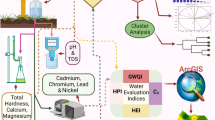
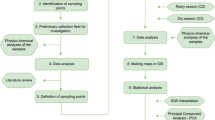
Abstract
Groundwater is one of the most valuable nature reserves globally and its availability and quality are essential for the welfare of human beings. Anthropogenic activity has a significant influence on the contamination of groundwater resources. This investigation was performed to understand this problem by calculating a water quality index (WQI) with a geographic information system (GIS) to assess groundwater quality in the coal mining region of the Ramgarh and Hazaribagh districts, Jharkhand, India. Groundwater samples were obtained during the pre-monsoon (n = 45) and post-monsoon (n = 31) seasons from multiple sampling sites in the study area. The samples were examined for 10 physicochemical and 5heavy metal parameters such as arsenic (As), copper (Cu), iron (Fe), manganese (Mn), and lead (Pb). Except Fe and Mn remaining elements were below the detection level (BDL). The WQI results showed that 189.76 km2 (22.34%) in the pre-monsoon and 694.93 km2 (81.83%) of the study areas lie under good and excellent water quality zones, respectively. Principal component analysis (PCA) was utilized to source ions that incorporate three factors, including eigenvalues cut off at higher than unity. Total variance achieved for both the pre and post-monsoon seasons was 65.20% and 73.16%. Factors thus extracted resemble the relationship with geology, widespread coal mining, transportation, and industrial origin of the elements. Results revealed that the maximum portion of the study area is under a poor to unsuitable zone (77.65%) for drinking purposes during pre-monsoon, whereas the same area found suitable for drinking usage in the post-monsoon season.











Similar content being viewed by others
References
Agrawal V, Jagetia M (1997) Hydrogeochemical assessment of groundwater quality in Udaipur city, Rajasthan, India. In Proceedings of National Conference on Dimension of Environmental Stress in India. Dept. of Geology, MS University, Baroda, pp 151-154.
Alberto WD, del Pilar DM, Valeria AM, Fabiana PS, Cecilia HA, de los Ángeles BM (2001) Pattern recognition techniques for the evaluation of spatial and temporal variations in water quality. a case study: Suquı́a River Basin (Córdoba-Argentina). Water Res 35(12):2881–2894. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0043-1354(00)00592-3
Annapoorna H, Janardhana MR (2015) Assessment of groundwater quality for drinking purpose in rural areas surrounding a defunct copper mine. Aquat Pr 4:685–692. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.aqpro.2015.02.088
Asadi S, Vuppala P, Reddy M (2007) Remote sensing and GIS techniques for evaluation of groundwater quality in municipal corporation of Hyderabad (Zone-V), India. Int J Environ Res Pu 4(1):45–52. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijerph2007010008
Astel A, Tsakovski S, Simeonov V, Reisenhofer E, Piselli S, Barbieri P (2008) Multivariate classification and modeling in surface water pollution estimation. Anal Bioanal Chem 390(5):1283–1292. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00216-007-1700-6
Avtar R, Kumar P, Singh CK, Sahu N, Verma RL, Thakur JK, Mukherjee S (2013) Hydrogeochemical assessment of groundwater quality of Bundelkhand, India using statistical approach. Water Qual Expo Health 5(3):105–115. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12403-013-0094-2
Banerji S, Mitra D (2019) Geographical information system-based groundwater quality index assessment of northern part of Kolkata, India for drinking purpose. Geocarto Int 34(9):943–958. https://doi.org/10.1080/10106049.2018.1451922
Barceloux DG, Barceloux D (1999) Cobalt. J Toxicol Clin Toxicol 37(2):201–216
Bhargava DS (1983) Use of water quality index for river classification and zoning of Ganga River. Environ Pollut B 6(1):51–67. https://doi.org/10.1016/0143-148X(83)90029-0
