Abstract
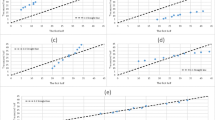
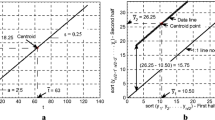
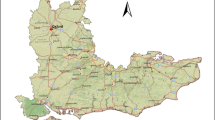
In this study, based on the Şen innovative trend analysis (ITA) method, another approach has been developed as innovative triangular trend analysis (ITTA), which helps to identify partial trends within a given time series comparatively with each other. The basis of this methodology is to divide a given time series into a set of equal length sub-series and then to compare them pairwise in the form of a triangular array. In this manner, the trends within the whole series can be identified separately in detail. Consequently, it is possible to make much more realistic assessments depending on these trends. The application of the proposed method is carried out by considering the longest annual rainfall measurement records from 1966 to 2015, inclusive for İstanbul, Rize, and Ankara provinces in Turkey. As a result, generally monotonically a negative trend in Ankara, no trend in Florya, and positive trend in Rize are determined by ITA methodology. On the other hand, instability of trends in time series is presented for these stations. Ankara has negative and no trend to the first 10 years and the last 20 years, respectively. Florya has successively positive and negative trends from the first to fifth part. As for Rize, according to ITTA, it has generally positive trends.





Similar content being viewed by others
References
Ahmad I, Zhang F, Tayyab M, Anjum MN, Zaman M, Liu J, Farid HU, Saddique Q (2018) Spatiotemporal analysis of precipitation variability in annual, seasonal and extreme values over upper Indus River basin. Atmos Res 213:346–360
Alashan S (2018) An improved version of innovative trend analyses. Arab J Geosci 11(3):50
Caloiero T (2018) SPI trend analysis of New Zealand applying the ITA technique. Geosciences 8(3):101
Caloiero T, Coscarelli R, Ferrari E (2018) Application of the innovative trend analysis method for the trend analysis of rainfall anomalies in southern Italy. Water Resour Manag 32(15):4971–4983
Chowdhury RK, Beecham S, Boland J, Piantadosi J (2015) Understanding South Australian rainfall trends and step changes. Int J Climatol 35(3):348–360
Cui L, Wang L, Lai Z, Tian Q, Liu W, Li J (2017) Innovative trend analysis of annual and seasonal air temperature and rainfall in the Yangtze River Basin, China during 1960–2015. J Atmos Sol Terr Phys 164:48–59
Dabanlı İ, Şen Z, Yeleğen MÖ, Şişman E, Selek B, Güçlü YS (2016) Trend assessment by the innovative-Şen method. Water Resour Manag 30(14):5193–5203
Denizolgun FS, Güçlü YS, Şen Z (2018) Kuzey Marmara Otoyolunda dere köprüsü tasarımı ve uygulaması: Alemdağ dere köprüsü örneği. Balıkesir Üniversitesi Fen Bilimleri Enstitüsü Dergisi 20(2):72–88
Douglas EB, Vogel RM, Knoll CN (2000) Trends in floods and low flows in the United States: impact of serial correlation. J Hydrol 240:90–105
Elouissi A, Şen Z, Habi M (2016) Algerian rainfall innovative trend analysis and its implications to Macta watershed. Arab J Geosci 9(4):303
Gedefaw M, Wang H, Yan D, Song X, Yan D, Dong G, Wang J, Girma A, Ali BA, Batsuren D, Abiyu A, Qin T (2018) Trend analysis of climatic and hydrological variables in the Awash River Basin, Ethiopia. Water 10:1554
Gocic M, Trajkovic S (2013) Analysis of changes in meteorological variables using Mann-Kendall and Sen’s slope estimator statistical tests in Serbia. Glob Planet Chang 100:172–182
Güçlü YS (2018a) Alternative trend analysis: half time series methodology. Water Resour Manag 32(7):2489–2504
Güçlü YS (2018b) Multiple Şen-innovative trend analyses and partial Mann-Kendall test. J Hydrol 566:685–704
Güçlü YS, Dabanlı İ, Şişman E, Şen Z (2019) Air quality (AQ) identification by innovative trend diagram and AQ index combinations in Istanbul megacity. Atmospheric Pollution Research 10(1):88–96
Haan CT (1977) Statistical methods in hydrology. Iowa State University Press, Iowa
