Abstract
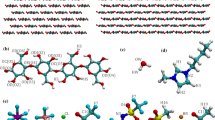
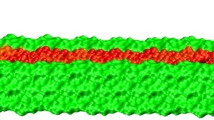
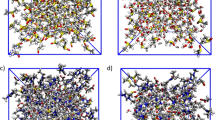
The use of ionic liquids for non-derivatized cellulose dissolution promises an alternative method for the thermochemical pretreatment of biomass that may be more efficient and environmentally acceptable than more conventional techniques in aqueous solution. Here, we performed equilibrium MD simulations of a cellulose microfibril in the ionic liquid 1-butyl-3-methylimidazolium chloride (BmimCl) and compared the solute structure and the solute-solvent interactions at the interface with those from corresponding simulations in water. The results indicate a higher occurrence of solvent-exposed orientations of cellulose surface hydroxymethyl groups in BmimCl than in water. Moreover, spatial and radial distribution functions indicate that hydrophilic surfaces are a preferred site of interaction between cellulose and the ionic liquid. In particular, hydroxymethyl groups on the hydrophilic fiber surface adopt a different conformation from their counterparts oriented towards the fiber’s core. Furthermore, the glucose units with these solvent-oriented hydroxymethyls are surrounded by the heterocyclic organic cation in a preferred parallel orientation, suggesting a direct and distinct interaction scheme between cellulose and BmimCl.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Berendsen, H.J.C., Postma, J.P.M., van Gunsteren, W.F., DiNola, A., Haak, J.R. 1984. Molecular dynamics with coupling to an external bath. J Chem Phys 81, 3684–3690.
Bergenstrahle, M., Berglund, L., Mazeau, K. 2007. Thermal response in crystalline Ibeta cellulose: a molecular dynamics study. J of Phys Chem B 111, 9138–9145.
Bussi, G., Donadio, D., Parrinello, M. 2007. Canonical sampling through velocity rescaling. J Chem Phys 126, 014101.
Cuissinat, C., Navard, P., Heinze, T. 2008. Swelling and dissolution of cellulose. Part IV: Free floating cotton and wood fibres in ionic liquids. Carbohyd Polym 72, 590–596.
Darden, T., York, D., Pedersen, L. 1993. Particle mesh Ewald: An Nlog(N) method for Ewald sums in large systems. J Chem Phys 98, 10089–10092.
El Seoud, O., Koschella, A., Fidale, L., Dorn, S., Heinze, T. 2007. Applications of ionic liquids in carbohydrate chemistry: A window of opportunities. Biomacromolecules 8, 2629–2647.
Erdmenger, T., Haensch, C., Hoogenboom, R., Schubert, U. 2007. Homogeneous tritylation of cellulose in 1-butyl-3-methylimidazolium chloride. Macromol Biosci 7, 440–445.
Fairley, P. 2011. Introduction: Next generation biofuels. Nature 474, S2–S5.
Fredlake, C., Crosthwaite, J., Hert, D., Aki, S., Brennecke, J. 2004. Thermophysical properties of imidazolium-based ionic liquids. J Chem Eng Data 49, 954–964.
Frisch, M. 1998. GAUSSIAN 98 (Pittsburgh, PA).
Fukaya, Y., Hayashi, K., Kim, S.S., Ohno, H. 2010. Design of Polar Ionic Liquids To Solubilize Cellulose without Heating. In: Liebert, T., Heinze, T., and Edgar, K. (eds) Cellulose Solvents: For Analysis, Shaping and Chemical Modification, Volume 1033, ACS, pp 55–66.
Geddes, C., Nieves, I., Ingram, L. 2011. Advances in ethanol production. Curr Opin Biotech 22, 312–319.
Gericke, M., Schlufter, K., Liebert, T., Heinze, T., Budtova, T. 2009. Rheological properties of cellulose/ ionic liquid solutions: From dilute to concentrated states. Biomacromolecules 10, 1188–1194.
Graenacher, C. 1934. U.S. Patent 1,946,176
Gross, A., Chu, J.-W. 2010. On the molecular origins of biomass recalcitrance: The interaction network and solvation structures of cellulose microfibrils. J Phys Chem B 114, 13333–13341.
Heinze, T., Liebert, T. 2001. Unconventional methods in cellulose functionalization. Prog Polym Sci 26, 1689–1762.
Heinze, T., Schwikal, K., Barthel, S. 2005. Ionic liquids as reaction medium in cellulose functionalization. Macromol Biosci 5, 520–525.
Hess, B., Bekker, H., Berendsen, H., Fraaije, J. 1997. LINCS: A linear constraint solver for molecular simulations. J Comput Chem 18, 1463–1472.