BIS (2003) Bureau of Indian Standards specification for drinking water. IS: 10500:91. Revised New Delhi
Bordalo AA, Teixeira R, Wiebe WJ (2006) A water quality index applied to an international shared river basin: the case of the Douro River. Environ Manag 38(6):910–920. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00267-004-0037-6
Brown RM., McClelland NI, Deininger RA, Tozer RG (1970) A Water Quality Index- do we Dare
Chaturvedi MK, Bassin JK (2010) Assessing the water quality index of water treatment plant and bore wells, in Delhi, India. Environ Monit Assess 163(1-4):449–453. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10661-009-0848-2
CPCB (2011). Impact of coal mine waste water discharge on surroundings with reference to heavy metals. Bhopal. Retrieved from http://www.cpcb.nic.in. Accessed 17 June 2018
Debels P, Figueroa R, Urrutia R, Barra R, Niell X (2005) Evaluation of water quality in the Chillán River (Central Chile) using physicochemical parameters and a modified water quality index. Environ Monit Assess 110(1-3):301–322. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10661-005-8064-1
Dreher GB, Finkelman RB (1992) Selenium mobilization in a surface coal mine, Powder River Basin, Wyoming, USA. Environmental Geolo Water S 19(3):155–167. https://doi.org/10.1007/BF01704083
Heath RC (2004) Basic ground-water hydrology (Vol. 2220). US Department of the Interior, US Geological Survey
Horton RK (1965) An index number system for rating water quality. J Water Pollut Control Fed 37(3):300–306
Hudak PF (2000) Regional trends in nitrate content of Texas groundwater. J Hydrol 228(1-2):37–47
Jacintha TGA, Rawat KS, Mishra A, Singh SK (2017) Hydrogeochemical characterization of groundwater of peninsular Indian region using multivariate statistical techniques. Appl Water Sci 7(6):3001–3013. https://doi.org/10.1007/s13201-016-0400-9
Johnston K, Ver Hoef JM, Krivoruchko K, Lucas N (2001) Using ArcGIS geostatistical analyst, vol 380. Esri, Redlands
Kaiser HF (1960) The application of electronic computers to factor analysis. Educ Psychol Meas 20(1):141–151
Kannel PR, Lee S, Lee YS, Kanel SR, Khan SP (2007) Application of water quality indices and dissolved oxygen as indicators for river water classification and urban impact assessment. Environ Monit Assess 132(1-3):93–110. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10661-006-9505-1
Karanth KR (1987) Ground water assessment: development and management. Tata McGraw-Hill Education
Khan AA, Paterson R, Khan H (2003) Modification and application of the CCME WQI for the communication of drinking water quality data in Newfoundland and Labrador. In 38th, Central Symposium on Water Quality Research, Canadian Association on Water Quality, pp 10-11
Kitanidis PK (1994) The concept of the dilution index. Water Resour Res 30(7):2011–2026. https://doi.org/10.1029/94WR00762
Kumar A, Krishna AP (2018) Assessment of groundwater potential zones in coal mining impacted hard-rock terrain of India by integrating geospatial and analytic hierarchy process (AHP) approach. Geocarto Int 33(2):105–129. https://doi.org/10.1080/10106049.2016.1232314
Kumar A, Krishna AP (2020) Groundwater vulnerability and contamination risk assessment using GIS-based modified DRASTIC-LU model in hard rock aquifer system in India. Geocarto Int 35(11):1149–1178. https://doi.org/10.1080/10106049.2018.1557259
Kumar A, Pandey AC (2013) Evaluating Impact of coal mining activity on landuse/landcover using temporal satellite images in South Karanpura coalfields and environs, Jharkhand State, India. International Journal of Advanced Remote Sensing and GIS 2(1):183–197 http://technical.cloud-journals.com/index.php/IJARSG/article/view/Tech-110
Kumar VS, Amarender B, Dhakate R, Sankaran S, Kumar KR (2016) Assessment of groundwater quality for drinking and irrigation use in shallow hard rock aquifer of Pudunagaram, Palakkad District Kerala. Appl Water Sci 6(2):149–167. https://doi.org/10.1007/s13201-014-0214-6
