Abstract
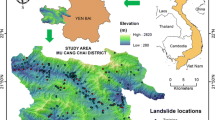
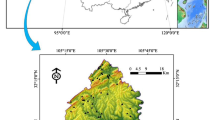
Landslide is considered one of the most dangerous natural hazards. Reasonable landslide susceptibility mapping can aid decision makers in landslide prevention. For this reason, based on the field survey data of landslide in Chenggu County, Shaanxi Province, China, 15 conditioning factors (altitude, slope, aspect, plan curvature, profile curvature, SPI, TWI, distance to roads, distance to rivers, distance to faults, rainfall, NDVI, soil, lithology, and land use) were selected and quantified by the certainty factor index. Then, 184 landslides data were divided into training and validation datasets according to the ratio of 7/3. Based on the GIS platform, three hybrid tree-based models, namely decision tree (DT), logistic model tree (LMT), and reduced error pruning tree (REPT), were established. Additionally, the bagging method was applied to build three bag-hybrid tree-based models: Bag-DT, Bag-LMT, and Bag-REPT. Finally, the landslide susceptibility maps were produced, and statistical indexes, seed cell area index and the ROC curve, were used for model validation and comparison. The results showed that the bagging method can significantly improve the classification ability of hybrid models. Furthermore, the Bag-REPT presented the best performance, with an accuracy value of 92.5%, being a suitable model for landslide susceptibility mapping in the study area.








Similar content being viewed by others
Data availability
Yes.
Code availability
Yes.
References
Abedini M, Ghasemian B, Shirzadi A, Bui DT (2019) A comparative study of support vector machine and logistic model tree classifiers for shallow landslide susceptibility modeling. Environ Earth Sci 78:560. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12665-019-8562-z
Aleotti P, Chowdhury R (1999) Landslide hazard assessment: Summary review and new perspectives. Bull Eng Geol Env 58:21–44. https://doi.org/10.1007/s100640050066
Al-Najjar HAH, Pradhan B (2021) Spatial landslide susceptibility assessment using machine learning techniques assisted by additional data created with generative adversarial networks. Geosci Front 12:625–637. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.gsf.2020.09.002
Arabameri A, Santosh M, Saha S, Ghorbanzadeh O, Roy J, Tiefenbacher JP et al (2021) Spatial prediction of shallow landslide: application of novel rotational forest-based reduced error pruning tree. Geomat Nat Haz Risk 12:1343–1370. https://doi.org/10.1080/19475705.2021.1914753
Argyroudis SA, Mitoulis SA, Hofer L, Zanini MA, Tubaldi E, Frangopol DM (2020) Resilience assessment framework for critical infrastructure in a multi-hazard environment: Case study on transport assets. Sci Total Environ 714:136854. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.scitotenv.2020.136854
Balogun AL, Rezaie F, Pham QB, Gigović L, Drobnjak S, Aina YA et al (2021) Spatial prediction of landslide susceptibility in western Serbia using hybrid support vector regression (SVR) with GWO, BAT and COA Algorithms. Geosci Front 12:009. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.gsf.2020.10.009
Beven KJ, Kirkby MJ (1979) A physically based, variable contributing area model of basin hydrology. Hydrol Sci Bull 24:43–69. https://doi.org/10.1080/02626667909491834
Breiman L (1996) Bagging Predictors. Mach Learn 24:123–140
Budimir MEA, Atkinson PM, Lewis HG (2015) A systematic review of landslide probability mapping using logistic regression. Landslides 12:419–436. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10346-014-0550-5
Bui DT, Shahabi H, Shirzadi A, Chapi K, Alizadeh M, Chen W et al (2018) Landslide detection and susceptibility mapping by AIRSAR data using support vector machine and index of entropy models in Cameron Highlands, Malaysia. Remote Sens 10:1527. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs10101527
Cao Y, Wei X, Fan W, Nan Y, Xiong W, Zhang S (2021) Landslide susceptibility assessment using the Weight of Evidence method: A case study in Xunyang area, China. PLoS ONE 16:1–18. https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0245668
Chang SH, Wan S (2015) Discrete rough set analysis of two different soil-behavior-induced landslides in National Shei-Pa Park, Taiwan. Geosci Front 6:807–816. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.gsf.2013.12.010
Chen W, Li Y (2020) GIS-based evaluation of landslide susceptibility using hybrid computational intelligence models. CATENA 195:104777. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.catena.2020.104777
