Abstract
Inferring gene regulatory networks (GRNs) from microarray data can help us understand the mechanisms of life and eventually develop effective therapies. Currently, many computational methods have been used in inferring GRNs. However, owing to high-dimensional data and small samples, these methods often tend to introduce redundant regulatory relationships. Therefore, a novel network inference method based on the improved Markov blanket discovery algorithm, IMBDANET, is proposed to infer GRNs. Specifically, for each target gene, data processing inequality was applied to the Markov blanket discovery algorithm for the accurate differentiation of direct regulatory genes from indirect regulatory genes. Finally, direct regulatory genes were used in constructing GRNs, and the network structure was optimized according to the importance degree score. Experimental results on six public network datasets show that the proposed method can be effectively used to infer GRNs.
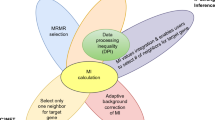
Graphic abstract





Similar content being viewed by others
Data availability and material
The reaction chains datasets used in this study are available at https://www.genome.jp. The DREAM3 datasets are available at https://www.synapse.org/#!Synapse: syn2853597.The Escherichia coli datasets are available at http://regulondb.ccg.unam.mx/inde x.jsp.
References
Liu H, Ren G, Chen H, Liu Q, Yang Y, Zhao Q (2020) Predicting lncRNA–miRNA interactions based on logistic matrix factorization with neighborhood regularized. Knowl-Based Syst. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.knosys.2019.105261
Lv Y, Bao E (2009) Apoptosis induced in chicken embryo fibroblasts in vitro by a polyinosinic:polycytidylic acid copolymer. Toxicol In Vitro 23(7):1360–1364. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.tiv.2009.06.026
Altay G, Emmert-Streib F (2010) Inferring the conservative causal core of gene regulatory networks. BMC Syst Biol 4:132. https://doi.org/10.1186/1752-0509-4-132
Zhang L, Yang P, Feng H, Zhao Q, Liu H (2021) Using network distance analysis to predict lncRNA-miRNA interactions. Interdiscip Sci 13(3):535–545. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12539-021-00458-z
Elnitski L, Jin VX, Farnham PJ, Jones SJ (2006) Locating mammalian transcription factor binding sites: a survey of computational and experimental techniques. Genome Res 16(12):1455–1464. https://doi.org/10.1101/gr.4140006
Maetschke SR, Madhamshettiwar PB, Davis MJ, Ragan MA (2014) Supervised, semi-supervised and unsupervised inference of gene regulatory networks. Brief Bioinform 15(2):195–211. https://doi.org/10.1093/bib/bbt034
Bar-Joseph Z (2004) Analyzing time series gene expression data. Bioinformatics 20(16):2493–2503. https://doi.org/10.1093/bioinformatics/bth283
Huang S (1999) Gene expression profiling, genetic networks, and cellular states: an integrating concept for tumorigenesis and drug discovery. J Mol Med (Berl) 77(6):469–480. https://doi.org/10.1007/s001099900023
Lim CY, Wang H, Woodhouse S, Piterman N, Wernisch L, Fisher J, Gottgens B (2016) BTR: training asynchronous Boolean models using single-cell expression data. BMC Bioinformatics 17(1):355. https://doi.org/10.1186/s12859-016-1235-y
Zhou JX, Samal A, d’Herouel AF, Price ND, Huang S (2016) Relative stability of network states in Boolean network models of gene regulation in development. Biosystems 142–143:15–24. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.biosystems.2016.03.002
Tan M, Alshalalfa M, Alhajj R, Polat F (2011) Influence of prior knowledge in constraint-based learning of gene regulatory networks. IEEE/ACM Trans Comput Biol Bioinform 8(1):130–142. https://doi.org/10.1109/TCBB.2009.58
Shi M, Shen W, Wang HQ, Chong Y (2016) Adaptive modelling of gene regulatory network using Bayesian information criterion-guided sparse regression approach. IET Syst Biol 10(6):252–259. https://doi.org/10.1049/iet-syb.2016.0005
Alter O, Brown PO, Botstein D (2000) Singular value decomposition for genome-wide expression data processing and modeling. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 97(18):10101–10106. https://doi.org/10.1073/pnas.97.18.10101
Cantone I, Marucci L, Iorio F, Ricci MA, Belcastro V, Bansal M, Santini S, di Bernardo M, di Bernardo D, Cosma MP (2009) A yeast synthetic network for in vivo assessment of reverse-engineering and modeling approaches. Cell 137(1):172–181. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cell.2009.01.055
Honkela A, Girardot C, Gustafson EH, Liu YH, Furlong EE, Lawrence ND, Rattray M (2010) Model-based method for transcription factor target identification with limited data. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 107(17):7793–7798. https://doi.org/10.1073/pnas.0914285107
Huppenkothen D, Heil LM, Hogg DW, Mueller A (2017) Using machine learning to explore the long-term evolution of GRS 1915+105. Mon Not R Astron Soc 466(2):2364–2377. https://doi.org/10.1093/mnras/stw3190
Betliński P, Ślęzak D (2012) The Problem of Finding the Sparsest Bayesian Network for an Input Data Set is NP-Hard, vol 7661. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-642-34624-8_3
Zhang X, Zhao J, Hao JK, Zhao XM, Chen L (2015) Conditional mutual inclusive information enables accurate quantification of associations in gene regulatory networks. Nucleic Acids Res 43(5):e31. https://doi.org/10.1093/nar/gku1315
Zhao J, Zhou Y, Zhang X, Chen L (2016) Part mutual information for quantifying direct associations in networks. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 113(18):5130–5135. https://doi.org/10.1073/pnas.1522586113