Haktanir T, Citakoglu H (2014) Trend, independence, stationarity, and homogeneity tests on maximum rainfall series of standard durations recorded in Turkey. J Hydrol Eng 19(9):05014009
Hosseinzadeh Talaee P, Tabari H, Abghari H (2013) Pan evaporation and reference evapotranspiration trend detection in western Iran with consideration of data persistence. Hydrol Res 45(2):213–225
Kendall MG (1975) Rank correlation method, 4th edition. Charless Griffin, London
Khan N, Shahid S, Ismail T, Ahmed K, Nawaz N (2018) Trends in heat wave related indices in Pakistan. In: Stochastic Environmental Research and Risk Assessment. Springer, New York LLC. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00477-018-1605-2
Li J, Zhu Z, Dong W (2017) Assessing the uncertainty of CESM-LE in simulating the trends of mean and extreme temperature and precipitation over China. Int J Climatol 37(4):2101–2110
Mann HB (1945) Nonparametric test against trend. Econometrica 13(3):245–259
Markus M, Demissie M, Short MB, Verma S, Cooke RA (2013) Sensitivity analysis of annual nitrate loads and the corresponding trends in the lower Illinois River. J Hydrol Eng 19(3):533–543
Martínez-Austria PF, Bandala ER, Patiño-Gómez C (2016) Temperature and heat wave trends in northwest Mexico. Physics and Chemistry of the Earth, Parts A/B/C 91:20–26
Matalas NC, Sankarasubramanian A (2003) Effect of persistence on trend detection via regression. Water Resour Res 39(12):WR002292
Mohorji AM, Şen Z, Almazroui M (2017) Trend analyses revision and global monthly temperature innovative multi-duration analysis. Earth Syst Environment 1(1):9
Onyutha C (2016) Identification of sub-trends from hydro-meteorological series. Stoch Env Res Risk A 30(1):189–205
Öztopal A, Şen Z (2017) Innovative trend methodology applications to precipitation records in Turkey. Water Resour Manag 31(3):727–737
Pingale SM, Khare D, Jat MK, Adamowski J (2014) Spatial and temporal trends of mean and extreme rainfall and temperature for the 33 urban centers of the arid and semi-arid state of Rajasthan, India. Atmos Res 138:73–90
Sen PK (1968) Estimates of the regression coefficient based on Kendall’s tau. J Am Stat Assoc 63:1379–1389
Şen Z (2012) Innovative trend analysis methodology. J Hydrol Eng 17(9):1042–1046
Şen Z (2013) Trend identification simulation and application. J Hydrol Eng 19(3):635–642
Şen Z (2017a) Hydrological trend analysis with innovative and over-whitening procedures. Hydrol Sci J 62(2):294–305
Şen Z (2017b) Innovative trend methodologies in science and engineering. Springer, Heidelberg, Germany, p 349
Tabari H, Willems P (2015) Investigation of streamflow variation using an innovative trend analysis approach in Northwest Iran. The 36th IAHR World Congress, 28 June–3 July, 2015, The Hague, the Netherlands
Von Storch H (1995) Misuses of statistical analysis in climate research. In: Analysis of climate variability: applications of statistical techniques (ed. by H. von Storch & A. Navara), 11–26. Springer-Verlag, Berlin, Germany
Wu H, Qian H (2017) Innovative trend analysis of annual and seasonal rainfall and extreme values in Shaanxi, China, since the 1950s. Int J Climatol 37(5):2582–2592
Yang P, Xia J, Zhang Y, Hong S (2017) Temporal and spatial variations of precipitation in Northwest China during 1960–2013. Atmos Res 183:283–295
Yue S, Pilon P, Phinney B, Cavadias G (2002) The influence of autocorrelation on the ability to detect trend in hydrological series. Hydrol Process 16:1807–1829
Zang C, Liu J (2013) Trend analysis for the flows of green and blue water in the Heihe River basin, northwestern China. J Hydrol 502:27–36
Zhang X, Harvey KD, Hogg WD, Yuzyk TR (2001) Trends in Canadian streamflow. Water Resour Res 37(4):987–998
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Responsible Editor: Huakun Zhou
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Güçlü, Y.S., Şişman, E. & Dabanlı, İ. Innovative triangular trend analysis. Arab J Geosci 13, 27 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12517-019-5048-y
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12517-019-5048-y