Chen W, Shirzadi A, Shahabi H, Ahmad BB, Zhang S, Hong H et al (2017a) A novel hybrid artificial intelligence approach based on the rotation forest ensemble and naïve Bayes tree classifiers for a landslide susceptibility assessment in Langao County, China. Geomat Nat Haz Risk 8:1955–1977. https://doi.org/10.1080/19475705.2017.1401560
Chen W, Xie X, Wang J, Pradhan B, Hong H, Tien D (2017b) A comparative study of logistic model tree, random forest, and classification and regression tree models for spatial prediction of landslide susceptibility. CATENA 151:147–160. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.catena.2016.11.032
Chen L, Guo Z, Yin K, Pikha Shrestha D, Jin S (2019a) The influence of land use and land cover change on landslide susceptibility: A case study in Zhushan Town, Xuan’en County (Hubei, China). Nat Hazard 19:2207–2228. https://doi.org/10.5194/nhess-19-2207-2019
Chen W, Panahi M, Tsangaratos P, Shahabi H, Ilia I, Panahi S et al (2019b) Applying population-based evolutionary algorithms and a neuro-fuzzy system for modeling landslide susceptibility. CATENA 172:212–231. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.catena.2018.08.025
Chowdhuri I, Pal SC, Arabameri A, Ngo PTT, Chakrabortty R, Malik S et al (2020) Ensemble approach to develop landslide susceptibility map in landslide dominated Sikkim Himalayan region, India. Environ Earth Sci 79:476. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12665-020-09227-5
Dehnavi A, Aghdam IN, Pradhan B, Morshed Varzandeh MH (2015) A new hybrid model using step-wise weight assessment ratio analysis (SWARA) technique and adaptive neuro-fuzzy inference system (ANFIS) for regional landslide hazard assessment in Iran. CATENA 135:122–148. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.catena.2015.07.020
Dikshit A, Satyam N, Pradhan B (2019) Estimation of Rainfall-Induced Landslides Using the TRIGRS Model. Earth Syst Environ 3:575–584. https://doi.org/10.1007/s41748-019-00125-w
Dou J, Yunus AP, Bui DT, Merghadi A, Sahana M, Zhu Z et al (2020) Improved landslide assessment using support vector machine with bagging, boosting, and stacking ensemble machine learning framework in a mountainous watershed, Japan. Landslides 17:641–658. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10346-019-01286-5
Evans IS, Cox NJ (2005) Relations between land surface properties: Altitude, slope and curvature. In: Hergarden S (ed) Process Modelling and Landform Evolution. Springer, Berlin, pp 13–45. https://doi.org/10.1007/bfb0009718
Fawcett T (2006) An introduction to ROC analysis. Pattern Recogn Lett 27:861–874. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.patrec.2005.10.010
Friedman J, Tibshirani R, Hastie T (2000) Additive logistic regression: a statistical view of boosting (With discussion and a rejoinder by the authors). Ann Stat 28:337–407. https://doi.org/10.1214/aos/1016120463
Gambella C, Ghaddar B, Naoum-Sawaya J (2021) Optimization problems for machine learning: A survey. Eur J Oper Res 290:807–828. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ejor.2020.08.045
Gameiro S, Riffel ES, de Oliveira GG, Guasselli LA (2021) Artificial neural networks applied to landslide susceptibility: The effect of sampling areas on model capacity for generalization and extrapolation. Appl Geogr 137:102598. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.apgeog.2021.102598
Ghasemain B, Asl DT, Pham BT, Avand M, Nguyen HD, Janizadeh S (2020) Shallow landslide susceptibility mapping: A comparison between classification and regression tree and reduced error pruning tree algorithms. Vietnam J Earth Sci 42:14952. https://doi.org/10.15625/0866-7187/42/3/14952
Guo X, Fu Q, Hang Y, Lu H, Gao F, Si J (2020) Spatial variability of soil moisture in relation to land use types and topographic features on hillslopes in the black soil (mollisols) area of northeast China. Sustainability (Switzerland) 12:093552. https://doi.org/10.3390/SU12093552
Hang HT, Tung H, Hoa PD, Phuong NV, Phong TV, Costache R et al (2021) Spatial prediction of landslides along National Highway-6, Hoa Binh province, Vietnam using novel hybrid models. Geocarto Int 1–26:1912195. https://doi.org/10.1080/10106049.2021.1912195
Henriques C, Zêzere JL, Marques F (2015) The role of the lithological setting on the landslide pattern and distribution. Eng Geol 189:17–31. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.enggeo.2015.01.025
Hong H, Liu J, Zhu A-X (2020) Modeling landslide susceptibility using LogitBoost alternating decision trees and forest by penalizing attributes with the bagging ensemble. Sci Total Environ 718:137231. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.scitotenv.2020.137231