Kumari S, Singh AK, Verma AK, Yaduvanshi NPS (2014) Assessment and spatial distribution of groundwater quality in industrial areas of Ghaziabad, India. Environ Monit Assess 186(1):501–514. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10661-013-3393-y
Lasagna M, De Luca DA, Debernardi L, Clemente P (2013) Effect of the dilution process on the attenuation of contaminants in aquifers. Environ Earth Sci 70(6):2767–2784. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12665-013-2336-9
Liang Z, Ren T, Ningbo W (2017) Groundwater impact of open cut coal mine and an assessment methodology: A case study in NSW. Int J Min Sci Technol 27:861–866. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijmst.2017.07.008
Mahato MK, Singh G, Singh PK, Singh AK, Tiwari AK (2017) Assessment of mine water quality using heavy metal pollution index in a coal mining area of Damodar River Basin, India. B Environ Contam Tox 99(1):54–61. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00128-017-2097-3
Mahato MK, Singh PK, Singh AK, Tiwari AK (2018) Assessment of hydrogeochemical processes and mine water suitability for domestic, irrigation, and industrial purposes in East Bokaro Coalfield, India. Mine Water Environ 37(3):493–504. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10230-017-0508-7
Mohanty AK, Lingaswamy M, Rao VG, Sankaran S (2018) Impact of acid mine drainage and hydrogeochemical studies in a part of Rajrappa coal mining area of Ramgarh District, Jharkhand State of India. Groundw Sustain Dev 7:164–175. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.gsd.2018.05.005
Mushtaq F, Nee Lala MG, Pandey AC (2015) Assessment of pollution level in a Himalayan Lake, Kashmir, using geomatics approach. Int J Environ An Ch 95(11):1001–1013. https://doi.org/10.1080/03067319.2015.1077517
Oinam JD, Ramanathan AL, Linda A, Singh G (2011) A study of arsenic, iron and other dissolved ion variations in the groundwater of Bishnupur District, Manipur, India. Environ Earth Sci 62(6):1183–1195. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12665-010-0607-2
Ozimek T, Sikorska U (1975) Field experiment on the effect of municipal sewage on macrophytes and epifauna in the lake littoral. Bulletin de l'Academie polonaise des sciences. Serie des sciences biologiques 23(7):447–455
Pandey AC, Kumar A (2014) Analysing topographical changes in open cast coal-mining region of Patratu, Jharkhand using CARTOSAT-I Stereopair satellite images. Geocarto Int 29(7):731–744. https://doi.org/10.1080/10106049.2013.838309
Patil VBB, Pinto SM, Govindaraju T, Hebbalu VS, Bhat V, Kannanur LN (2020) Multivariate statistics and water quality index (WQI) approach for geochemical assessment of groundwater quality-a case study of Kanavi Halla Sub-Basin, Belagavi, India. Environ Geochem Health 42(9):2667–2684. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10653-019-00500-6
Pesce SF, Wunderlin DA (2000) Use of water quality indices to verify the impact of Córdoba City (Argentina) on Suquı́a River. Water Res 34(11):2915–2926. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0043-1354(00)00036-1
Pradhan SK, Patnaik D, Rout SP (2001) Water Quality Index for the ground water around a phosphatic fertilizer plant. Indian J Environ Prot 21(4):355–358
Prathap A, Chakraborty S (2019) Hydro chemical characterization and suitability analysis of groundwater for domestic and irrigation uses in open cast coal mining areas of Charhi and Kuju, Jharkhand, India. Groundw Sustain Dev 9:100244. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.gsd.2019.100244
Raju NJ, Patel P, Gurung D, Ram P, Gossel W, Wycisk P (2015) Geochemical assessment of groundwater quality in the Dun valley of central Nepal using chemometric method and geochemical modeling. Groundw Sustain Dev 1(1-2):135–145. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.gsd.2016.02.002
