Abstract
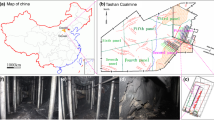
Roof management in coal mines is a critical technology challenge to realize safe production. Dynamic disasters can be induced by a sudden collapse of the roof when encountering a thick hard roof above a coal seam. To solve this problem, directional hydraulic fracturing technology was utilized in the coal mine WP with a thick hard limestone roof. To effectively cut artificial transverse grooves in a fracturing hole in rock with a high strength, the KZ54-type transverse grooving bit was developed. Furthermore, the developed small-aperture high-pressure span-type expansion sealer can effectively seal the holes and ensure hydraulic crack expansion. The field observations show that the radii of extension of the hydraulic fractures were 15–20 m and that the rupture pressure at various depths in the holes ranged from 9 to 32 MPa from the orifice to the bottom of the hole. The deeper the fracturing location in the hole, the higher the fracturing pressure was. The principal stresses in front of the working face and the resistance forces of the hydraulic supports at the working face were monitored when the working face advanced. The first weighting of the roof decreased from 38.3 to 26 m, and the periodic weighting decreased from 26 to 13.7 m. Hydraulic fracturing reduced the resistance force of the supports at the working face.



















Similar content being viewed by others
References
Banerjee G, Ray AK, Singh GSP, Yadava KP (2003) Hard roof management-a key for high productivity in longwall coal mines. J Mines Met Fuels 51(7–8):238–244
Dou LM, He J, Cao AY, Gong SY (2015) Rock burst prevention methods based on theory of dynamic and static combined load induced in coal mine. J China Coal Soc 40(7):1469–1476
Fan J, Dou LM, He H, Du TT, Zhang SB, Gui B, Sun XL (2012) Directional hydraulic fracturing to control hard-roof rockburst in coal mines. Int J Min Sci Technol 22(2):177–181
Hayashi K, Ito T, Abe H (1989) In situ stress determination by hydraulic fracturing-a method employing an artificial notch. Int J Rock Mech Min Sci 26(3–4):197–202. https://doi.org/10.1016/0148-9062(90)95045-3
He H, Dou LM, Fan J, Du TT, Sun XL (2012) Deep-hole directional fracturing of thick hard roof for rockburst prevention. Tunn Undergr Space Technol 32:34–43. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.tust.2012.05.002
He J, Dou LM, Wang SW, Shan CH (2017) Study on mechanism and types of hard roof inducing rock burst. J Mining Saf Eng 34(6):1122–1127
Huang BX, Chen QY, Liu CY, Wei MT, Fu JH (2011) Hydraulic fracturing theory of coal-rock mass and its technical framework. J Mining Safe Eng 28(2):167–173
Huang BX, Yu B, Feng F, Li Z, Wang YZ, Liu JR (2013) Field experimental investigation on directional hydraulic fracturing for hard roof in Tashan coal mine. J Coal Sci Eng (China) 19(2):153–159
Huang BX, Chen SL, Ma J (2014) Method for strong strata behavior control of gob-side entry by hydraulic fracturing. Chinese patent: CN103758570A, 30 April
Huang BX, Chen SL, Zhao XL (2017a) Hydraulic fracturing stress transfer methods to control the strong strata behaviours in gob-side gateroads of longwall mines. Arab J Geosci 10(11):236. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12517-017-3024-y
Huang BX, Zhao XL, Chen SL, Liu JW (2017b) Theory and technology of controlling hard roof with hydraulic fracturing in underground mining. Chin J Rock Mech Eng 36(12):2954–2970
Huang BX, Liu JW, Zhang Q (2018) The reasonable breaking location of overhanging hard roof for directional hydraulic fracturing to control strong strata behaviors of gob-side entry. Int J Rock Mech Min Sci 103:1–11. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijrmms.2018.01.013
Hubbert MK, Willis DG (1957) Mechanics of hydraulic fracturing. Petrol Trans AIME 210:153–166
Jeffrey RG, Mills KW (2000) Hydraulic fracturing applied to inducing longwall coal mine goaf falls. In 4th North American rock mechanics symposium. American Rock Mechanics Association, January
Jin ZM, Xu LS (1994) Control hard roof of mining. Beijing (Chinese): China Coal Industry Publishing House
Ju JF, Xu JL (2013) Structural characteristics of key strata and strata behaviour of a fully mechanized longwall face with 7.0 m height chocks. Int J Rock Mech Min Sci 58:46–54. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijrmms.2012.09.006
Karacan CÖ, Esterhuizen GS, Schatzel SJ, Diamond WP (2007) Reservoir simulation-based modeling for characterizing longwall methane emissions and gob gas venthole production. Int J Coal Geol 71:225–245. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.coal.2006.08.003
Lama RD, Bodziony J (1998) Management of outburst in underground coal mines. Int J Coal Geol 35(1-4):83–115. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0166-5162(97)00037-2
Lekontsev YM, Sazhin PV (2014) Directional hydraulic fracturing in difficult caving roof control and coal degassing. J Min Sci 50(5):914–917. https://doi.org/10.1134/S106273911405010X
Moon JS (2011) Representativeness of jointed rock mass hydraulic conductivity obtained from packer tests for tunnel inflow rate estimate. Int J Rock Mech Min Sci 48(5):836–844. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijrmms.2011.05.001
Sawmliana C, Pal RPA (2012) New blast ability index for hard roof management in blasting gallery method. Geotech Geol Eng 30(6):1357–1367
Wei CC, Zhang CG, Canbulat I, Cao AY, Dou LM (2018) Evaluation of current coal burst control techniques and development of a coal burst management framework. Tunneling Undergr Space Technol 81:129–143. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.tust.2018.07.008
Wu K, Shao ZS, Qin S (2020) An analytical design method for ductile support structures in squeezing tunnels. Arch Civ Mech Eng 20:91. https://doi.org/10.1007/s43452-020-00096-0
Wu K, Shao ZS, Qin S, Wei W, Chu ZF (2021) A critical review on the performance of yielding supports in squeezing tunnels. Tunn Undergr Space Technol 114:103815. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.tust.2021.103815
Ye Q, Jia ZZ, Zheng CS (2017) Study on hydraulic-controlled blasting technology for pressure relief and permeability improvement in a deep hole. J Pet Sci Eng 159:433–442. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.petrol.2017.09.045
Yew CH (1997) Mechanics of hydraulic fracturing. Gulf Publishing Company, Houston, pp 2–4
Yu B, Xia BW, Yu P (2018) Effect of hard roof breaking on gas emission in fully-mechanized sublevel caving mining of extremely thick coal seam. J China Coal Soc 43(8):2243–2249
Zhao XL, Huang BX, Wang Z (2018) Experimental investigation on the basic law of directional hydraulic fracturing controlled by dense linear multi-hole drilling. Rock Mech Rock Eng 51:1739–1754. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00603-018-1439-8
Funding
This investigation acknowledges gratefully for the Young Scientist Fund of the National Natural Science Foundation of China (No. 51804159), the National Key Research and Development Program of China (No. 2017YFC0804205) and Science and Technology Innovation Project of China Coal Technology Engineering (2018MS021).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Responsible Editor: Santanu Banerjee
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Sun, Y., Fu, Y. & Wang, T. Field application of directional hydraulic fracturing technology for controlling thick hard roof: a case study. Arab J Geosci 14, 438 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12517-021-06790-4
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12517-021-06790-4