Abstract
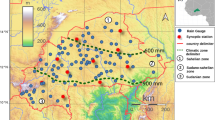
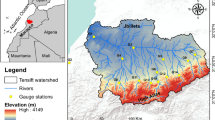
Under the inaccessibility of optimum networks and lack of well-organized rain gauge data, the provided high-resolution satellite estimates serve as a vital baseline for hydro climate-associated studies. In the rugged topography of South Gojjam Basin, satellite rainfall estimates from the African Rainfall Climatology (ARC2), Climate Hazard Group Infrared Precipitation with Stations Data (CHIRPSv2), African Rainfall Estimations Algorithm (REFv2), and Tropical Applications of Meteorology using Satellite (TAMSATv3) were evaluated and compared with rain gauge rainfall data. Satellite rainfall estimates were evaluated at spatiotemporal scales with observed data using approaches of point observed rainfall data and areal averaged rainfall comparisons for the period of 2001–2018. The basin was divided into two parts, according to geographical region, to identify the effect of topographical variation. Besides, the spatial map of the annual satellite rainfall estimate pattern was illustrated with observed rainfall data for comparison. The result showed that TAMSATv3 and RFEv2 rainfall estimates showed the best performance than ARC2 and CHIRPSv3 products at daily time scales and in both spatial scales (i.e., higher, and lower elevations). On a monthly and wet season timescale, the CHIRPSv2 product was outperformed, even though the four satellite products performed better. CHIRPSv2 and TAMSATv3 products presented overestimated rainfall in the lower elevation region at daily and monthly scales, while ARC2 and RFEv2 products were underestimated at all spatiotemporal scales. Overall, CHIRPSv2 and TAMSATv3 satellite rainfall estimates showed good relation to the rain gauge rainfall data in the rugged topography and a limited number of rain gauges in the South Gojjam basin. Thus, this study decided that CHIRPSv2 and TAMSATv3 satellite rainfall data could be used as an alternative to rain gauge rainfall on a monthly and wet season time scale for hydroclimate studies.






Similar content being viewed by others
Data Availability
The data that support the findings of this study are available from the corresponding author upon reasonable request.
References
Abdelmoneim, H., Soliman, M. R., & Moghazy, H. M. (2020). Evaluation of TRMM 3B42V7 and CHIRPS satellite precipitation products as an input for hydrological model over Eastern Nile Basin. Earth Systems and Environment, 4, 685–698. https://doi.org/10.1007/s41748-020-00185-3
Abera, W., Brocca, L., & Rigon, R. (2016). Comparative evaluation of different satellite rainfall estimation products and bias correction in the Upper Blue Nile (UBN) basin. Atmospheric Research, 178–179, 471–483. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.atmosres.2016.04.017
Adane, G. B., Hirpa, B. A., Lim, C. H., & Lee, W. K. (2021). Evaluation and comparison of satellite-derived estimates of rainfall in the diverse climate and terrain of central and northeastern ethiopia. Remote Sensing. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs13071275
Adler, R. F., Kidd, C., Petty, G., Morissey, M., & Goodman, H. M. (2001). Intercomparison of global precipitation products: The third precipitation intercomparison project (PIP-3). Bulletin of the American Meteorological Society, 82, 1377–1396. https://doi.org/10.1175/1520-0477(2001)082%3c1377:IOGPPT%3e2.3.CO;2
Akay, H., Baduna Koçyiğit, M., & Yanmaz, A. M. (2018). Effect of using multiple stream gauging stations on calibration of hydrologic parameters and estimation of hydrograph of ungauged neighboring basin. Arabian Journal of Geosciences, 11, 282. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12517-018-3642-z
Aksu, H., & Akgül, M. A. (2020). Performance evaluation of CHIRPS satellite precipitation estimates over Turkey. Theoretical and Applied Climatology, 142, 71–84. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00704-020-03301-5
Andualem, T. G., Malede, D. A., & Ejigu, M. T. (2020). Performance evaluation of integrated multi-satellite retrieval for global precipitation measurement products over Gilgel Abay watershed, Upper Blue Nile Basin, Ethiopia. Modeling Earth Systems and Environment, 6, 1853–1861. https://doi.org/10.1007/s40808-020-00795-w