Hu X, Huang C, Mei H, Zhang H (2021) Landslide susceptibility mapping using an ensemble model of Bagging scheme and random subspace–based naïve Bayes tree in Zigui County of the Three Gorges Reservoir Area, China. Bull Eng Geol Environ. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10064-021-02275-6
Huang F, Cao Z, Guo J, Jiang S-H, Li S, Guo Z (2020) Comparisons of heuristic, general statistical and machine learning models for landslide susceptibility prediction and mapping. CATENA 191:104580. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.catena.2020.104580
Kadavi PR, Lee CW, Lee S (2019) Landslide-susceptibility mapping in Gangwon-do, South Korea, using logistic regression and decision tree models. Environ Earth Sci 78:116. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12665-019-8119-1
Kavzoglu T, Sahin EK, Colkesen I (2014) Landslide susceptibility mapping using GIS-based multi-criteria decision analysis, support vector machines, and logistic regression. Landslides 11:425–439. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10346-013-0391-7
Khosravi K, Pham BT, Chapi K, Shirzadi A, Shahabi H, Revhaug I et al (2018) A comparative assessment of decision trees algorithms for flash flood susceptibility modeling at Haraz watershed, northern Iran. Sci Total Environ 627:744–755. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.scitotenv.2018.01.266
Kim JC, Lee S, Jung HS, Lee S (2018) Landslide susceptibility mapping using random forest and boosted tree models in Pyeong-Chang, Korea. Geocarto Int 33:1000–1015. https://doi.org/10.1080/10106049.2017.1323964
Kinnell PIA (2010) Event soil loss, runoff and the Universal Soil Loss Equation family of models: A review. J Hydrol 385:384–397. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jhydrol.2010.01.024
Landwehr N, Hall M, Frank E (2005) Logistic Model Trees. Mach Learn 59:161–205
Lee S, Talib JA (2005) Probabilistic landslide susceptibility and factor effect analysis. Environ Geol 47:982–990. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00254-005-1228-z
Lee DH, Kim YT, Lee SR (2020) Shallow landslide susceptibility models based on artificial neural networks considering the factor selection method and various non-linear activation functions. Remote Sensing 12:071194. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs12071194
Li Y, Chen W (2020) Landslide susceptibility evaluation using hybrid integration of evidential belief function and machine learning techniques. Water (switzerland) 12:010133. https://doi.org/10.3390/w12010113
Liu J, Duan Z (2018) Quantitative assessment of landslide susceptibility comparing statistical index, index of entropy, and weights of evidence in the Shangnan Area, China. Entropy 20:868. https://doi.org/10.3390/e20110868
Liu Z, Gilbert G, Cepeda JM, Lysdahl AOK, Piciullo L, Hefre H et al (2021) Modelling of shallow landslides with machine learning algorithms. Geosci Front 12:385–393. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.gsf.2020.04.014
Luo X, Lin F, Chen Y, Zhu S, Xu Z, Huo Z et al (2019) Coupling logistic model tree and random subspace to predict the landslide susceptibility areas with considering the uncertainty of environmental features. Sci Rep 9:15369. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41598-019-51941-z
Ma Z, Mei G, Piccialli F (2021) Machine learning for landslides prevention: a survey. Neural Comput Appl 33:10881–10907. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00521-020-05529-8
Merghadi A, Yunus AP, Dou J, Whiteley J, Pham BT, Bui DT et al (2020) Machine learning methods for landslide susceptibility studies: A comparative overview of algorithm performance. Earth Sci Rev 207:103225. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.earscirev.2020.103225
Meten M, PrakashBhandary N, Yatabe R (2015) Effect of Landslide Factor Combinations on the Prediction Accuracy of Landslide Susceptibility Maps in the Blue Nile Gorge of Central Ethiopia. Geoenviron Dis 2:9. https://doi.org/10.1186/s40677-015-0016-7
Mokhtari M, Abedian S (2019) Spatial prediction of landslide susceptibility in Taleghan basin, Iran. Stochastic Environ Res Risk Assess 33:1297–1325. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00477-019-01696-w
Mondal S, Mandal S (2019) Landslide susceptibility mapping of Darjeeling Himalaya, India using index of entropy (IOE) model. Appl Geomat 11:129–146. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12518-018-0248-9
