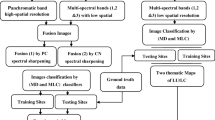
Abstract
Remote sensing plays a significant role in monitoring of the undulating the Himalayas. With continuous monitoring, the preservation of natural resources and mitigation of natural hazards is possible. Currently, satellite sensors are not capable enough to deliver the earth surface image at a very high temporal, spectral, and spatial resolution, simultaneously. Therefore, it is essential to perform the pan-sharpening of spatially high-resolution (HR) panchromatic (PAN) spectral band with low-resolution (LR) multispectral (MS) imagery which must be acquired on the same temporal date from multiple sensors. On the other hand, due to the rugged topography of the Himalayas, topographic effects are generally induced in the form of shadow and affect the spatial information or spectral information. Therefore, the focus of the present work is to implement and analyze the performance of topographic correction on nearest-neighbor diffusion (NND)-based pan-sharpening algorithm. In order to evaluate the effectiveness, K-mean classification (KMC) has been implemented over topographically corrected and topographically uncorrected NND pan-sharpened images. From the experimental outcomes, it is inferred that topographically corrected NND pan-sharpened classified image has achieved better accuracy (81.33%) as compared with topographically uncorrected NND pan-sharpened classified imagery (78%). It is expected that the integration of topographic correction and NND algorithm facilitates the better extraction of spectral and spatial information and leads to improvement in results for further analysis such as change detection procedure and classification. The applications of the present study are in monitoring of climate change and mapping land cover changes over rugged terrain regions.



Similar content being viewed by others
References
Alparone L, Aiazzi B, Baronti S, Garzelli A, Nencini F, Selva M (2008) Multispectral and panchromatic data fusion assessment without reference. Photogramm Eng Remote Sens 74(2):193–200. https://doi.org/10.14358/pers.74.2.193
Amro I, Mateos J, Vega M, Molina R, Katsaggelos AK (2011) A survey of classical methods and new trends in pansharpening of multispectral images. EURASIP J Adv Sign Process 2011(1):79. https://doi.org/10.1186/1687-6180-2011-79
Choi J, Yu K, Kim Y (2010) A new adaptive component-substitution-based satellite image fusion by using partial replacement. IEEE Trans Geosci Remote Sens 49(1):295–309. https://doi.org/10.1109/TGRS.2010.2051674
Choi J, Park H, Seo D (2019) Pansharpening using guided filtering to improve the spatial clarity of VHR satellite imagery. Remote Sens 11(6):633. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs11060633
Cliche F (1985) Integration of the SPOT panchromatic channel into its multispectral mode for image sharpness enhancement. PE & RS 51(3):311–316. https://doi.org/10.1016/0034-4257(87)90049-6
Congalton RG (1991) A review of assessing the accuracy of classifications of remotely sensed data. Remote Sens Environ 37(1):35–46. https://doi.org/10.1016/0034-4257(91)90048-B
Garzelli A, Nencini F, Capobianco L (2007) Optimal MMSE pan sharpening of very high-resolution multispectral images. IEEE Trans Geosci Remote Sens 46(1):228–236. https://doi.org/10.1109/TGRS.2007.907604
González-Audícana M, Saleta JL, Catalán RG, García R (2004) Fusion of multispectral and panchromatic images using improved IHS and PCA mergers based on wavelet decomposition. IEEE Trans Geosci Remote Sens 42(6):1291–1299. https://doi.org/10.1109/TGRS.2004.825593
Gusain HS, Singh A, Ganju A Singh D (2004) Characteristics of the seasonal snow cover of Pir Panjal and Great Himalayan ranges in Indian Himalaya. Proceedings ISSMA-2004, Manali, pp.97-102
Jensen JR (2009) Remote sensing of the environment: An earth resource perspective 2nd Edn. Pearson Education India, pp. 45
Kahraman S, Ertürk A (2017) A comprehensive review of pansharpening algorithms for GÖKTÜRK-2 satellite images. ISPRS Ann Photogramm Remote Sens Spat Inform Sci 4:263–270. https://doi.org/10.5194/isprs-annals-IV-4-W4-263-2017
Khajoue M, Nikrouz R, Goudarzi A (2018) Application of undecimated discrete wavelet transforms (UDWT) for seismic refraction velocity analysis improvement. Arab J Geosci 11(11):245. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12517-018-3539-x
Kim Y, Lee C, Han D, Kim Y, Kim Y (2010) Improved additive-wavelet image fusion. IEEE Geosci Remote Sens Lett 8(2):263–267. https://doi.org/10.1109/LGRS.2010.2067192
Laben CA, Brower BV, Eastman Kodak Co (2000) Process for enhancing the spatial resolution of multispectral imagery using pan-sharpening. US Patent 6,011,875
Mishra VD, Sharma JK, Khanna R (2010) Review of topographic analysis methods for the western Himalaya using AWiFS and MODIS satellite imagery. Ann Glaciol 51(54):153–160. https://doi.org/10.3189/172756410791386526
Nichol J, Hang LK, Sing WM (2006) Empirical correction of low Sun angle images in steeply sloping terrain: a slope-matching technique. Int J Remote Sens 27(3):629–635. https://doi.org/10.1080/02781070500293414
Schott JR (2007) Remote sensing: the image chain approach. Oxford University Press, New York, pp. 549–555
