Abstract
Background
Infectious mononucleosis (IM) is a self-limited disease, but a few cases may have severe complications. This retrospective study was to explore the epidemiologic and clinical characteristics of IM associated with Epstein-Barr virus infection (EBV-IM) in children.
Methods
Hospitalized patients with EBV-IM were enrolled during January 2005 to October 2008 in Beijing Children’s Hospital Affi liated to Capital Medical University. All patients were divided into four groups: <1 year (group I), 1 to 3 years (group II), 3 to 6 years (group III), and ≥6 years (group IV). The epidemiology and clinical characteristics were compared among the four groups.
Results
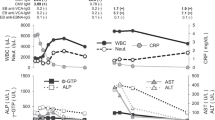
Totally 418 patients were enrolled, with 245 boys and 173 girls. Fever, lymphadenopathy and pharyngitis were three main manifestations of the patients. The incidences of hepatomegaly, splenomegaly and rash were higher in the patients aged below 6 years, and with age increment the incidences lowered. In contrast, the patients aged <1 year had the lowest incidence of tonsillopharyngitis. The total white blood cell count was higher in the infantile group than in the other groups (P=0.038). The infantile group had significantly lower levels of serum alanine aminotransferase and aspartate aminotransferase than the older groups (P=0.007 and P=0.012 respectively). The percentage of CD4+ T cell subset decreased and the percentage of CD8+ T cell subset increased with age increment.
Conclusions
The incidence of EBV-IM peaked in children at age of 4 to 6 years in Northern China. Most of the patients had the classic triad of fever, lymphadenopathy and pharyngitis. Clinical symptoms, signs, laboratory findings and complications of patients varied with ages.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Cohen JI. Epstein-Barr virus infection. N Engl J Med 2000;343:481–492.
Hallee TJ, Evans AS, Niederman JC, Brooks CM, Voegtly H. Infectious mononucleosis at the United States Military Academy. A prospective study of a single class over four years. Yale J Biol Med 1974;47:182–195.
Kangro HO, Osman HK, Lau YL, Heath RB, Yeung CY, Ng MH. Seroprevalence of antibodies to human herpesviruses in England and Hong Kong. J Med Virol 1994;43:91–96.
Chan CW, Chiang AK, Chan KH, Lau AS. Epstein-Barr virusassociated infectious mononucleosis in Chinese children. Pediatr Infect Dis J 2003;22:974–978.
Tsai MH, Hsu CY, Yen MH, Yan DC, Chiu CH, Huang YC, et al. Epstein-Barr virus-associated infectious mononucleosis and risk factor analysis for complications in hospitalized children. J Microbiol Immunol Infect 2005;38:255–261.
Henter JI, Horne A, Aricó M, Egeler RM, Filipovich AH, Imashuku S, et al. HLH-2004: diagnostic and therapeutic guidelines for hemophagocytic lymphohistiocytosis. Pediatr Blood Cancer 2007;48:124–131.
Moffat LE. Infectious mononucleosis. Prim Care Update Ob Gyns 2001;8:73–77.
Papesch M, Watkins R. Epstein-Barr virus infectious mononucleosis. Clin Otolaryngol Allied Sci 2001;26:3–8.
Williams H, Crawford DH. Epstein-Barr virus: the impact of scientific advances on clinical practice. Blood 2006;107:862–864.
Balfour HH Jr, Holman CJ, Hokanson KM, Lelonek MM, Giesbrecht JE, White DR, et al. A prospective clinical study of Epstein-Barr virus and host interactions during acute infectious mononucleosis. J Infect Dis 2005;192:1505–1512.
Cheng CC, Chang LY, Shao PL, Lee PI, Chen JM, Lu CY, et al. Clinical manifestations and quantitative analysis of virus load in Taiwanese children with Epstein-Barr virus-associated infectious mononucleosis. J Microbiol Immunol Infect 2007;40:216–221.
Hu L, Yang J, Cui T, Xing H, Cai P. Diagnosis of infectious mononucleosis by combined detection of atypical lymphocytes and transaminase. J Huazhong Univ Sci Technolog Med Sci 2006;26:384–385.
Doğan I, Ergün M, Cindoruk M, Unal S. Acute hepatitis induced by Epstein-Barr virus infection: a case report. Turk J Gastroenterol 2007;18:119–121.
Celtik C, Kucukugu Y, Balci DB, Oner N, Duran R, Karasalihoglu S. Evaluation of clinical and laboratory features of Epstein-Barr virus-associated acute infectious mononucleosis in children. Trakay Univ Tip Fak Derg 2008;25:221–227.
Ishikawa T, Zhu BL, Li DR, Zhao D, Maeda H. Epstein-Barr virus myocarditis as a cause of sudden death: two autopsy cases. Int J Legal Med 2005;119:231–235.
Williams H, Macsween K, McAulay K, Higgins C, Harrison N, Swerdlow A, et al. Analysis of immune activation and clinical events in acute infectious mononucleosis. J Infect Dis 2004;190:63–71.
Jenson HB. Acute complications of Epstein-Barr virus infectious mononucleosis. Curr Opin Pediatr 2000;12:263–268.
Zhao F, Peng H, Zeng B. Clinical analysis of infectious mononucleosis children with different ages. Clin J General Pract 2008;6:1133–1134.
Grotto I, Mimouni D, Huerta M, Mimouni M, Cohen D, Robin G, et al. Clinical and laboratory presentation of EBV positive infectious mononucleosis in young adults. Epidemiol Infect 2003;131:683–689.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Gao, LW., Xie, ZD., Liu, YY. et al. Epidemiologic and clinical characteristics of infectious mononucleosis associated with Epstein-Barr virus infection in children in Beijing, China. World J Pediatr 7, 45–49 (2011). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12519-011-0244-1
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12519-011-0244-1