Moore ID, Grayson RB, Ladson AR (1991) Digital terrain modelling: A review of hydrological, geomorphological, and biological applications. Hydrol Process 5:3–30. https://doi.org/10.1002/hyp.3360050103
Ng CWW, Pang YW (2000) Influence of Stress State on Soil-Water Characteristics and Slope Stability. J Geotech Geoenviron Eng 126:157–166. https://doi.org/10.1061/(ASCE)1090-0241(2000)126:2(157)
Nhu VH, Mohammadi A, Shahabi H, Ahmad BB, Al-Ansari N, Shirzadi A et al (2020) Landslide Susceptibility Mapping Using Machine Learning Algorithms and Remote Sensing Data in a Tropical Environment. Int J Environ Res Public Health 17:144933. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijerph17144933
Persichillo MG, Bordoni M, Meisina C (2017) The role of land use changes in the distribution of shallow landslides. Sci Total Environ 574:924–937. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.scitotenv.2016.09.125
Pham BT, Prakash I (2019) A novel hybrid model of Bagging-based Naïve Bayes Trees for landslide susceptibility assessment. Bull Eng Geol Env 78:1911–1925. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10064-017-1202-5
Pham BT, Prakash I, Singh SK, Shirzadi A, Shahabi H, Tran T-T-T et al (2019a) Landslide susceptibility modeling using Reduced Error Pruning Trees and different ensemble techniques: Hybrid machine learning approaches. CATENA 175:203–218. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.catena.2018.12.018
Pham BT, Shirzadi A, Shahabi H, Omidvar E, Singh SK, Sahana M et al (2019b) Landslide susceptibility assessment by novel hybrid machine learning algorithms. Sustainability (switzerland) 11:1–25. https://doi.org/10.3390/su11164386
Phong TV, Phan TT, Prakash I, Singh SK, Shirzadi A, Chapi K et al (2019) Landslide susceptibility modeling using different artificial intelligence methods: a case study at Muong Lay district, Vietnam. Geocarto Int 1–24:1665715. https://doi.org/10.1080/10106049.2019.1665715
Pourghasemi HR, Rahmati O (2018) Prediction of the landslide susceptibility: Which algorithm, which precision? CATENA 162:177–192. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.catena.2017.11.022
Pourghasemi HR, Pradhan B, Gokceoglu C (2012) Application of fuzzy logic and analytical hierarchy process (AHP) to landslide susceptibility mapping at Haraz watershed, Iran. Natural Hazards 63:965–996. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11069-012-0217-2
Pourghasemi HR, Pradhan B, Gokceoglu C, Mohammadi M, Moradi HR (2013) Application of weights-of-evidence and certainty factor models and their comparison in landslide susceptibility mapping at Haraz watershed, Iran. Arab J Geosci 6:2351–2365. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12517-012-0532-7
Pourghasemi HR, Kornejady A, Kerle N, Shabani F (2020) Investigating the effects of different landslide positioning techniques, landslide partitioning approaches, and presence-absence balances on landslide susceptibility mapping. CATENA 187:104364. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.catena.2019.104364
Qiu H, Cui Y, Pei Y, Yang D, Hu S, Wang X et al (2020) Temporal patterns of nonseismically triggered landslides in Shaanxi Province, China. Catena 187:104356. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.catena.2019.104356
Quevedo RP, Maciel DA, Uehara TDT, Vojtek M, Rennó CD, Pradhan B et al (2021) Consideration of Spatial Heterogeneity in Landslide Susceptibility Mapping using Geographical Random Forest Model. Geocarto Int 1–20:1996637. https://doi.org/10.1080/10106049.2021.1996637
Quinlan JR (1987) Simplifying decision trees. Int J Man Mach Stud 27:221–234. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0020-7373(87)80053-6
Razavi-Termeh SV, Shirani K, Pasandi M (2021) Mapping of landslide susceptibility using the combination of neuro-fuzzy inference system (ANFIS), ant colony (ANFIS-ACOR), and differential evolution (ANFIS-DE) models. Bull Eng Geol Env 80:2045–2067. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10064-020-02048-7
Reichenbach P, Rossi M, Malamud BD, Mihir M, Guzzetti F (2018) A review of statistically-based landslide susceptibility models. Earth Sci Rev 180:60–91. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.earscirev.2018.03.001
Rossi M, Guzzetti F, Reichenbach P, Mondini AC, Peruccacci S (2010) Optimal landslide susceptibility zonation based on multiple forecasts. Geomorphology 114:129–142. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.geomorph.2009.06.020