Ayehu, G. T., Tadesse, T., Gessesse, B., & Dinku, T. (2018). Validation of new satellite rainfall products over the Upper Blue Nile Basin, Ethiopia. Atmospheric Measurement Techniques, 11, 1921–1936. https://doi.org/10.5194/amt-11-1921-2018
Baduna Koçyiğit, M., Akay, H., & Yanmaz, A. M. (2017). Effect of watershed partitioning on hydrologic parameters and estimation of hydrograph of an ungauged basin: A case study in Gokirmak and Kocanaz, Turkey. Arabian Journal of Geosciences. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12517-017-3132-8
Bayissa, Y., Tadesse, T., Demisse, G., & Shiferaw, A. (2017). Evaluation of satellite-based rainfall estimates and application to monitor meteorological drought for the Upper Blue Nile Basin, Ethiopia. Remote Sensing. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs9070669
Belay, A. S., Fenta, A. A., Yenehun, A., Nigate, F., Tilahun, S. A., Moges, M. M., Dessie, M., Adgo, E., Nyssen, J., Chen, M., van Griensven, A., & Walraevens, K. (2019). Evaluation and application of multi-source satellite rainfall product CHIRPS to assess spatio-temporal rainfall variability on data-sparse western margins of Ethiopian highlands. Remote Sensing, 11, 1–22. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs11222688
Belete, M., Deng, J., Wang, K., Zhou, M., Zhu, E., Shifaw, E., & Bayissa, Y. (2020). Evaluation of satellite rainfall products for modeling water yield over the source region of Blue Nile Basin. Science of the Total Environment, 708, 134834. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.scitotenv.2019.134834
Bharti, V., & Singh, C. (2015). Evaluation of error in TRMM 3B42V7 precipitation estimates over the himalayan region. Journal of Geophysical Research, 120, 12458–12473. https://doi.org/10.1002/2015JD023779
Bhatti, H. A., Rientjes, T., Haile, A. T., Habib, E., & Verhoef, W. (2016). Evaluation of bias correction method for satellite-based rainfall data. Sensors (switzerland). https://doi.org/10.3390/s16060884
Bitew, M. M., Gebremichael, M., Ghebremichael, L. T., & Bayissa, Y. A. (2012). Evaluation of high-resolution satellite rainfall products through streamflow simulation in a hydrological modeling of a small mountainous watershed in Ethiopia. Journal of Hydrometeorology, 13, 338–350. https://doi.org/10.1175/2011JHM1292.1
Degefu, M. A., Rowell, D. P., & Bewket, W. (2017). Teleconnections between Ethiopian rainfall variability and global SSTs: Observations and methods for model evaluation. Meteorology and Atmospheric Physics, 129, 173–186. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00703-016-0466-9
Dembélé, M., & Zwart, S. J. (2016). Evaluation and comparison of satellite-based rainfall products in Burkina Faso, West Africa. International Journal of Remote Sensing, 37, 3995–4014. https://doi.org/10.1080/01431161.2016.1207258
Dinku, T., Ceccato, P., Grover-Kopec, E., Lemma, M., Connor, S. J., & Ropelewski, C. F. (2007). Validation of satellite rainfall products over East Africa’s complex topography. International Journal of Remote Sensing, 28, 1503–1526. https://doi.org/10.1080/01431160600954688
Dinku, T., Chidzambwa, S., Ceccato, P., Connor, S. J., & Ropelewski, C. F. (2008). Validation of high-resolution satellite rainfall products over complex terrain. International Journal of Remote Sensing, 29, 4097–4110. https://doi.org/10.1080/01431160701772526
Dinku, T., Funk, C., Peterson, P., Maidment, R., & Tadesse, T. (2018). Validation of the CHIRPS satellite rainfall estimates over eastern. Quarterly Journal of the Royal Meteorological Society. https://doi.org/10.1002/qj.3244
Fenta, A. A., Yasuda, H., Shimizu, K., Ibaraki, Y., Haregeweyn, N., Kawai, T., Belay, A. S., Sultan, D., & Ebabu, K. (2018). Evaluation of satellite rainfall estimates over the Lake Tana basin at the source region of the Blue Nile River. Atmospheric Research, 212, 43–53. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.atmosres.2018.05.009
Funk, C., Peterson, P., Landsfeld, M., Pedreros, D., Verdin, J., Shukla, S., Husak, G., Rowland, J., Harrison, L., Hoell, A., & Michaelsen, J. (2015). The climate hazards infrared precipitation with stations—A new environmental record for monitoring extremes. Scientific Data. https://doi.org/10.1038/sdata.2015.66
