Abstract
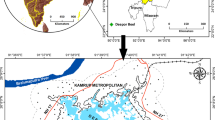
A morphometric analysis has been carried out for Rampur watershed of Mahanadi river basin, and its nine sub-watersheds have been prioritized according to the linear, aerial and relief characteristics. Based on digital elevation model, delineation of sub-watersheds (SWs) has been done by using ArcMap 10.2.2. The drainage analysis and their respective parameters such as stream order, stream length, stream frequency, drainage density, texture ratio, form factor, circulatory ratio, elongation ratio, bifurcation ratio and compactness coefficient for the sub-watersheds have been evaluated by applying remote sensing and geospatial techniques. Based on the behaviour of morphometric parameters of each sub-watershed (SW), the prioritized score has been allocated, and thereafter, the most sensitive parameters have been distinguished by the evaluated combined scores. The results achieved from the analysis show that the stream order varies from 1 to 6 and the first order covers 30.5% of the total catchment area. The watershed has 2087 stream segment numbers of all order. Based on morphometric analysis, prioritizing each SW has been the primary objective of this study. The final score of each sub-watershed has been allocated as per erosion threat. The highest priority has been allocated to the SW which shows the least compound parameter value. Eventually, the grouping of SWs has been done according to the high (4.0–4.7), medium (4.8–5.3) and low (> 5.4) priority classes depending on their prioritized score, maximum (6.0) and minimum (4.0).



Similar content being viewed by others
References
Aher, P., Jagarlapudi, A., & Gorantiwar, S. (2014). Quantification of morphometric characterization and prioritization for management planning in semi-arid tropics of India: A remote sensing and GIS approach. Journal of Hydrology. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jhydrol.2014.02.028.
Astras, T., & Soulankellis, N. (1992). Contribution of digital image analysis techniques on Landsat-5 TM imageries for drainage delineation. A case study from the Olympus Mountain, west Macedonia, Greece. In Proceedings of the 18th annual conference of remote sensing society, University of Dundee, Dundee, Scotland (pp. 15–17).
Baumgardner, R. W. (1987). Morphometric studies of sub-humid and semiarid drainage basin Texas Panhandle and Northeastern New Mexico: The University of Texas at Austin, Bureau of Economic Geology, Report of Investigations No. 163.
Biswas, S., Sudhakar, S., & Desai, V. (1999). Prioritisation of subwatersheds based on morphometric analysis of drainage basin: A remote sensing and GIS approach. Journal of the Indian Society of Remote Sensing,27, 155–166.
Chopra, R., Dhiman, R. D., & Sharma, P. K. (2005). Morphometric analysis of sub-watersheds, District Gurdaspur, Punjab. Journal of the Indian Society of Remote Sensing,33(4), 531–539.
Chow, V. T. (1964). ‘Runoff’. In V. T. Chow (Ed.), Handbook of applied hydrology (pp. 14.1–14.54). New York: McGraw-Hill.
Esper Angillieri, M. Y. (2008). Morphometric analysis of Colanguil river basin and flash flood hazard, San Juan, Argentina. Environmental Geology,55, 107–111.
Gajbhiye, S., Mishra, S. K., & Pandey, A. (2014). Prioritizing erosion-prone area through morphometric analysis: An RS and GIS perspective. Applied Water Science,4(1), 51–61.
Gardiner, V. (1990). Drainage basin morphometry. In A. S. Goudie (Ed.), Geomorphological techniques (pp. 71–81). London: Unwin Hyman.
Gregory, J. K., & Walling, D. E. (1973). Drainage basin form and process: A geomorphological approach. London: Edward Arnold.
Horton, R. E. (1932). Drainage-basin characteristics. Transactions of the American Geophysical Union,13, 350–361.
Horton, R. E. (1945). Erosional development of streams and their drainage basins: Hydrophysical approach to quantitative morphology. Geological Society of America Bulletin,56, 275–370.
Javed, A., Khanday, M. Y., & Ahmad, R. (2009). Prioritization of subwatersheds based on Morphometric and Land use analysis in Guna district (M.P.). A remote sensing and GIS based approach. Journal of the Indian Society of Remote Sensing,2(37), 261–274.
Javed, A., Khanday, M. Y., & Ahmed, R. (2011). Watershed prioritization using morphometric and land use/land cover parameters: A remote sensing and GIS-based approach. Journal Geological Society of India,78(1), 63–75.
Kumar, A., Jayappa, K., & Deepika, B. (2011). Prioritization of sub-basins based on geomorphology and morphometric analysis using remote sensing and geographic information system (GIS) techniques. Geocarto International, 26, 569–592. https://doi.org/10.1080/10106049.2011.606925.
Langbein, W. B. (1947). Topographic characteristics of drainage basins. U.S. Geological Survey Water-Supply Paper, 986(C), 157–159.
Magesh, N. S., Chandrasekar, N., & Soundranayagam, J. P. (2011). Morphometric evaluation of Papanasam and Manimuthar watersheds, parts of Western Ghats, Tirunelveli district, Tamil Nadu, India: A GIS approach. Environmental Earth Sciences,64(2), 373–381.
