Abstract
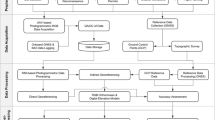
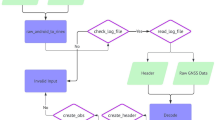
Among several instruments and techniques that can be used for monitoring purposes, GNSS technology has undergone a fast evolution and provides a large choice of solutions. Despite the best performances can be achieved by using double frequency geodetic receivers, capable to maintain high precisions even for wide-scale monitoring, in the recent years, several interesting solutions were presented in the low-cost market. In this work, a monitoring system based on a couple of low-cost GNSS receivers has been developed and tested in the field (Ponte Motta in Cavezzo - Modena, Italy). The two receivers were positioned about 50 m from each other and data were acquired at 1-Hz frequency. The position solutions were calculated both in post processing, through two different free and open-source software packages, and using an embedded RTK processor. The analysis aims to assess on one hand the capability of the system to perform the monitoring of slow displacements with the best possible precision, and, on the other hand, the performances of the real-time solutions that can be used for early warning purposes. The precisions evidenced by the tests show that such low-cost instrumentation can be used for many monitoring purposes, especially considering the cost that is about a tenth of geodetic instruments.













Similar content being viewed by others
References
Caldera S, Realini E, Barzaghi R, Reguzzoni M, Sansò F (2016) Experimental study on low-cost satellite-based geodetic monitoring over short baselines. J Surv Eng 142:04015016. https://doi.org/10.1061/(ASCE)SU.1943-5428.0000168
Celebi M, Sanli A (2002) GPS in pioneering dynamic monitoring of long-period structures. Earthquake Spectra 18:47–61. https://doi.org/10.1193/1.1461375
Cina A, Piras M (2015) Performance of low-cost GNSS receiver for landslides monitoring: test and results. Geomat Nat Haz Risk 6:497–514. https://doi.org/10.1080/19475705.2014.889046
Cliff A, Ord J (1973) Spatial autocorrelation. Pion Limited, London 178 pp
Estey L, Meertens C (1999) TEQC: the multi-purpose toolkit for GPS/GLONASS data. GPS Solutions 3(1):42–49
Gandolfi S, Poluzzi L, Tavasci L (2015) Structural monitoring using GNSS technology and sequential filtering. In FIG Working Week 2015 From the Wisdom of the Ages to the Challenges of the Modern World, 17–21 May 2015, Sofia, Bulgaria.
Gandolfi S, Tavasci L, Poluzzi L (2016) Study on GPS-PPP precision for short observation sessions. GPS Solutions 21(3):887–896. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10291-016-0575-4
Herrera AM, Suhandri HF, Realini E, Reguzzoni M, de Lacy MC (2016) goGPS: open-source MATLAB software. GPS Solutions 20:595–603. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10291-015-0469-x
Hudnut KW, Behr JA (1998) Continuous GPS monitoring of structural deformation at Pacoima dam, California. Seismol Res Lett 69:299–308. https://doi.org/10.1785/gssrl.69.4.299
Nones M (2018) Learning from the past: the Secchia River case study. In: Nucci A, Armanini E (eds) 5th IAHR Europe Congress - New Challenges in Hydraulic Research and Engineering. Trento
Realini E, Reguzzoni M (2013) goGPS: open source software for enhancing the accuracy of low-cost receivers by single-frequency relative kinematic positioning. Meas Sci Technol 24(11):115010
Squarzoni C, Delacourt C, Allemand P (2005) Differential single-frequency GPS monitoring of the La Valette landslide (French Alps). Eng Geol 79:215–229. https://doi.org/10.1016/J.ENGGEO.2005.01.015
Takasu T (2007) RTKLIB: an open source program package for GNSS positioning. Available online:http://www.rtklib.com/. Accessed 1 Dec 2018
Takasu T, Kubo N, Yasuda A (2007) Development, evaluation and application of RTKLIB: a program library for RTK-GPS. In: GPS/GNSS Symposium 2007. p213–218
Takasu T, Yasuda A (2009) Development of the low-cost RTK-GPS receiver with an open source program package RTKLIB. In: International symposium on GPS/GNSS. International Convention Center Jeju Korea, pp 4–6
Wiśniewski B, Bruniecki K, Moszyński M (2013) Evaluation of RTKLIB’s positioning accuracy usingn low-cost GNSS receiver and ASG-EUPOS. TransNav - Int J Mar Navig Saf Sea Transp 7(1):79–85
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Poluzzi, L., Tavasci, L., Corsini, F. et al. Low-cost GNSS sensors for monitoring applications. Appl Geomat 12 (Suppl 1), 35–44 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12518-019-00268-5
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12518-019-00268-5