Hess, B., Kutzner, C., van der Spoel, D., Lindahl, E. 2008. GROMACS 4: Algorithms for highly efficient, load-balanced, and scalable molecular simulation. J Chem Theory Comput 4, 435–447.
Himmel, M., Ding, S.-Y., Johnson, D., Adney, W., Nimlos, M., Brady, J., Foust, T. 2007. Biomass recalcitrance: Engineering plants and enzymes for biofuels production. Science 315, 804–807.
Huddleston, J., Visser, A., Reichert, M., Willauer, H., Broker, G., Rogers, R. 2001. Characterization and comparison of hydrophilic and hydrophobic room temperature ionic liquids incorporating the imidazolium cation. Green Chem 3, 156–164.
Inamura, Y., Yamamuro, O., Hayashi, S., Hamaguchi, H. 2006. Dynamics structure of a room-temperature ionic liquid bmimCl. Physica B: Condensed Matter 385-386, 732–734.
Jorgensen, W., Chandrasekhar, J., Madura, J., Impey, R., Klein, M. 1983. Comparison of simple potential functions for simulating liquid water. J Chem Phys 79, 926–935.
Kirschner, K., Yongye, A., Tschampel, S., Gonzalez-Outeirino, J., Daniels, C., Foley, L., Woods, R. 2008. GLYCAM06: A generalizable biomolecular force field. Carbohydrates. J Comput Chem 29, 622–655.
Klein, H.C., Cheng, X., Smith, J.C., Shen, T. 2011. Transfer matrix approach to the hydrogen-bonding in cellulose I-alpha fibrils describes the recalcitrance to thermal deconstruction. J Chem Phys 135, 085106.
Kowsari, M.H., Alavi, S., Ashrafizaadeh, M., Najafi, B. 2008. Molecular dynamics simulation of imidazolium-based ionic liquids. I. Dynamics and diffusion coefficient. J Chem Phys 129, 224508.
Liebert, T. 2010. Cellulose solvents — remarkable history, bright future. In: Liebert, T., Heinze, T., and Edgar, K. (eds.) Cellulose Solvents: For Analysis, Shaping and Chemical Modification, Volume 1033, ACS, pp 3–54.
Liu, Z., Huang, S., Wang, W. 2004. A refined force field for molecular simulation of imidazolium-based ionic liquids. J Phys Chem B 108, 12978–12989.
Liu, H., Sale, K., Holmes, B., Simmons, B., Singh, S. 2010. Understanding the interactions of cellulose with ionic liquids: a molecular dynamics study. J Phys Chem B 114, 4293–4301.
Matthews, J., Bergenstrahle, M., Beckham, G., Himmel, M., Nimlos, M., Brady, J., Crowley, M. 2011. High-temperature behavior of cellulose I. J Phys Chem B 115, 2155–2166.
Matthews, J., Skopec, C., Mason, P., Zuccato, P., Torget, R., Sugiyama, J., Himmel, M., Brady, J. 2006. Computer simulation studies of microcrystalline cellulose I-beta. Carbohyd Res 341, 138–152.
Mazeau, K. 2005. Structural micro-heterogeneities of crystalline ibeta-cellulose. Cellulose 12, 339–349.
Mazza, M., Catana, D.-A., Vaca-Garcia, C., Cecutti, C. 2009. Influence of water on the dissolution of cellulose in selected ionic liquids. Cellulose 16, 207–215.
Mosier, N. 2005. Features of promising technologies for pretreatment of lignocellulosic biomass. Bioresource Technol 96, 673–686.
Murray, R. 2006. The analytical chemistry measurement cop on buzzwords. Anal Chem 78, 2080–2080.
Nishiyama, Y., Langan, P., Chanzy, H. 2002. Crystal structure and hydrogen-bonding system in cellulose Ibeta from synchrotron X-ray and neutron fiber diffraction. J Am Chem Soc 124, 9074–9082.
Novoselov, N., Sashina, E., Petrenko, V., Zaborsky, M. 2007. Study of dissolution of cellulose in ionic liquids by computer modeling. Fibre Chem 39, 153–158.
Philipp, B., Lukanoff, B., Schleicher, H., Wagenknecht, W. 1986. Homogene umsetzung an cellulose in organischen loesemittelsystemen. Z Chem 26, 50–58.
Ragauskas, A., Williams, C., Davison, B., Britovsek, G., Cairney, J., Eckert, C., Frederick, W., Hallett, J., Leak, D., Liotta, C., Mielenz, J., Murphy, R., Templer, R., Tschaplinski, T. 2006. The path forward for biofuels and biomaterials. Science 311, 484–489.
Remsing, R., Hernandez, G., Swatloski, R., Massefski, W., Rogers, R., Moyna, G. 2008. Solvation of carbohydrates in n,n′-dialkylimidazolium ionic liquids: A multinuclear NMR spectroscopy study. J Phys Chem B 112, 11071–11078.