Saha A, Saha S (2020) Comparing the efficiency of weight of evidence, support vector machine and their ensemble approaches in landslide susceptibility modelling: A study on Kurseong region of Darjeeling Himalaya, India. Remote Sens Appl Soc Environ 19:100323. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.rsase.2020.100323
Saha S, Arabameri A, Saha A, Blaschke T, Ngo PTT, Nhu VH et al (2021a) Prediction of landslide susceptibility in Rudraprayag, India using novel ensemble of conditional probability and boosted regression tree-based on cross-validation method. Sci Total Environ 764:142928. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.scitotenv.2020.142928
Saha S, Roy J, Pradhan B, Hembram TK (2021b) Hybrid ensemble machine learning approaches for landslide susceptibility mapping using different sampling ratios at East Sikkim Himalayan, India. Adv Space Res 68:2819–2840. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.asr.2021.05.018
Sahana M, Sajjad H (2017) Evaluating effectiveness of frequency ratio, fuzzy logic and logistic regression models in assessing landslide susceptibility: a case from Rudraprayag district, India. J Mt Sci 14:2150–2167. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11629-017-4404-1
Saito H, Nakayama D, Matsuyama H (2009) Comparison of landslide susceptibility based on a decision-tree model and actual landslide occurrence: The Akaishi Mountains, Japan. Geomorphology 109:108–121. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.geomorph.2009.02.026
Schillaci C, Braun A, Kropáček J (2015) Terrain analysis and landform recognition. In: Clarcke LE, Nield JM (eds) Geomorphological Techniques. British Society for Geomorphology, London, pp 1–18
Shi G, Yang X, Chen W, Chen H, Zhang J, Tao Z (2021) Characteristics of failure area and failure mechanism of a landslide in Yingjiang County, Yunnan, China. Landslides 18:721–735. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10346-020-01544-x
Shortliffe EH, Buchanan BG (1975) A Model of Inexact Reasoning in Medicine. Math Biosci 23:351–379
Stanley T, Kirschbaum DB (2017) A heuristic approach to global landslide susceptibility mapping. Nat Hazards 87:145–164. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11069-017-2757-y
Süzen ML, Doyuran V (2004) A comparison of the GIS based landslide susceptibility assessment methods: Multivariate versus bivariate. Environ Geol 45:665–679. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00254-003-0917-8
Thi Ngo PT, Panahi M, Khosravi K, Ghorbanzadeh O, Kariminejad N, Cerda A et al (2021) Evaluation of deep learning algorithms for national scale landslide susceptibility mapping of Iran. Geosci Front 12:505–519. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.gsf.2020.06.013
Tien Bui D, Ho TC, Pradhan B, Pham BT, Nhu VH, Revhaug I (2016a) GIS-based modeling of rainfall-induced landslides using data mining-based functional trees classifier with AdaBoost, Bagging, and MultiBoost ensemble frameworks. Environ Earth Sci 75:1–22. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12665-016-5919-4
Tien Bui D, Tuan TA, Klempe H, Pradhan B, Revhaug I (2016b) Spatial prediction models for shallow landslide hazards: a comparative assessment of the efficacy of support vector machines, artificial neural networks, kernel logistic regression, and logistic model tree. Landslides 13:361–378. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10346-015-0557-6
Truong X, Mitamura M, Kono Y, Raghavan V, Yonezawa G, Truong X et al (2018) Enhancing Prediction Performance of Landslide Susceptibility Model Using Hybrid Machine Learning Approach of Bagging Ensemble and Logistic Model Tree. Appl Sci 8:1046. https://doi.org/10.3390/app8071046
Tsangaratos P, Ilia I (2016) Landslide susceptibility mapping using a modified decision tree classifier in the Xanthi Perfection, Greece. Landslides 13:305–320. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10346-015-0565-6
Vakhshoori V, Zare M (2018) Is the ROC curve a reliable tool to compare the validity of landslide susceptibility maps? Geomat Nat Haz Risk 9:249–266. https://doi.org/10.1080/19475705.2018.1424043
Varnes DJ (1984) Landslide hazard zonation: a review of principles and pratice. UNESCO, Paris
Villagra PE, Defossé GE, del Valle HF, Tabeni S, Rostagno M, Cesca E et al (2009) Land use and disturbance effects on the dynamics of natural ecosystems of the Monte Desert: Implications for their management. J Arid Environ 73:202–211. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jaridenv.2008.08.002
Wang X, Zhao J, Zhou Y, Li J (2014) The geospatial data cloud: An implementation of applying cloud computing in geosciences. Data Sci J 13:254–264. https://doi.org/10.2481/dsj.14-042
