Abstract
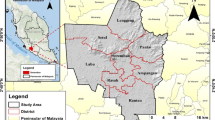
In India the last 30 years had witnessed a radical transformation of urban scene. In particular, during this period, the one lakh cities and million plus cities began to grow rapidly. In the present study, urban growth of Jaipur city in the last 31 years (1975–2006) was assessed. Jaipur ranks 11th in India with a total population of 2.3 million and has shown a consistent increase in the past 50 years. It is one of the fastest growing mega cities of the country with an annual average growth rate of 4.5% which is quite high from the national urban growth rate. Remote sensing and GIS have been used to extract the information related to urban growth-built up area and its spatial and temporal variation. The Shannon’s entropy at two levels (city as a whole and ward wise) is computed in order to quantify the form and patterns of urban growth using built up area as spatial phenomena. Further, multivariate statistical techniques have been used to establish the relationship between the urban growth and its causative and determining factors. Results of this study reveal that the growth rate of built up in Jaipur has outstripped the rate of population growth. Shannon’s entropy quantifies as dispersed form of urban growth till 2000 and after it, there is relative compactness in 2006.







Similar content being viewed by others
References
Allefsen, R.A. (1962). City hinterland relationship in India. University of California Press.
Chen, Z., Chen, J., Shi, P., & Tamura, M. (2003). An IHS-based change detection approach for assessment of urban expansion impact on arable land loss in China. International Journal of Remote Sensing, 24, 1353–60.
Epstein, J., Payne, K., & Kramer, E. (2002). Techniques for mapping suburban sprawl. Photogrammetric Engineering and Remote Sensing, 63, 913–918.
Hardin, P. J., Jackson, M. W., & Otterstrom, S. M. (2007). Geo-Spatial Technologies in Urban Environments (pp. 141–176). Berlin: Springer.
Jat, M. K., Garg, P. K., & Khare, D. (2008). Modeling of urban growth using spatial analysis techniques: a case study of Ajmer city (India). International Journal of Remote Sensing, 29(2), 543–567.
Joshi, P. K., Lele, N., & Agarwal, S. P. (2006). Entropy as an indicator of fragmented landscape. Current Sciences, 91, 276–278.
Kundu, A. (2006). Trends & patterns of urbanization and their economic implications. India Infrastructure Report, pp. 28–41.
Kundu, A., Bagchi, S., & Kundu, D. (1999). Regional Distribution of Infrastructure and Basic Amenities in Urban India—Issues Concerning Empowerment of Local Bodies. Economic and Political Weekly, 34(28), 1893–1906.
Lata, K. M., Sankar, R. C. H., Krishna, P. V., Badrinath, K. V. S., & Raghavaswamy. (2001). Measuring urban sprawl: a case study of Hyderabad. GIS Development, 5, 8–13.
Li, X., & Yeh, A. G. O. (1998). Principal component analysis of stacked multi temporal images for the monitoring of rapid urban expansion in the Pearl River delta. International Journal of Remote Sensing, 19, 1501–18.
Madhavan, B. B., Kubo, S., Kurisaki, N., & Sivakumar, T. V. L. N. (2001). Appraising the anatomy and spatial growth of the Bangkok Metropolitan area using a vegetation-impervious-soil model through remote sensing. International Journal of Remote Sensing, 22, 789–806.
Mahmood, A. (1977). Statistical methods in geographical studies. Rajesh Publications New Delhi.
Mundia, C. N., & Aniya, M. (2005). Analysis of land use/cover changes and urban expansion in Nairobi city using remote sensing and GIS. International Journal of Remote Sensing, 26, 2831–49.
Pathan, S. K., Sastry, S. V. C., Dhinwa, P. S., Mukund, R., & Majumdar, K. L. (1993). Urban growth trend analysis using GIS technique-a case study of the Bombay metropolitan region. International Journal of Remote Sensing, 14(17), 3169–3179.
Sudhira, H. S., Ramachandra, T. V., & Jagadish, K. S. (2004). Urban sprawl: metrics, dynamics and modeling using GIS. International Journal of Applied Earth Observation and Geoinformation, 5, 29–39.
Sunar, F. (1998). Analysis of changes in a multidate set: a case study in Ikitelli Area, Istanbul, Turkey. International Journal of Remote Sensing, 19, 225–35.
White, R., Engelen, C., Uljee, I., Lavalle, C. & Erlich, D. (1999). Developing an Urban Land Use Simulator for European Cities. In Proceedings of the 5th EC-GIS workshop, European Communities, Italy, pp 1–43.
Yeh, A. G. O., & Li, X. (2001). Measurement and monitoring of urban sprawl in a rapidly growing region using entropy. Photogrammetric Engineering and Remote Sensing, 67, 83–90.
Yu, X., & Ng, C. (2006). An integrated evaluation of landscape change using remote sensing and landscape metrics: a case study of Panyu, Guangzhou. International Journal of Remote Sensing, 27, 1075–92.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
About this article
Cite this article
Punia, M., Singh, L. Entropy Approach for Assessment of Urban Growth: A Case Study of Jaipur, INDIA. J Indian Soc Remote Sens 40, 231–244 (2012). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12524-011-0141-z
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12524-011-0141-z