Remsing, R., Swatloski, R., Rogers, R., Moyna, G. 2006. Mechanism of cellulose dissolution in the ionic liquid 1-n-butyl-3-methylimidazolium chloride: A 13C and 35/37Cl NMR relaxation study on model systems. Chem Commun 12, 1271–1273.
Rinaldi, R., Palkovits, R., Schueth, F. 2008. Depolymerization of cellulose using solid catalysts in ionic liquids13. Angew Chem Int Edit 47, 8047–8050.
Rockwell, G., Grindley, B. 1998. Effect of solvation on the rotation of hydroxymethyl groups in carbohydrates. J Am Chem Soc 120, 10953–10963.
Schubert, C. 2006. Can biofuels finally take center stage? Nature Biotechnol 24, 777–784.
Sellin, M., Ondruschka, B., Stark, A. 2010. Hydrogen bond acceptor properties of ionic liquids and their effect on cellulose solubility. In: Liebert, T., Heinze, T., and Edgar, K. (eds.), Cellulose Solvents: For Analysis, Shaping and Chemical Modification, Volume 1033, (ACS), pp. 121–135.
Swatloski, R. 2003. World Patent number 1,029,329
Swatloski, R., Spear, S., Holbrey, J., Rogers, R. 2002. Dissolution of cellose with ionic liquids. J Am Chem Soc 124, 4974–4975.
Thibaudeau, C., Stenutz, R., Hertz, B., Klepach, T., Zhao, S., Wu, Q., Carmichael, I., Serianni, A. 2004. Correlated C-C and C-O bond conformations in saccharide hydroxymethyl groups: Parametrization and application of redundant 1H-1H, 13C-1H, and 13C-13C NMR J-couplings. J Am Chem Soc 126, 15668–15685.
Urahata, S.R., Ribeiro, M. 2005. Single particle dynamics in ionic liquids of 1-alkyl-3-methylimidazolium cations. J Chem Phys 122, 024511.
Vitz, J., Erdmenger, T., Haensch, C., Schubert, U. 2009. Extended dissolution studies of cellulose in imidazolium based ionic liquids. Green Chem 11, 417–424.
Wyman, C., Dale, B., Elander, R., Holtzapple, M., Ladisch, M., Lee, Y.Y. 2005. Coordinated development of leading biomass pretreatment technologies. Bioresource Technol 96, 1959–1966.
Yamamuro, O., Minamimoto, Y., Inamura, Y., Hayashi, S., Hamaguchi, H. 2006. Heat capacity and glass transition of an ionic liquid 1-butyl-3-methylimidazolium chloride. Chem Phys Lett 423, 371–375.
Yoshida, M., Liu, Y., Uchida, S., Kawarada, K., Ukagami, Y., Ichinose, H., Kaneko, S., Fukuda, K. 2008. Effects of cellulose crystallinity, hemicellulose, and lignin on the enzymatic hydrolysis of miscanthus sinensis to monosaccharides. Biosci Biotech Bioch 72, 805–810.
Youngs, T., Holbrey, J., Deetlefs, M., Nieuwenhuyzen, M., Costa Gomes, M., Hardacre, C. 2006. A molecular dynamics study of glucose solvation in the ionic liquid 1,3-dimethylimidazolium chloride. ChemPhysChem 7, 2279–2281.
Youngs, T.G., Hardacre, C., Holbrey, J.D. 2007. Glucose solvation by the ionic liquid 1,3-dimethylimidazolium chloride: A simulation study. J Phys Chem B 111, 13765–13774.
Yui, T., Nishimura, S., Akiba, S., Hayashi, S. 2006. Swelling behavior of the cellulose Ibeta crystal models by molecular dynamics. Carbohyd Res 341, 2521–2530.
Zhang, H., Wu, J., Zhang, J., He, J. 2005. 1-Allyl-3-methylimidazolium chloride room temperature ionic liquid: A new and powerful nonderivatizing solvent for cellulose. Macromolecules 38, 8272–8277.
Zhao, H., Xia, S., and Ma, P. 2005. Use of ionic liquids as lsquogreenrsquo solvents for extractions. J Chem Technol Biot 80, 1089–1096.
Zhu, S., Wu, Y., Chen, Q., Yu, Z., Wang, C., Jin, S., Ding, Y., Wu, G. 2006. Dissolution of cellulose with ionic liquids and its application: A mini-review. Green Chem 8, 325–327.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Mostofian, B., Smith, J.C. & Cheng, X. The solvation structures of cellulose microfibrils in ionic liquids. Interdiscip Sci Comput Life Sci 3, 308–320 (2011). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12539-011-0111-8
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12539-011-0111-8