Gebere, S. B., Alamirew, T., Merkel, B. J., & Melesse, A. M. (2015). Performance of high resolution satellite rainfall products over data scarce parts of eastern ethiopia. Remote Sensing, 7, 11639–11663. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs70911639
Gebremicael, T., Mohamed, Y., van der Zaag, P., Berhe, A., Haile, G., Hagos, E., & Hagos, M. (2017). Comparison and validation of eight satellite rainfall products over the rugged topography of Tekeze-Atbara Basin at different spatial and temporal scales. Hydrology and Earth System Sciences Discussions. https://doi.org/10.5194/hess-2017-504
Gebremicael, T. G., Mohamed, Y. A., van der Zaag, P., Gebremedhin, A., Gebremeskel, G., Yazew, E., & Kifle, M. (2019). Evaluation of multiple satellite rainfall products over the rugged topography of the Tekeze-Atbara basin in Ethiopia. International Journal of Remote Sensing, 40, 4326–4345. https://doi.org/10.1080/01431161.2018.1562585
Geleta, C. D., & Deressa, T. A. (2021). Evaluation of climate hazards group infrared precipitation station (CHIRPS) <scp>satellite-based</scp> rainfall estimates over Finchaa and Neshe Watersheds, Ethiopia. Engineering Reports. https://doi.org/10.1002/eng2.12338
Ghozat, A., Sharafati, A., & Hosseini, S. A. (2021). Long-term spatiotemporal evaluation of CHIRPS satellite precipitation product over different climatic regions of Iran. Theoretical and Applied Climatology, 143, 211–225. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00704-020-03428-5
Hailesilassie, W. T., Ayenew, T., & Tekleab, S. (2021). Analysing trends and spatio-temporal variability of precipitation in the main central Rift Valley Lakes Basin, Ethiopia. Environmental and Earth Sciences Research Journal, 8, 37–47. https://doi.org/10.18280/eesrj.080104
Herman, A., Kumar, V. B., Arkin, P. A., & Kousky, J. V. (1997). Objectively determined 10-day African rainfall estimates created for famine early warning systems. International Journal of Remote Sensing, 18, 2147–2159. https://doi.org/10.1080/014311697217800
Hughes, D. A. (2006). Comparison of satellite rainfall data with observations from gauging station networks. Journal of Hydrology, 327, 399–410. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jhydrol.2005.11.041
Kabite Wedajo, G., Kebede Muleta, M., & Gessesse Awoke, B. (2021). Performance evaluation of multiple satellite rainfall products for Dhidhessa River Basin (DRB), Ethiopia. Atmospheric Measurement Techniques, 14, 2299–2316. https://doi.org/10.5194/amt-14-2299-2021
Katsanos, D., Retalis, A., Tymvios, F., & Michaelides, S. (2016). Analysis of precipitation extremes based on satellite (CHIRPS) and in situ dataset over Cyprus. Natural Hazards, 83, 53–63. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11069-016-2335-8
Kidd, C., & Levizzani, V. (2011). Status of satellite precipitation retrievals. Hydrology and Earth System Sciences, 15, 1109–1116. https://doi.org/10.5194/hess-15-1109-2011
Li, Z., Wen, Y., Schreier, M., Behrangi, A., Hong, Y., & Lambrigtsen, B. (2021). Advancing satellite precipitation retrievals with data driven approaches: Is black box model explainable? Earth and Space Science, 8, 1–15. https://doi.org/10.1029/2020EA001423
Maidment, R. I., Grimes, D., Black, E., Tarnavsky, E., Young, M., Greatrex, H., Allan, R. P., Stein, T., Nkonde, E., Senkunda, S., & Alcántara, E. M. U. (2017). A new, long-term daily satellite-based rainfall dataset for operational monitoring in Africa. Scientific Data. https://doi.org/10.1038/SDATA.2017.63
Mengistu, D., Bewket, W., & Lal, R. (2014). Recent spatiotemporal temperature and rainfall variability and trends over the Upper Blue Nile River Basin, Ethiopia. International Journal of Climatology, 34, 2278–2292. https://doi.org/10.1002/joc.3837
Musie, M., Sen, S., & Srivastava, P. (2019). Comparison and evaluation of gridded precipitation datasets for streamflow simulation in data scarce watersheds of Ethiopia. Journal of Hydrology, 579, 124168. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jhydrol.2019.124168
Novella, N. S., & Thiaw, W. M. (2013). African rainfall climatology version 2 for famine early warning systems. Journal of Applied Meteorology and Climatology, 52, 588–606. https://doi.org/10.1175/JAMC-D-11-0238.1
Ntwali, D., Ogwang, B. A., & Ongoma, V. (2016). The impacts of topography on spatial and temporal rainfall distribution over Rwanda based on WRF model. Atmospheric and Climate Science, 6, 145–157.
