Abstract
Purpose
Both relaxin and insulin-like growth factor (IGF) are members of the insulin super family. This study aimed to investigate the effect of relaxin and IGF-I on the pre-implantation of Mongolian gerbil of blastocyst development in vitro.
Methods
Blastocysts and eight-cell stage embryos were collected from female gerbils. Eight-cell embryos and blastocysts were cultured in mM16 medium supplemented with or without relaxin or IGF-I for 24 h. Blastocysts were counted for total, inner cell mass (ICM) and trophectoderm (TE) cell numbers, and assessed apoptosis incidence. In addition, to measure incorporation of 3H-methionine, blastocysts were cultured for 3 h with relaxin or IGF-I, washed with trichloroacetic acid and measured by liquid scintiration counter.
Results
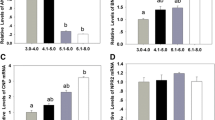
Relaxin (200 ng/ml) increased total, TE and ICM cell numbers of blastocyst (P < 0.05) when it was compared with the control. IGF-I (150 ng/ml) also has influence on total and ICM cell numbers of blastocyst when compared with control. Apoptosis incidence was relatively low, and a significant difference was not observed between each group. The effect of relaxin on incorporation of 3H-methionine was higher than the control group (P < 0.05). Relaxin increased the developmental rate from the eight-cell stage to blastocyst (P < 0.05).
Conclusions
In conclusion, relaxin and IGF-I stimulated protein synthesis and increased cell numbers of blastocysts, promoting development of the gerbil embryo in vitro culture.



Similar content being viewed by others
References
Blundell TL, Humbel RE. Hormone families: pancreatic hormones and homologous growth factors. Nature. 1980;287:781–7.
Weiss G, Goldsmith LT, Scoenfeld C, D’Eletto R. Partial purification of relaxin from human seminal plasma. Am J Obstet Gynecol. 1986;154:749–55.
Zhang Q, Bagnell CA. Relaxin stimulation of porcine granulosa cell deoxyribonucleic acid synthesis in vitro: interactions with insulin-like growth factor I. Endocrinology. 1993;132:1643–50.
Zhang Q, Bagnell CA. Trophic actions of relaxin on porcine theca cells: interactions with insulin and insulin-like growth factor-I in vitro. Endocrine J. 1994;2:349–55.
Han YJ, Miah AG, Yoshida M, Sasada H, Hamano K, Kohsaka T, et al. Effect of relaxin on in vitro fertilization of porcine oocytes. J Reprod Dev. 2006;52:657–62.
Miah AG, Tareq KMA, Hamano K, Kohsaka T, Tsujii H. Effect of relaxin on acrosome reaction and utilization of glucose in boar spermatozoa. J Reprod Dev. 2006;52:773–9.
Pantaleon M, Kaye PL. IGF-I and insulin regulate glucose transport in mouse blastocysts via IGF-I receptor. Mol Reprod Dev. 1996;44:71–6.
Chi MM, Schlein AL, Moley KH. High insulin-like growth factor 1 (IGF–1) and insulin concentrations trigger apoptosis in the mouse blastocyst via down- regulation of the IGF-1 receptor. Endocrinology. 2000;141:4784–92.
Carayannopoulos M, Chi M, Cui Y, Pingsterhaus J, Moley K. GLUT8, a glucose transporter responsible for insulin-stimulated uptake in the blastocyst. Proc Natl Acad Sci. 2000;97:7313–8.
Palma GA, Müller M, Brem G. Effect of insulin-like growth factor I (IGF-I) at high concentrations on blastocyst development of bovine embryos produced in vitro. J Reprod Fertil. 1997;110:347–53.
Fabian D, Il’ková G, Rehák P, Czikková S, Baran V, Koppel J. Inhibitory effect of IGF-I on induced apoptosis in mouse preimplantation embryos cultured in vitro. Theriogenology. 2004;61:745–55.
Lin TC, Yen JM, Gong KB, Hsu TT, Chen LR. IGF-1/IGFBP-1 increases blastocyst formation and total blastocyst cell number in mouse embryo culture and facilitates the establishment of a stem-cell line. BMC Cell Biol. 2003;4:14–27.
Byrne AT, Southgate J, Brison DR, Leese HJ. Regulation of apoptosis in the bovine blastocyst by insulin and the insulin-like growth factor (IGF) superfamily. Mol Reprod. 2002;62:489–95.
Pike IL. Comparative studies of embryo metabolism in early pregnancy. J Reprod Fertil Suppl. 1981;29:203–13.
Tsujii H, Taniguchi N, Hamano K. Development of Mongolian gerbil embryos in chemically defined media: effects of osmolarity, glucose and phosphate. J Reprod Dev. 2004;50:653–9.
Tsujii H, Saruwatari T, Hamano K. Development of Mongolian gerbil 1-cell embryos to blastocysts in co-culture with oviductal cells in TCM 199 supplemented with pyruvate, lactate and fetal calf serum. J Reprod Dev. 2002;48:287–92.
Kaye PL, Bell KL, Beebe LF, Dunglison GF, Gardner HG, Harvey MB. Insulin and the insulin-like growth factors (IGFs) in pre-implantation development. Reprod Fertil Dev. 1992;4:373–86.
Harvey MB, Kaye PL. Mouse blastocysts respond metabolically to short-term stimulation by insulin and IGF-1 through the insulin receptor. Mol Reprod Dev. 1991;29:253–8.
Yao L, Agoulnik AI, Cooke PS, Meling DD, Sherwood OD. Relaxin acts on stromal cells to promote epithelial and stromal proliferation and inhibit apoptosis in the mouse cervix and vagina. Endocrinology. 2008;149:2072–9.
Lee HY, Zhao S, Fields PA, Sherwood OD. The extent to which relaxin promotes proliferation and inhibits apoptosis of cervical epithelial and stromal cells is greatest during late pregnancy in rats. Endocrinology. 2005;146:511–8.
Acknowledgments
We are thankful to Prof. T. Kohsaka, Shizuoka University, Japan for providing the relaxin which was used in this study.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
About this article
Cite this article
Yoshida, M., Obata, R. & Tsujii, H. Effect of relaxin and IGF-I on the pre-implantation development of Mongolian gerbil (Meriones unguiculatus) embryos in vitro. Reprod Med Biol 8, 39–43 (2009). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12522-008-0007-4
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12522-008-0007-4