Simhachalam B, Ganesan G (2016) Performance comparison of fuzzy and non-fuzzy classification methods. Egypt Inf J 17(2):183–188. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.eij.2015.10.004
Singh S, Talwar R (2015) A quantitative analysis of different change detection algorithms over rugged terrain MODIS sensor satellite imagery. In 2015 international conference on signal processing and communication (ICSC) (pp. 273-278). IEEE. https://doi.org/10.1109/ICSPCom.2015.7150661
Singh S, Talwar R (2017) Response of fuzzy clustering on different threshold determination algorithms in spectral change vector analysis over Western Himalaya, India. J Mt Sci 14(7):1391–1404. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11629-016-4248-0
Singh S, Talwar R (2018) An intercomparison of different topography effects on discrimination performance of fuzzy change vector analysis algorithm. Meteorog Atmos Phys 130(1):125–136. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00703-016-0494-5
Singh S, Sood V, Kaur R (2016) A comparative analysis of different topographic corrections over North Indian Himalayan. In 2016 5th International Conference on Wireless Networks and Embedded Systems (WECON) (pp. 1-5). IEEE. https://doi.org/10.1109/WECON.2016.7993490
Singh S, Sood V, Kaur R, Prashar S (2019) An efficient algorithm for detection of seasonal snow cover variations over undulating North Indian Himalayas, India. Adv Space Res 64(2):314–327. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.asr.2019.04.016
Snehmani, Gore, A., Ganju, A., Kumar, S. and Srivastava, P.K., 2017. A comparative analysis of pansharpening techniques on QuickBird and WorldView-3 images. Geocarto Int, 32(11), pp.1268–1284. https://doi.org/10.1080/10106049.2016.1206627
Sood V, Singh S (2018) Analytical analysis of different shadow removing algorithms over land-use 1 and land-cover classification. Himal Geol 39(2):223–232
Sood V, Gupta S, Gusain HS, Singh S (2018) Spatial and quantitative comparison of topographically derived different classification algorithms using AWiFS data over Himalayas, India. J Indian Soc Remote Sens 46(12):1991–2002. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12524-018-0861-4
Sood V, Gupta S, Gusain HS, Singh S (2019) Performance assessment of different topographic correction techniques over subpixel classification. In 2019 Fifth International Conference on Image Information Processing (ICIIP) (pp. 536-541). IEEE, https://doi.org/10.1109/ICIIP47207.2019.8985790
Sun W, Chen B, Messinger D (2014) Nearest-neighbor diffusion-based pan-sharpening algorithm for spectral images. Opt Eng 53(1):013107. https://doi.org/10.1117/1.OE.53.1.013107
Tu TM, Huang PS, Hung CL, Chang CP (2004) A fast intensity-hue-saturation fusion technique with spectral adjustment for IKONOS imagery. IEEE Geosci Remote Sens Lett 1(4):309–312. https://doi.org/10.1109/LGRS.2004.834804
Vivone G, Alparone L, Chanussot J, Dalla Mura M, Garzelli A, Licciardi GA, Restaino R, Wald L (2014) A critical comparison among pansharpening algorithms. IEEE Trans Geosci Remote Sens 53(5):2565–2586. https://doi.org/10.1109/TGRS.2014.2361734
Wang Z, Ziou D, Armenakis C, Li D, Li Q (2005) A comparative analysis of image fusion methods. IEEE Trans Geosci Remote Sens 43(6):1391–1402. https://doi.org/10.1109/TGRS.2005.846874
Wong FH, Orth R (1980) Registration of SEASAT/LANDSAT composite images to UTM coordinates. In International Symposium on Remote Sensing of Environment, 14 th, San Jose, Costa Rica, pp. 1841-1847
Zhang J (2010) Multi-source remote sensing data fusion: status and trends. Int J Image Data Fusion 1(1):5–24. https://doi.org/10.1080/19479830903561035
Zhang N, Wu Q (2008). Effects of Brovey transform and wavelet transform on the information capacity of SPOT-5 imagery. In International Symposium on Photoelectronic Detection and Imaging 2007: Image Processing (Vol. 6623, p. 66230W). International Society for Optics and Photonics. https://doi.org/10.1117/12.791423
Zhao J, Huang L, Yang H, Zhang D, Wu Z, Guo J (2016) Fusion and assessment of high-resolution WorldView-3 satellite imagery using NNDiffuse and Brovey algorithms. In 2016 IEEE International Geoscience and Remote Sensing Symposium (IGARSS) (pp. 2606–2609). https://doi.org/10.1109/IGARSS.2016.7729673
Acknowledgements
We greatly appreciate the constructive comments and valuable suggestions from the anonymous reviewers and editor to improve the earlier version of the manuscript. We would like to thank the National Remote Sensing (NRSC), ISRO, for their great efforts in developing and distributing remotely sensed AWiFS satellite data via online portal (https://bhuvan.nrsc.gov.in/). Thanks are also due to United States Geological Survey (USGS) and NASA for providing ASTER Global DEM and MODIS data via website (https://earthexplorer.usgs.gov/).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Additional information
Responsible Editor: Mahesh Kumar Jat
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Singh, S., Sood, V., Prashar, S. et al. Response of topographic control on nearest-neighbor diffusion-based pan-sharpening using multispectral MODIS and AWiFS satellite dataset. Arab J Geosci 13, 668 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12517-020-05686-z
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12517-020-05686-z