Melton, M. (1957). An analysis of the relations among elements of climate, sur-face properties and geomorphology. Department of Geology, Columbia University, Technical Report, 11, Project NR. Office of Navy Research, New York. 389-042.
Miller, V. C. (1953). A quantitative geomorphic study of drainage basin characteristics in the Clinch Mountain Area, Virginia and Tennessee. Issue 3 of Technical Report, Department of Geology, Columbia University.
Nag, S. K. (1998). Morphometric analysis using remote sensing techniques in the Chaka sub-basin Purulia District, West Bengal. Journal of the Indian Society of Remote Sensing,26(1&2), 69–76.
Nautiyal, M. D. (1994). Morphometric analysis of a drainage basin using aerial photographs: A case study of Khairkuli basin, District Dehradun, Uttar Pradesh. Journal of the Indian Society of Remote Sensing,22(4), 251–261.
Patel, D. P., Gajjar, C. A., & Srivastava, P. K. (2013). Prioritization of Malesari mini-watersheds through morphometric analysis: A remote sensing and GIS perspective. Environmental Earth Sciences,69, 2643–2656.
Rahaman, A. S., Abdul Ajeezb, A. S., Aruchamy, S., & Jegankumar, D. (2015). Prioritization of sub watershed based on morphometric characteristics using fuzzy analytical hierarchy process and geographical information system—A study of Kallar Watershed, Tamil Nadu. Aquatic Procedia,4, 1322–1330.
Ratnam, K. N., Srivastava, Y. K., Rao, V. V., Amminedu, E., & Murthy, K. S. R. (2005). Check dam positioning by prioritization of micro-watersheds using SYI model and morphometric analysis—remote sensing and GIS perspective. Journal of the Indian Society of Remote Sensing, 33(1), 25–38. https://doi.org/10.1007/BF02989988.
Rekha, V., George, A., & Rita, M. (2011). Morphometric analysis and micro-watershed prioritization of Peruvanthanam sub-watershed, the Manimala River Basin, Kerala, South India. Environmental Research, Engineering and Management,57, 6–14.
Schumm, S. A. (1956). Evolution of drainage systems and slopes in badlands at Perth Amboy, New Jersey. Geological Society of America Bulletin,67, 597–646.
Singh, S., & Singh, M. C. (1997). Morphometric analysis of Kanhar River Basin. National Geographical Journal of India,43(1), 31–43.
Smith, K. G. (1950). Standards for grading textures of erosional topography. American Journal of Science,248(9), 655–668.
Solanke, P. C., Srivastava, S., Prasad, J., Nagrajan, M. S. S., Saxena, R. K., & Barthwal, A. K. (2005). Application of remote sensing and GIS in watershed characterization and management. Journal of the Indian Society of Remote Sensing,33(2), 239–244.
Srinivasa, V. S., Govindainah, S., & Home, G. H. (2004). Morphometric analysis of sub-watersheds in the Pavagada area of Tumkur district, South India using Remote Sensing and GIS techniques. Journal of the Indian Society of Remote Sensing,32(4), 351–362.
Srivastava, V. K. (1997). Study of drainage pattern of Jharia Coalfield (Bihar), India, through remote sensing technology. Journal of the Indian Society of Remote Sensing,25(1), 41–46.
Strahler, A. N. (1957). Quantative analysis of watershed geomorphology. Transactions American Geophysical Union, 38, 913–920.
Strahler, A. N. (1964). Quantitative geomorphology of drainage basins and channel networks. In V. T. Chow (Ed.), Handbook of applied hydrology (pp. 4.39–4.76). New York: McGraw-Hill.
Thakkar, A. K., & Dhiman, S. D. (2007). Morphometric analysis and prioritization of mini-watersheds in a Mohr watershed, Gujarat using remote sensing and GIS techniques. Journal of the Indian Society of Remote Sensing,35(4), 313–321.
Thomas, J., Joseph, S., & Thrivikramaji, K. P. (2010). Morphometric aspects of a small tropical mountain river system, the southern Western Ghats, India. International Journal of Digital Earth,3(2), 135–156.
Vijith, H., & Satheesh, R. (2006). GIS based morphometric analysis of two major Upland Subwatersheds of Meenachil River in Kerala. Journal of the Indian Society of Remote Sensing,34(2), 181–185.
Yadav, S. K., Singh, S. K., Gupta, M., & Srivastava, P. K. (2014). Morphometric analysis of Upper Tons basin from Northern Foreland of Peninsular India using CARTOSAT satellite and GIS. Geocarto International,29(8), 895–914. https://doi.org/10.1080/10106049.2013.868043.
Zavoianu, I. (1985). Morphometry of drainage basin (Developments in Water Science, 20). Amsterdam: Elsevier.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
About this article
Cite this article
Gunjan, P., Mishra, S.K., Lohani, A.K. et al. The Study of Morphological Characteristics for Best Management Practices Over the Rampur Watershed of Mahanadi River Basin Using Prioritization. J Indian Soc Remote Sens 48, 35–45 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12524-019-01061-y
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12524-019-01061-y