Abstract
Background
Ingestion of foreign objects is a common problem in children. Ingestion of one more magnets may require surgical intervention because of risk of perforation.
Methods
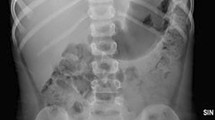
A 4-year-old girl was admitted to our department with complaints of abdominal pain and bilious vomiting. She had been treated at another clinic with repeated abdominal X-rays because of ingestion of a magnet 5 days ago. Physical examination revealed diffuse abdominal tenderness and bilious drainage from the nasogastric tube. The magnet was observed by radiopaque imaging in the right epigastric region of the upright abdomen but there was no free air. The magnet was presumed to be in the duodenum and exploratory laparotomy was performed.
Results
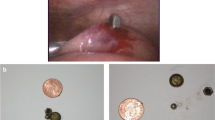
During the operation, a perforation was found between the pylorus and duodenum due to the magnet. The foreign body was found to be two magnets adherent to each; the interposed and compressed tissue was necrotized and perforated between the two magnets. The necrotized segment was excised and primary anastomosis was made. The postoperative period of the patient was uneventful and she was discharged on the seventh postoperative day.
Conclusions
Ingestion of foreign objects such as one more magnets may cause intestinal perforation in early stages. If the object stays in the same location shown by repeated X-rays, surgical intervention should not be delayed.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Hebra A, Tagge EP. Esophagoscopy and Esophageal Foreign Bodies. In: Ziegler MM, Azizkhan RG, Weber TR, eds. Operative Pediatric Surgery. New York: Mc Graw-Hill, 2003: 331–339.
Hernández Anselmi E, Gutiérrez San Román C, Barrios Fontoba JE, Ayuso González L, Valdés Dieguez E, Lluna González J, et al. Intestinal perforation caused by magnetic toys. J Pediatr Surg 2007;42:E13–16.
Lee SK, Beck NS, Kim HH. Mischievous magnets: unexpected health hazard in children. J Pediatr Surg 1996;31:1694–1695.
Ilçe Z, Samsum H, Mammadov E, Celayir S. Intestinal volvulus and perforation caused by multiple magnet ingestion: report of a case. Surg Today 2007;37:50–52.
Honzumi M, Shigemori C, Ito H, Mohri Y, Urata H, Yamamoto T. An intestinal fistula in a 3-year-old child caused by the ingestion of magnets: report of a case. Surg Today 1995;25:552–553.
Hachimi-Idrissi S, Corne L, Vandenplas Y. Management of ingested foreign bodies in childhood: our experience and review of the literature. Eur J Emerg Med 1998;5:319–323.
Kim JK, Kim SS, Kim JI, Kim SW, Yang YS, Cho SH, et al. Management of foreign bodies in the gastrointestinal tract: an analysis of 104 cases in children. Endoscopy 1999;31:302–304.
Cauchi JA, Shawis RN. Multiple magnet ingestion and gastrointestinal morbidity. Arch Dis Child 2002;87:539–540.
Chung JH, Kim JS, Song YT. Small bowel complication caused by magnetic foreign body ingestion of children: two case reports. J Pediatr Surg 2003;38:1548–1550.
Kircher MF, Milla S, Callahan MJ. Ingestion of magnetic foreign bodies causing multiple bowel perforations. Pediatr Radiol 2007;37:933–936.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Sahin, C., Alver, D., Gulcin, N. et al. A rare cause of intestinal perforation: ingestion of magnet. World J Pediatr 6, 369–371 (2010). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12519-010-0237-5
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12519-010-0237-5