Ramachandra TV, Solanki M (2007) Ecological assessment of lentic water bodies of Bangalore. The Ministry of Science and Technology
Rao SM, Mamatha P (2004) Water quality in sustainable water management. Curr Sci India:942–947 https://www.jstor.org/stable/24109398
Rao GS, Nageswararao G (2013) Assessment of ground water quality using water quality index. Archive of Environmental Sciences 7:1–5
Rattan RK, Datta SP, Chhonkar PK, Suribabu K, Singh AK (2005) Long-term impact of irrigation with sewage effluents on heavy metal content in soils, crops and groundwater-a case study. Agric Ecosyst Environ 109(3-4):310–322. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.agee.2005.02.025
Rawat KS, Singh SK (2018) Water Quality Indices and GIS-based evaluation of a decadal groundwater quality. Geology, Ecology, and Landscapes 2(4):240–255. https://doi.org/10.1080/24749508.2018.1452462
Sánchez E, Colmenarejo MF, Vicente J, Rubio A, García MG, Travieso L, Borja R (2007) Use of the water quality index and dissolved oxygen deficit as simple indicators of watersheds pollution. Ecol Indic 7(2):315–328. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ecolind.2006.02.005
Sarkar BC, Mahanata BN, Saikia K, Paul PR, Singh G (2007) Geo environmental quality assessment in Jharia coalfield, India, using multivariate statistics and geographic information system. Environ Geol 51:1177–1196. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00254-006-0409-8
Sawyer CN, McCarty PL, Parkin GF (1978) Chemistry for environmental engineers. Mc Graw-Hill Book Company, New York
Şener Ş, Şener E, Davraz A (2017) Evaluation of water quality using water quality index (WQI) method and GIS in Aksu River (SW-Turkey). Sci Total Environ 584:131–144. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.scitotenv.2017.01.102
Sharma S (1996) Applied multivariate techniques. Wiley, New York
Simeonov V, Stratis JA, Samara C, Zachariadis G, Voutsa D, Anthemidis A, Sofoniou M, Kouimtzis T (2003) Assessment of the surface water quality in Northern Greece. Water Res 37(17):4119–4124. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0043-1354(03)00398-1
Singh TN (1992) Underground winning of coal. Oxford & IBH Publishing Company
Singh KP, Malik A, Mohan D, Sinha S (2004) Multivariate statistical techniques for the evaluation of spatial and temporal variations in water quality of Gomti River (India)- a case study. Water research 38(18):3980–3992. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.watres.2004.06.011
Singh AK, Mondal GC, Kumar S, Singh TB, Tewary BK, Sinha A (2008) Major ion chemistry, weathering processes and water quality assessment in upper catchment of Damodar River basin, India. Environ Geol 54:745–758. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00254-007-0860-1
Singh SK, Srivastava PK, Singh D, Han D, Gautam SK, Pandey AC (2015) Modeling groundwater quality over a humid subtropical region using numerical indices, earth observation datasets, and X-ray diffraction technique: a case study of Allahabad district, India. Environ Geochem Hlth 37(1):157–180. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10653-014-9638-z
Singh UK, Ramanathan AL, Subramanian V (2018) Groundwater chemistry and human health risk assessment in the mining region of East Singhbhum, Jharkhand, India. Chemosphere 204:501–513. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.chemosphere.2018.04.060
Sonwane DV, Lawande SP, Gaikwad VB, Kamble PN, Kuchekar SR (2009) Studies on ground water quality around Kurkumbh industrial area, Daund, Pune district. Rayasan J Chem 12(2):421–423
Srivastava PK, Han D, Gupta M, Mukherjee S (2012a) Integrated framework for monitoring groundwater pollution using a geographical information system and multivariate analysis. Hydrol Sci J 57(7):1453–1472. https://doi.org/10.1080/02626667.2012.716156
Srivastava PK, Gupta M, Mukherjee S (2012b) Mapping spatial distribution of pollutants in groundwater of a tropical area of India using remote sensing and GIS. Applied Geomatics 4(1):21–32. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12518-011-0072-y
