Abstract
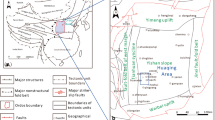
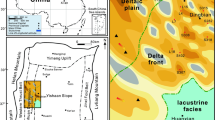
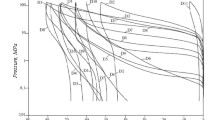
The clastic rocks of the late Triassic Xujiahe Formation in the Sichuan Basin of southwestern China are typical unconventional tight sandstone reservoirs with proven natural gas reserves of up to one trillion cubic meters. In particular, the Xu-6 member of the Xujiahe Formation in the Guang'an area of the central Sichuan Basin is a gas reservoir with great exploration and development potential. In this study, we studied the petrography, measured the geophysical properties, and performed mercury injection tests and calculations based on fractal theory on a suite of tight gas sandstone samples from the Xu-6 member to evaluate the pore types and volumes, permeability, and heterogeneity of the reservoirs. The results show that the sandstone reservoirs of the Xu-6 member of the Xujiahe Formation can be divided into the following three types. Type I reservoirs, which are generally of high quality (an average porosity of 12.59% and an average permeability coefficient of 6.8231 × 10-3 μm2), are dominated by macroscale pores and a uniform distribution of mesoscale and microscale pores; the fractal dimension is 2.45 to 2.59. Type II reservoirs (an average porosity of 8.9% and an average permeability coefficient of 1.3504 × 10-3 μm2) are dominated by mesoscale pores, followed by microscale pores, whereas the macroscale pores are poorly developed; the fractal dimension range is 2.42–2.69. Type III reservoirs, typically of low quality (an average porosity of 4.67% and an average permeability coefficient of 0.2947 × 10-3 μm2), are dominated by microscale pores, followed by mesoscale pores with poorly developed or undeveloped macroscale pores; the fractal dimension is 2.46 to 2.81. The varying distribution of pore types leads to significant differences in pore heterogeneity for the three types of reservoirs, suggesting that type III reservoirs are more heterogeneous than type I reservoirs. Our correlation analysis reveals that the physical properties are related to the reservoir heterogeneity, as proxied by the fractal dimension. When the fractal dimension is between 2.45 and 2.6, porosity is variable, but generally high, whereas permeability shows no obvious relationship to the fractal dimension. When the fractal dimension is greater than 2.6, there is a decreasing trend in porosity, and permeability remains at a constant low value as the fractal dimension increases. Based on our quantitative study of physical properties and fractal characteristics of the Xu-6 member sandstone reservoir, microscopic pore characteristics such as fractal dimension hold great theoretical and practical significance as evaluation criteria for unconventional high-quality natural gas reservoirs and can potentially be used for guiding their exploration and development.










Similar content being viewed by others
References
Albrecht D, Reitenbach V (2015) Investigations on fluid transport properties in the North-German Rotliegend tight gas sandstones and applications. Environ Earth Sci 73:5791–5799. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12665-015-4322-x
Chen G, Lin LB, Wang W, Chen HD, Guo TL (2014) Diagenesis and porosity evolution of sandstones in Xujiahe Formation, Yuanba area. Pet Geol Exp 36(4):405–410 (in Chinese with English abstract)
Deng T, Li Y, Wang ZJ, Yu Q, Hu WC, Zhao SZ, Dong SL (2018) The difference of pore structures and fractal features in the Xujiahe Formation shales from Well LD-1, Sichuan Basin, China. J Chengdu Univ Technol (SciTechnol Ed) 45(6):709–721 (in Chinese with English abstract)
Ehrenberg SN, Nadeau PH (2005) Sandstone vs. carbonate petroleum reservoirs: a global perspective on porosity-depth and porosity-permeability relationships. AAPG Bull 89:435–445. https://doi.org/10.1306/11230404071
Ehrenberg SN, Nadeau PH, Steen Ø (2009) Petroleum reservoir porosity versus depth: Influence of geological age. AAPG Bull 93:1281–1296. https://doi.org/10.1306/06120908163
Feng XZ, Zhu HH (2019) Micro-pore structure and fractal characteristics of the Xiashihezi Formation tight sandstone reservoirs in Sulige Area, Ordos Basin. Geol Sci Technol Inform 38(3):147–156 (in Chinese with English abstract)
Fu X, Wang ZH, Zhong B, Feng X, Li N (2010) Characteristics of single phase gas seepage in sandstone gas reservoirs with low-permeability and high water saturation in the sixth member of the Xujiahe Formation, Guang'an Gas Field. Nat Gas Ind 30(07):39–41+130 (in Chinese with English abstract)
