Abstract
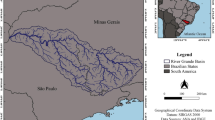
The response of a watershed to produce runoff after rain event depends on the characteristics of the basin. This characteristic is peculiar to every basin and varies depending on the type of rock, geology, soil, climatic belt, and extent of anthropogenic activities. Information regarding these controlling factors is vital for a sustainable management of the basin. However, many of the watersheds especially in the developing world lack the basic facilities for acquiring the runoff data or other basin’s response to rainfall event like sediment yield. The simplest approach to obtaining such information is via the morphometric parameters of the basin. This necessitated the need for this study. The study carried out a morphometric analysis of the Idemili Basin in southeastern Nigeria by employing geospatial tools in ArcMap to investigate the basin’s characteristics. The basin is a fourth-order basin with a rectilinear drainage pattern. The shape parameters indicate a pear-shaped basin. The mean bifurcation ratio indicates the basin developed in a hilly terrain with somewhat geologic influences over time as it developed on a weak, porous sandstone. Intensive watershed management is needed in the basin to ensure the sustainability of the basin and its ecosystem. The study also demonstrates that geospatial techniques and the digital elevation model are vital tools for watershed characterisation especially in data-scarce regions.






Similar content being viewed by others
Change history
26 April 2019
The authors wish update Tables 1 and 2 due to few minor corrections to make due to oversight. The corrections were emphasized as bold.
References
Bagyaraj M, Gurugnanam B, Nagar A (2011) Significance of morphometry studies, soil characteristics, erosion phenomena and landform processes using remote sensing and GIS for Kodaikanal Hills, a global biodiversity hotpot in Western Ghats, Dindigul District, Tamil Nadu, South India. Res J Environ Earth Sci 3:221–233
Biswas A, Majumdar DD, Banerjee S (2014) Morphometry governs the dynamics of a drainage basin: analysis and implications. Geogr J 2014:1–14
Danielson T (2013) Utilizing a high resolution Digital Elevation Model (DEM) to develop a Stream Power Index (SPI) for the Gilmore creek watershed in Winona County, Minnesota. In: Papers in resource analysis, vol 15. Saint Marys University of Minnesota University Central Services Press, Winona, pp 1–11
Doornkamp JC, King CA (1971) Numerical analysis in geomorphology-an introduction. Edwardand Arnold, London, pp 3–20
Farhan Y (2017) Morphometric assessment of Wadi Wala Watershed, Southern Jordan using ASTER (DEM) and GIS. J Geogr Inf Syst 9:158–190
Giusti EV, Schneider WJ (1965) The distribution of branches in river networks. Professional paper, United States Geological Survey, Washington DC, pp 1–422
Gregory K, Walling D (1968) The variation of drainage density within a catchment. Hydrol Sci J 13:61–68
Gundekar H, Arya D, Goel° N (2011) Morphometric study of the Dudhana river basin(Maharashtra). Hydrol J 34:33–41
Horacio J (2014) River sinuosity index: geomorphological characterisation. Technical note 2. CIREF and Wetlands International, Ede, p 6
Horton RE (1932) Drainage-basin characteristics. EOS Trans Am Geophys Union 13:350–361
Horton RE (1945) Erosional development of streams and their drainage basins; hydrophysical approach to quantitative morphology. Geol Soc Am Bull 56:275–370
Howe GM, Slaymaker HO, Harding DM (1966) Flood hazard in mid-Wales. Nature 212(5062):584–585
Ifeka A, Akinbobola A (2015) Trend analysis of precipitation in some selected stations in Anambra State. Atmos Clim Sci 5:1–12
Igwe C (2012) Gully erosion in southeastern Nigeria: role of soil properties and environmental factors. In: Godone D, Stanchi S (eds) Research on soil erosion. IntechOpen. https://doi.org/10.5772/51020
Jain S, Seth S, Nema R (1995) Morphometric analysis of Sei dam catchment using GIS. Proceedings of National Symposium on Hydrology, Jaipur, 5–7
Kirchner JW (1993) Statistical inevitability of Horton’s laws and the apparent randomness of stream channel networks. Geology 21:591–594
Kumar V (2011) Elongation ratio. In: Singh VP, Singh P, Haritashya UK (eds) Encyclopedia of snow, ice and glaciers. Springer Netherlands, Dordrecht, p 1232
Miller, V. C. (1953) A quantitative geomorphic study of drainage basin characteristics in the Clinch mountain areas. USA, Technical Report, Columbia University, Department of Geology, Issue 3, p.51
Moeini A, Zarandi NK, Pazira E, Badiollahi Y (2015) The relationship between drainage density and soil erosion rate: a study of five watersheds in Ardebil Province, Iran. WIT Trans Ecol Environ 1:129–138
Ofomata GEK (1987) Soil erosion in Nigeria: the views of a geomorphologist. University of Nigeria Press, p 42
Rao NK, Latha SP, Kumar AP, Krishna HM (2010) Morphometric analysis of Gostani River basin in Andhra Pradesh state, India using Spatial information technology. Intl J Geomat Geosci 1(2):179–187
Ratnam KN, Srivastava Y, Rao VV, Amminedu E, Murthy K (2005) Check dam positioning by prioritization of micro-watersheds using SYI model and morphometric analysis—remote sensing and GIS perspective. J Indian Soc Remote Sens 33:25–38
Schumm SA (1956) Evolution of drainage systems and slopes in badlands at Perth Amboy, New Jersey. Geol Soc Am Bull 67:597–646
Selby M (1989) Fluvial forms and processes. By David Knighton. N Z Geogr 45:96–96
Sreedevi PD, Subrahmanyan K, Ahmed S (2004) The significance of morphometric analysis for obtaining groundwater potential zones in a structurally controlled terrain. Environ Geology 47:412-420
Strahler AN (1957) Quantitative analysis of watershed geomorphology. EOS Trans Am Geophys Union 38:913–920
Strahler AN (1964) Quantitative geomorphology of drainage basin and channel networks. In: Chow V (ed) Handbook of applied hydrology. McGraw Hill, New York, pp 439–476
Udo RK (1975) Geogrpahical regions of Nigeria. Heinemann Educational Press Ltd, London
Verstappen HT (1983) Applied geomorphology: geomorphological surveys for environmental development. Elsevier, Amsterdam, p 437
Yunus AP, Oguchi T, Hayakawa YS (2014) Morphometric analysis of drainage basins in the Western Arabian Peninsula using multivariate statistics. Int J Geosci 5:527–539
Zavoiance I (1985) Morphometry of drainage basins (developments in water science), vol 20. Elsevier, New York, pp 1–251
Zavoianu I (2011) Morphometry of drainage basins (developments in water science). Elsevier, Amsterdam, p 237
Zhang L, Guilbert E (2012) A study of variables characterizing drainage patterns in river networks. ISPRS 39:B2
Acknowledgements
Many thanks go to my supervisor, Mr. A. T. Mozie, for his guidance throughout the duration of the project from which this piece is a product.
Funding
The NsukkaUSA Inc. is highly appreciated for financially supporting the project.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Editorial handling: Biswajeet Pradhan
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Ezeh, C.U., Mozie, A.T. Morphometric analysis of the Idemili Basin using geospatial techniques. Arab J Geosci 12, 208 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12517-019-4336-x
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12517-019-4336-x