Sun L, Gui H, Peng W (2014) Heavy metals in groundwater from the Wolonghu coal mine, northern Anhui Province, China and their hydrological implications. Water Practice and Technology 9(1):79–87. https://doi.org/10.2166/wpt.2014.009
Syed RQ, Edward MM, Guang Z (2002) Water Works Engineering. Prentice Hall of India Pvt. Ltd, New Delhi
Thakur JK, Singh P, Singh SK, Baghel B (2013) Geochemical modelling of fluoride concentration in hard rock terrain of Madhya Pradesh, India. Acta Geol Sin 87(5):1421–1433. https://doi.org/10.1111/1755-6724.12139
Thapa R, Gupta S, Kaur H (2020) Introducing an irrigation water quality index (IWQI) based on the case study of the Dwarka River basin, Birbhum, West Bengal, India. Sustainable Water Resources Management 6(5):1–10. https://doi.org/10.1007/s40899-020-00450-3
Tirkey P, Bhattacharya T, Chakraborty S, Baraik S (2017) Assessment of groundwater quality and associated health risks: a case study of Ranchi city, Jharkhand, India. Groundw Sustain Dev 5:85–100. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.gsd.2017.05.002
Tiwary RK (2001) Environmental impact of coal mining on water regime and its management. Water Air Soil Pollut 132:185–199. https://doi.org/10.1023/A:1012083519667
Ustaoğlu F, Tepe Y, Taş B (2020) Assessment of stream quality and health risk in a subtropical Turkey river system: A combined approach using statistical analysis and water quality index. Ecol Indic 113:105815. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ecolind.2019.105815
Vutla BMS, Ravichandran S (2011) Groundwater quality and role of the monsoon in Chennai city, South India. Asian J Chem 23(10):4659–4664
Wellen C, Shatilla NJ, Carey SK (2018) The influence of mining on hydrology and solute transport in the Elk Valley, British Columbia. Canada Environ Res Lett 13(07):1–12 https://iopscience.iop.org/article/10.1088/1748-9326/aaca9d/meta
WHO (1998) Guidelines for drinking-water quality (Vol. 2), Health criteria and other supporting information: addendum (No. WHO/EOS/98.1).World Health Organization
WHO (2006) Guideline for drinking-water quality: recommendations, vol 1. World Health Organization, Geneva, p 130
Wu G, de Leeuw J, Skidmore AK, Liu Y, Prins HH (2010) Comparison of extrapolation and interpolation methods for estimating daily photosynthetically active radiation (PAR). Geo-spatial information science 13(4):235–242. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11806-010-0372-0
Younger PL (2001) Mine water pollution in Scotland: nature, extent and preventive strategies. Sci Total Environ 265:309–326. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0048-9697(00)00673-2
Acknowledgements
Authors are extremely grateful to the anonymous referees for their technical comments for the improvement of the manuscript. Birla Institute of Technology (BIT), Mesra, Ranchi, India supported this research, under the Institute research fellowship for Ph.D. programme. Authors are thankful to Central Instrumentation Facility (CIF) of BIT, Mesra to provide Perkin Elmer Optical 2100DV, Inductively Coupled Plasma- Optical Emission Spectroscopy (ICP-OES) instrument for heavy metals analysis. The authors are also grateful to Mr. Jamshed Alam and Mr. Sams Raza for their kind support during the groundwater sample collection in the study area.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Additional information
Responsible Editor: Biswajeet Pradhan
Supplementary Information
ESM 1
(DOCX 22 kb)
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Kumar, A., Krishna, A.P. Groundwater quality assessment using geospatial technique based water quality index (WQI) approach in a coal mining region of India. Arab J Geosci 14, 1126 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12517-021-07474-9
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12517-021-07474-9