Gu ZY (2017) Influences of diagenesis evolution difference on the Xu-2 and Xu-6 reservoir in the Dongfengchang area, southern Sichuan, China. J Chengdu Univ Technol (SciTechnol Ed) 44(02):139–148 (in Chinese with English abstract)
Hou Z, Xie H, Zhou H, Were P, Kolditz O (2015) Unconventional gas resources in China. Environ Earth Sci 73:5785–5789. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12665-015-4393-8
Huang JL, Dong DZ, Li JZ, Hu JW, Wang YM, Li DH, Wang SF (2016) Reservoir characteristics and its influence on continental shales: an example from Triassic Xujiahe Formation shale, Sichuan Basin. Earth Sci Front 23(2):158–166 (in Chinese with English abstract)
Huang W, Lu S, Hersi OS, Wang M, Deng S, Lu R (2017) Reservoir spaces in tight sandstones: classification, fractal characters, and heterogeneity. J Nat Gas Sci Eng 46:80–92. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jngse.2017.07.006
Lai J, Wang G, Ran Y, Zhou Z (2015) Predictive distribution of high-quality reservoirs of tight gas sandstones by linking diagenesis to depositional facies: evidence from Xu-2 sandstones in the Penglai area of the central Sichuan basin, China. J Nat Gas Sci Eng 23:97–111. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jngse.2015.01.026
Lai J, Wang G, Cai C, Fan Z, Wang S, Chen J, Luo G (2018a) Diagenesis and reservoir quality in tight gas sandstones: the fourth member of the Upper Triassic Xujiahe Formation, Central Sichuan Basin, Southwest China. Geol J 53:629–646. https://doi.org/10.1002/gj.2917
Lai J, Wang G, Wang S, Cao J, Li M, Pang X, Zhou Z, Fan X, Dai Q, Yang L, He Z, Qin Z (2018b) Review of diagenetic facies in tight sandstones: diagenesis, diagenetic minerals, and prediction via well logs. Earth Sci Rev 185:234–258. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.earscirev.2018.06.009
Law BE, Curtis JB (2002) Introduction to unconventional petroleum systems. AAPG Bull 86:1851–1852. https://doi.org/10.1306/61EEDDA0-173E-11D7-8645000102C1865D
Li Y, Chen SJ, Wu BY, Qiu D, Lin RP, Li JL (2017) Controlling factors on complex gas-water distribution in Xu-6 tight sandstone gas reservoir in Guang’An area. Xinjiang Petrol Geol 38(02):198–203 (in Chinese with English abstract)
Lin XB, Tian JC, Liu LP, Li MT (2019) Dissolution mechanism of siliciclastic particles in Xujiahe Formation, West Sichuan Depression, Sichuan Basin. Pet Geol Exp 41(3):404–410 (in Chinese with English abstract)
Lundegard PD (1992) Sandstone porosity loss; a big picture view of the importance of compaction. J Sediment Res 62:250–260. https://doi.org/10.1306/D42678D4-2B26-11D7-8648000102C1865D
Luo C, Jia AL, He DB, Guo JL, Zhang G, Cheng ZJ (2016) A new method for binomial deliverability equation of horizontal gas well. Nat Gas Geosci 27(02):359–370 +376 (in Chinese with English abstract)
Nelson PH (2009) Pore-throat sizes in sandstones, tight sandstones, and shales. AAPG Bull 93:329–340. https://doi.org/10.1306/10240808059
Paxton ST, Szabo JO, Ajdukiewicz JM, Klimentidis RE (2002) Construction of an intergranular volume compaction curve for evaluating and predicting compaction and porosity loss in rigid-grain sandstone reservoirs. AAPG Bull 86:2047–2067. https://doi.org/10.1306/61EEDDFA-173E-11D7-8645000102C1865D
Pittman ED, Larese RE (1991) Compaction of lithic sands: experimental results and applications (1). AAPG Bull 75:1279–1299
Schmoker JW (2002) Resource-assessment perspectives for unconventional gas systems. AAPG Bull 86:1993–1999. https://doi.org/10.1306/61EEDDDC-173E-11D7-8645000102C1865D
Shi ZS, Xie WR, Ma SY, Li GX (2012) Transgression sedimentary records of the Members 4-6 of Upper Triassic Xujiahe Formation in Sichuan Basin. J Palaeogeogr 14(05):583–595
Taylor TR, Giles MR, Hathon LA, Diggs TN, Braunsdorf NR, Birbiglia GV, Kittridge MG, Macaulay CI, Espejo IS (2010) Sandstone diagenesis and reservoir quality prediction: models, myths, and reality. AAPG Bull 94:1093–1132. https://doi.org/10.1306/04211009123
Tong CG (2000) Relationship between Neotectonic movement and structural evolution and gas pools formation of Sichuan Basin. J Chengdu Univ Technol (SciTechnol Ed) 27(02):123–130 (in Chinese with English abstract)
Wang Z, Huang S, Gong D, Wu W, Yu C (2013) Geochemical characteristics of natural gases in the Upper Triassic Xujiahe Formation in the southern Sichuan Basin, SW China. Int J Coal Geol 120:15–23. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.coal.2013.09.002
Yu C, Gong DY, Huang SP, Wu W, Liao FR, Liu D (2014) Geochemical characteristics of carbon and hydrogen isotopes for the Xujiahe Formation natural gas in Sichuan Basin. Nat Gas Geosci 25(1):87–97