Rivera, J. A., Marianetti, G., & Hinrichs, S. (2018). Validation of CHIRPS precipitation dataset along the Central Andes of Argentina. Atmospheric Research, 213, 437–449. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.atmosres.2018.06.023
Romilly, T. G., & Gebremichael, M. (2011). Evaluation of satellite rainfall estimates over Ethiopian river basins. Hydrology and Earth System Sciences, 15, 1505–1514. https://doi.org/10.5194/hess-15-1505-2011
Saeidizand, R., Sabetghadam, S., Tarnavsky, E., & Pierleoni, A. (2018). Evaluation of CHIRPS rainfall estimates over Iran. Quarterly Journal of the Royal Meteorological Society, 144, 282–291. https://doi.org/10.1002/qj.3342
Shawul, A. A., & Chakma, S. (2020). Suitability of global precipitation estimates for hydrologic prediction in the main watersheds of Upper Awash basin. Environmental Earth Sciences, 79, 1–18. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12665-019-8801-3
Shrestha, D., Singh, P., & Nakamura, K. (2012). Spatiotemporal variation of rainfall over the central Himalayan region revealed by TRMM Precipitation Radar. Journal of Geophysical Research, 117, 1–14. https://doi.org/10.1029/2012JD018140
Stillman, S., Ninneman, J., Zeng, X., Franz, T., Scott, R. L., Shuttleworth, W. J., & Cummins, K. (2014). Summer Soil Moisture Spatiotemporal Variability in Southeastern Arizona. Journal of Hydrometeorology, 15, 1473–1485. https://doi.org/10.1175/jhm-d-13-0173.1
Tarnavsky, E., Grimes, D., Maidment, R., Black, E., Allan, R. P., Stringer, M., Chadwick, R., & Kayitakire, F. (2014). Extension of the TAMSAT satellite-based rainfall monitoring over Africa and from 1983 to present. Journal of Applied Meteorology and Climatology, 53, 2805–2822. https://doi.org/10.1175/JAMC-D-14-0016.1
Taye, M., Simane, B., Zaitchik, B. F., Selassie, Y. G., & Setegn, S. (2019). Rainfall variability across the agro-climatic zones of a tropical highland: The case of the jema watershed, northwestern ethiopia. Environments - MDPI. https://doi.org/10.3390/environments6110118
Thiemig, V., Rojas, R., Zambrano-Bigiarini, M., Levizzani, V., & de Roo, A. (2012). Validation of satellite-based precipitation products over sparsely Gauged African River basins. Journal of Hydrometeorology, 13, 1760–1783. https://doi.org/10.1175/JHM-D-12-032.1
Wang, W., Lu, H., Zhao, T., Jiang, L., & Shi, J. (2017). Evaluation and comparison of daily rainfall from latest GPM and TRMM products over the Mekong River Basin. IEEE Journal of Selected Topics in Applied Earth Observations and Remote Sensing, 10, 2540–2549. https://doi.org/10.1109/JSTARS.2017.2672786
Weldegerima, T. M., Zeleke, T. T., Birhanu, B. S., Zaitchik, B. F., & Fetene, Z. A. (2018). Analysis of rainfall trends and its relationship with SST signals in the Lake Tana Basin, Ethiopia. Advances in Meteorology. https://doi.org/10.1155/2018/5869010
Wilheit, T. T., & Hutchison, K. D. (1997). Water vapour profile retrievals from SSM/T-2 data constrained by infrared-based cloud parameters. International Journal of Remote Sensing, 18, 3263–3277. https://doi.org/10.1080/014311697217071
WMO, 2015. Status of the Global Observing System for Climate. World Meteorological Organization 358.
Young, M. P., Williams, C. J. R., Christine Chiu, J., Maidment, R. I., & Chen, S. H. (2014). Investigation of discrepancies in satellite rainfall estimates over Ethiopia. Journal of Hydrometeorology, 15, 2347–2369. https://doi.org/10.1175/JHM-D-13-0111.1
Funding
This study was carried out with the support of the Africa Center of Excellence for Water Management, Addis Ababa University.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
D.A.M. contributed to the original idea; D.A.M. and J.R.K. elaborated on the idea; D.A.M., and J.R.K. involved in methodology; D.A.M. involved in data collection, processing, and analyzing; D.A.M. and T.A.A. involved in formula analysis and investigation; D.A.M. involved in writing original draft; D.A.M., Q.B.P., and T.G.A. involved in writing, review, and editing; D.A.M., Q.B.P and T.G.A. involved in visualization; T.A.A and J.R.K involved in supervision.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
This manuscript has not been published or presented elsewhere in part or entirety and is not under consideration by another journal. There is no conflict of interest to declare.
Ethical Approval
Not applicable.
Consent to Participate
Not applicable.
Consent to Publish
Not applicable.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
About this article
Cite this article
Malede, D.A., Agumassie, T.A., Kosgei, J.R. et al. Evaluation of Satellite Rainfall Estimates in a Rugged Topographical Basin Over South Gojjam Basin, Ethiopia. J Indian Soc Remote Sens 50, 1333–1346 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12524-022-01530-x
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12524-022-01530-x