Wang Y, Seijmonsbergen AC, Bouten W, Chen Q (2015) Using statistical learning algorithms in regional landslide susceptibility zonation with limited landslide field data. J Mt Sci 12:268–288. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11629-014-3134-x
Wang Y, Feng L, Li S, Ren F, Du Q (2020a) A hybrid model considering spatial heterogeneity for landslide susceptibility mapping in Zhejiang Province, China. Catena 188:104425. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.catena.2019.104425
Wang Z, Liu Q, Liu Y (2020b) Mapping Landslide Susceptibility Using Machine Learning Algorithms and GIS: A Case Study in Shexian County, Anhui Province, China. Symmetry 12:1954. https://doi.org/10.3390/sym12121954
Willmott CJ, Matsuura K (2005) Advantages of the mean absolute error (MAE) over the root mean square error (RMSE) in assessing average model performance. Newark Available at: www.int-res.com. Accessed March 15, 2021
Wu Y, Ke Y, Chen Z, Liang S, Zhao H, Hong H (2020) Application of alternating decision tree with AdaBoost and bagging ensembles for landslide susceptibility mapping. CATENA 187:104396. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.catena.2019.104396
Xie W, Li X, Jian W, Yang Y, Liu H, Robledo LF et al (2021) A Novel Hybrid Method for Landslide Susceptibility Mapping-Based GeoDetector and Machine Learning Cluster: A Case of Xiaojin County, China. ISPRS Int J Geo-Inf 10:93. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijgi10020093
Youssef AM, Pourghasemi HR (2021) Landslide susceptibility mapping using machine learning algorithms and comparison of their performance at Abha Basin, Asir Region, Saudi Arabia. Geosci Front 12:639–655. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.gsf.2020.05.010
Zêzere JL, Pereira S, Melo R, Oliveira SC, Garcia RAC (2017) Mapping landslide susceptibility using data-driven methods. Sci Total Environ 589:250–267. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.scitotenv.2017.02.188
Zhang K, Wang S, Bao H, Zhao X (2019) Characteristics and influencing factors of rainfall-induced landslide and debris flow hazards in Shaanxi Province, China. Nat Hazard 19:93–105. https://doi.org/10.5194/nhess-19-93-2019
Zhang T, Mao Z, Wang T (2020) GIS-based evaluation of landslide susceptibility using a novel hybrid computational intelligence model on different mapping units. J Mt Sci 17:2929–2941. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11629-020-6393-8
Zhao Z, Liu ZY, Xu C (2021) Slope Unit-Based Landslide Susceptibility Mapping Using Certainty Factor, Support Vector Machine, Random Forest, CF-SVM and CF-RF Models. Front Earth Sci 9:1–16. https://doi.org/10.3389/feart.2021.589630
Zhou X, Wen H, Zhang Y, Xu J, Zhang W (2021) Landslide susceptibility mapping using hybrid random forest with GeoDetector and RFE for factor optimization. Geosci Front 12:101211. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.gsf.2021.101211
Funding
This study is funded by Coordenação de Aperfeiçoamento de Pessoal de Nível Superior Brasil (CAPES) (Finance Code 001), Opening Fund of Key Laboratory of Land Remediation of Shaanxi Province (300102351502), National Natural Science Foundation of China (211035210511), Internal scientific research project of Shaanxi Land Engineering Construction Group (DJNY2021-10) and Shaanxi Province Natural Science Basic Research Project (2021JQ-961).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
Tingyu Zhang done conceptualization; Tingyu Zhang and Renata performed methodology, writing—original draft preparation, and funding acquisition; Dan Luo contributed to software; Tao Wang validated the study; Renata done formal analysis and writing—review and editing; Huanyuan Wang investigated the study;Quan Fu searched resources; Guilherme Garcia de Oliveira done data curation;;Laurindo Antonio Guasselli visualized the study; Huanyuan Wang done supervision; Camilo Daleles Renno was involved in project administration;.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Ethics approval
Not applicable.
Consent for publication
All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Conflicts of interest
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Additional information
Responsible Editor: Zeynal Abiddin Erguler
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Zhang, T., Quevedo, R., Wang, H. et al. Improved tree-based machine learning algorithms combining with bagging strategy for landslide susceptibility modeling. Arab J Geosci 15, 183 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12517-022-09488-3
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12517-022-09488-3