disease association prediction based on an lncRNA-disease association network. IEEE/ACM Trans Comput Biol Bioinf 16(2):688–693. https://doi.org/10.1109/TCBB.2018.2827373
Lan W, Li M, Zhao K, Liu J, Wu F, Pan Y, Wang J (2016) LDAP: a web server for lncRNA-disease association prediction. Bioinformatics 33(3):458–460. https://doi.org/10.1093/bioinformatics/btw639
Fu G, Wang J, Domeniconi C, Yu G (2018) Matrix factorization-based data fusion for the prediction of lncRNA-disease associations. Bioinformatics 34(9):1529–1537. https://doi.org/10.1093/bioinformatics/btx794
Lu C, Yang M, Luo F, Wu F, Li M, Pan Y, Li Y, Wang J (2018) Prediction of lncRNA-disease associations based on inductive matrix completion. Bioinformatics 34(19):3357–3364. https://doi.org/10.1093/bioinformatics/bty327
Ning S, Zhang J, Wang P, Zhi H, Wang J, Liu Y, Gao Y, Guo M, Yue M, Wang L et al (2016) Lnc2cancer: a manually curated database of experimentally supported lncRNAs associated with various human cancers. Nucleic Acids Res 44(D1):D980–D985. https://doi.org/10.1093/nar/gkv1094
Ning S, Zhang J, Peng W, Zhi H, Wang J, Yue L, Gao Y, Guo M, Ming Y, Wang L (2016) Lnc2cancer: a manually curated database of experimentally supported lncRNAs associated with various human cancers. Nucleic Acids Res D1:D980–D985. https://doi.org/10.1093/nar/gkv1094
Lu Z, Bretonnel CK, Hunter L (2007) Generif quality assurance as summary revision. 269–280. https://doi.org/10.1142/9789812772435_026
Li J, Liu S, Zhou H, Qu L, Yang J (2014) starbase v2.0: decoding miRNA–ceRNA, miRNA–ncRNA and protein-RNA interaction networks from large-scale clip-seq data. Nucleic Acids Res 42:92–97. https://doi.org/10.1093/nar/gkt1248
Li Y, Qiu C, Tu J, Geng B, Yang J, Jiang T, Cui Q (2014) HMDD v2.0: a database for experimentally supported human microRNA and disease associations. Nucleic Acids Res 42(D1):D1070–D1074. https://doi.org/10.1093/nar/gkt1023
Cheng L, Hu Y, Sun J, Zhou M, Jiang Q (2018) DincRNA: a comprehensive web-based bioinformatics toolkit for exploring disease associations and ncRNA function. Bioinformatics 34(11):1953–1956. https://doi.org/10.1093/bioinformatics/bty002
Wang D, Wang J, Lu M, Song F, Cui Q (2010) Inferring the human microRNA functional similarity and functional network based on microRNA-associated diseases. Bioinformatics 26(13):1644–1650. https://doi.org/10.1093/bioinformatics/btq241
Xu Y, Guo M, Liu X, Wang C, Liu Y (2014) Inferring the soybean (glycine max) microRNA functional network based on target gene network. Bioinformatics 30(1):94–103. https://doi.org/10.1093/bioinformatics/btt605
Xuan P, Pan S, Zhang T, Liu Y, Sun H (2019) Graph convolutional network and convolutional neural network based method for predicting lncRNA-disease associations. Cells 8(9):1012. https://doi.org/10.3390/cells8091012
Chao P, Zhang X, Gang Y, Luo G, Jian S (2017) Large kernel matters-improve semantic segmentation by global convolutional network. In: Proceedings of the IEEE conference on computer vision and pattern recognition, pp 4353–4361. https://doi.org/10.1109/CVPR.2017.189
Fu J, Liu J, Tian H, Li Y, Bao Y, Fang Z, Lu H (2019) Dual attention network for scene segmentation. In: Computer vision and pattern recognition, pp 3146–3154. https://doi.org/10.1109/CVPR.2019.00326
Yarotsky Dmitry (2017) Error bounds for approximations with deep ReLU networks. Neural Netw 94:103–114. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.neunet.2017.07.002
Bahdanau D, Cho K, Bengio Y (2014) Neural machine translation by jointly learning to align and translate. In: Computation and language. arXiv:1409.0473
Sheng N, Cui H, Zhang T, Xuan P (2020) Attentional multi-level representation encoding based on convolutional and variance autoencoders for lncRNA-disease association prediction. Brief Bioinform. https://doi.org/10.1093/bib/bbaa067
Zhang H, Goodfellow I, Metaxas D, Odena A (2018) Self-attention generative adversarial networks. In: Machine learning. arXiv:1805.08318
Xuan P, Shen T, Wang X, Zhang T, Zhang W (2018) Inferring disease-associated microRNAs in heterogeneous networks with node attributes. IEEE/ACM Trans Comput Biol Bioinf. https://doi.org/10.1109/TCBB.2018.2872574
Feichtenhofer C, Pinz A, Zisserman A (2016) Convolutional two-stream network fusion for video action recognition. In: Proceedings of the IEEE conference on computer vision and pattern recognition, pp 1933–1941. https://doi.org/10.1109/CVPR.2016.213
Wang X, Yu K, Dong C, Loy CC (2018) Recovering realistic texture in image super-resolution by deep spatial feature transform. In: Computer vision and pattern recognition, pp 606–615. arXiv:1804.02815
Lin T, Goyal P, Girshick R, He K, Dollar P (2017) Focal loss for dense object detection. In: Computer vision and pattern recognition, pp 2999–3007. https://doi.org/10.1109/ICCV.2017.324
Hajian-Tilaki K (2013) Receiver operating characteristic (ROC) curve analysis for medical diagnostic test evaluation. Caspian J Intern Med 4(2):627–635
Sun X, Xin Y, Wang M, Li S, Miao S, Xuan Y, Wang Y, Lu T, Liu J, Jiao W (2018) Overexpression of long non-coding RNA kcnq1ot1 is related to good prognosis via inhibiting cell proliferation in non-small cell lung cancer. Thoracic Cancer. https://doi.org/10.1111/1759-7714.12599
Bahari F, Emadibaygi M, Nikpour P (2015) mir-17-92 host gene, uderexpressed in gastric cancer and its expression was negatively correlated with the metastasis. Indian J Cancer 52(1):22–25. https://doi.org/10.4103/0019-509X.175605
Zhang J, Lu S, Zhu JF, Yang KP (2016) Up-regulation of LncRNA HULC predicts a poor prognosis and promotes growth and metastasis in non-small cell lung cancer. Int J Clin Exp Pathol 9(12):12415–12422
Sun B, Yang N (2017) Long non-coding RNA mir155hg promotes proliferation, migration and invasion of a549 human lung cancer cells. Journal of Chongqing Medical University
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declared that they have no conflicts of interest to this work.
Research involving human participants and/or animals
This article does not contain any studies with human participants and animals performed by any of the authors.
Informed consent
Informed consent was obtained from all individual participants included in the study.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Liu, Y., Yu, Y. & Zhao, S. Dual Attention Mechanisms and Feature Fusion Networks Based Method for Predicting LncRNA-Disease Associations. Interdiscip Sci Comput Life Sci 14, 358–371 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12539-021-00492-x
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12539-021-00492-x