Zeng L (2010) Microfracturing in the Upper Triassic Sichuan Basin tight-gas sandstones: tectonic, overpressure, and diagenetic origins. AAPG Bull 94:1811–1825. https://doi.org/10.1306/06301009191
Zhang L, Wang W, Shu ZG, Hao F, Zou YH, Yang S (2019) Distribution and genesis of calcite-replaced and calcite-cemented tight reservoirs in Xujiahe Formation, Yuanba area, Northeast Sichuan. Acta Pet Sin 40(6):692–705 (in Chinese with English abstract)
Zhao W, Wang H, Xu C, Bian C, Wang Z, Gao X (2010) Reservoir-forming mechanism and enrichment conditions of the extensive Xujiahe Formation gas reservoirs, central Sichuan Basin. Pet Explor Dev 37:146–157. https://doi.org/10.1016/S1876-3804(10)60022-5
Zhao ZW, Li N, Liu M, Wang XJ, Wu CJ, Li L (2019) Origin of gas accumulation and high yield in tight gas reservoirs of Xujiahe Formation, Sichuan Basin. Nat Gas Explor Develop 42(2):39–47 (in Chinese with English abstract)
Zhao XF, Zhao TY, Zhang WL (2019) An introduction to the developments of tidal rhythmite studies and its implication to the natural gas exploration of Xujiahe Formation. Nat Gas Explor Develop 42(2):29–38 (in Chinese with English abstract)
Zheng RC, Dai CC, Zhu RK (2009) Sequence-based lithofacies and paleogeographic characteristics of Upper Triassic Xujiahe Formation in Sichuan Basin. Geol Rev 55(4):484–495 (in Chinese with English abstract)
Zhu T, Duan XG, He D, Peng X (2014) Reservoir characteristics in the 6th Member of Xujiahe Formation in Guang’an area of Sichuan Province. Journal of Yangtze University(Nat Sci Edit), 11(26): 5–7+35+3. (in Chinese with English abstract)
Zhu HH, Zhong DK, Zhang YX, Sun HT, Du BQ, Meng H, Zhang CW, Yang Z (2014) Pore types and controlling factors on porosity and permeability of Upper Triassic Xujiahe tight sandstone reservoir in Southern Sichuan Basin. OIL Gas Geol 35(1):65–76 (in Chinese with English abstract)
Zhu F, Hu W, Cao J, Sun F, Liu Y, Sun Z (2018) Micro/nanoscale pore structure and fractal characteristics of tight gas sandstone: a case study from the Yuanba area, northeast Sichuan Basin, China. Mar Pet Geol 98:116–132. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.marpetgeo.2018.08.013
Zhu H, Zhang T, Zhong D, Li Y, Zhang J, Chen X (2019) Binary pore structure characteristics of tight sandstone reservoirs. Pet Explor Dev 46:1297–1306. https://doi.org/10.1016/S1876-3804(19)60283-1
Zou C, Tao S, Zhu R, Yuan X, Li W, Guangya Z, Xiangxiang Z, Xiaohui G, Liuhong L, Chunchun X, Jiarong S, Guohui L (2009) Formation and distribution of “continuous” gas reservoirs nd their giant gas province: a case from the Upper riassic Xujiahe Formation giant gas province, Sichuan Basin. Pet Explor Dev 36:307–319. https://doi.org/10.1016/S1876-3804(09)60128-2
Zou C, Zhu R, Liu K, Su L, Bai B, Zhang X, Yuan X, Wang J (2012) Tight gas sandstone reservoirs in China: characteristics and recognition criteria. J Pet Sci Eng 88–89:82–91. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.petrol.2012.02.001
Zou CN, Yang Z, Tao SZ, Yuan XJ, Zhu RK, Hou LH, Wu ST, Sun L, Zhang GS, Bai B, Wang L, Gao XH, Pang ZL (2013) Continuous hydrocarbon accumulation over a large area as a distinguishing characteristic of unconventional petroleum: the Ordos Basin, North-Central China. Earth Sci Rev 126:358–369. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.earscirev.2013.08.006
Zou CN, Yang Z, Zhu RK, Zhang GS, Hou LH, Wu ST, Tao SZ, Yuan XJ, Dong DZ, Wang YM, Wang L, Huang JL, Wang SF (2015) Progress in China’s unconventional oil&gas exploration and development and theoretical technologies. Acta Geol Sin 89(06):979–1007 (in Chinese with English abstract)
Funding
This work was supported by the Special Project of Deep Resource Exploration of the National Key Research and Development Program of China (No. 2018YFC0604201) and the Open Fund of State Key Laboratory of Oil and Gas Reservoir Geology and Exploitation (Chengdu University of Technology) (No. PLC201901013).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no competing interests.
Additional information
Responsible Editor: Santanu Banerjee
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Shen, F., Yue, L., Liu, Z. et al. Heterogeneity of tight sandstone reservoirs based on fractal theory: the Xu-6 member of Xujiahe Formation in Guang'an area, central Sichuan Basin. Arab J Geosci 14, 1515 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12517-021-07851-4
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12517-021-07851-4