Faith JJ, Hayete B, Thaden JT, Mogno I, Wierzbowski J, Cottarel G, Kasif S, Collins JJ, Gardner TS (2007) Large-scale mapping and validation of Escherichia coli transcriptional regulation from a compendium of expression profiles. PLoS Biol 5(1):e8. https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pbio.0050008
Margolin AA, Nemenman I, Basso K, Wiggins C, Stolovitzky G, Dalla Favera R, Califano A (2006) ARACNE: an algorithm for the reconstruction of gene regulatory networks in a mammalian cellular context. BMC Bioinformatics 7(Suppl 1):S7. https://doi.org/10.1186/1471-2105-7-S1-S7
Meyer PE, Kontos K, Lafitte F, Bontempi G (2007) Information-theoretic inference of large transcriptional regulatory networks. EURASIP J Bioinform Syst Biol. https://doi.org/10.1155/2007/79879
Liu W, Zhu W, Liao B, Chen X (2016) Gene regulatory network inferences using a maximum-relevance and maximum-significance strategy. PLoS One 11(11):e0166115. https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0166115
Liu W, Zhu W, Liao B, Chen H, Ren S, Cai L (2017) Improving gene regulatory network structure using redundancy reduction in the MRNET algorithm. RSC Adv 7(37):23222–23233. https://doi.org/10.1039/c7ra01557g
Hasman A (1991) Probabilistic reasoning in intelligent systems: networks of plausible inference. Int J Biomed Comput 28(3):221–225. https://doi.org/10.1016/0020-7101(91)90056-k
Peña JM, Nilsson R, Björkegren J, Tegnér J (2007) Towards scalable and data efficient learning of Markov boundaries. Int J Approximate Reasoning 45(2):211–232. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijar.2006.06.008
Yaramakala S, Margaritis D (2005) Speculative Markov blanket discovery for optimal feature selection. Paper presented at the Data Mining, Fifth IEEE International Conference on. https://doi.org/10.1109/ICDM.2005.134.
Jain A, Zongker D (1997) Feature selection: evaluation, application, and small sample performance. IEEE Trans Pattern Anal Mach Intell 19(2):153–158. https://doi.org/10.1109/34.574797
Zhao F, Qiu HM, Pan LQ, Zhu H, Zhang YP, Guo ZG, Yin JH, Zhao XD, Xiao JQ (2008) Ferromagnetism analysis of Mn-doped CuO thin films. J Phys. https://doi.org/10.1088/0953-8984/20/42/425208
Zhang Y, Zhang Z, Liu K, Qian G (2010) An improved IAMB algorithm for Markov Blanket Discovery. J Comp. https://doi.org/10.4304/jcp.5.11.1755-1761
Tsamardinos I, Aliferis C, Statnikov A (2003) Time and Sample Efficient Discovery of Markov Blankets And Direct Causal Relations. https://doi.org/10.1145/956750.956838
Ramanan N, Natarajan S (2020) Causal learning from predictive modeling for observational data. Front Big Data 3:535976. https://doi.org/10.3389/fdata.2020.535976
Fu S, Fast Desmarais MC (2008) Markov Blanket Discovery Algorithm Via Local Learning within Single Pass. In, Berlin, Heidelberg. Adv Artif Intell. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-540-68825-9_10
Yang Y (2012) Elements of information theory. J Am Stat Assoc 103(481):429–429. https://doi.org/10.1198/jasa.2008.s218
Altay G, Emmert-Streib F (2010) Revealing differences in gene network inference algorithms on the network level by ensemble methods. Bioinformatics 26(14):1738–1744. https://doi.org/10.1093/bioinformatics/btq259
Samoilov M, Arkin A, Ross J (2001) On the deduction of chemical reaction pathways from measurements of time series of concentrations. Chaos 11(1):108–114. https://doi.org/10.1063/1.1336499
Marbach D, Prill RJ, Schaffter T, Mattiussi C, Floreano D, Stolovitzky G (2010) Revealing strengths and weaknesses of methods for gene network inference. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 107(14):6286–6291. https://doi.org/10.1073/pnas.0913357107
Ronen M, Rosenberg R, Shraiman BI, Alon U (2002) Assigning numbers to the arrows: parameterizing a gene regulation network by using accurate expression kinetics. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 99(16):10555–10560. https://doi.org/10.1073/pnas.152046799
Boughorbel S, Jarray F, El-Anbari M (2017) Optimal classifier for imbalanced data using Matthews Correlation Coefficient metric. PLoS ONE 12(6):e0177678. https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0177678
Zhang X, Liu K, Liu ZP, Duval B, Richer JM, Zhao XM, Hao JK, Chen L (2013) NARROMI: a noise and redundancy reduction technique improves accuracy of gene regulatory network inference. Bioinformatics 29(1):106–113. https://doi.org/10.1093/bioinformatics/bts619
Funding
This study was supported by the National Natural Science Foundation of China (Grant No. 61902125), Natural Science Foundation of Hunan Province (2019JJ50187), and Scientific Research Project of Hunan Education Department (Grant No. 19C1788).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
WL and YJ participated in the design of the study, developed the code and wrote the manuscript. QZ and HT conceived and coordinated the study and helped to revise the manuscript. LP and XS analyzed the results and provided the constructive discussions. WG helped to revise the manuscript. All authors read and approved the final manuscript.
Corresponding authors
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Supplementary Information
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Liu, W., Jiang, Y., Peng, L. et al. Inferring Gene Regulatory Networks Using the Improved Markov Blanket Discovery Algorithm. Interdiscip Sci Comput Life Sci 14, 168–181 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12539-021-00478-9
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12539-021-00478-9