Abstract
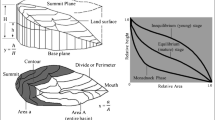
In this paper, the hypsometric curves and integrals of four neighboring micro-watersheds draining into Patiala-Ki-Rao stream which is situated in the Shivalik foothills of district SAS Nagar in the Punjab state (India) has been presented to access and compare the erosion regimes under different management practices. Area-elevation ratio method has been used to compute hypsometric curve and integral values for each micro-watershed through ArcGIS 10.3 and Microsoft Excel. The 9-year data of runoff and sediment yield for all these micro-watersheds under different management practices has been analyzed for their effect on land cover and soil quality. Thus, the results of present study are very useful for comparing, planning, implementing, and controlling soil erosion in similar watersheds.








Similar content being viewed by others
References
Awasthi KD, Sitaula BK, Singh BR, Bajacharaya RM (2002) Land-use changes in two Nepalese watersheds: GIS and geomorphometric analysis. Land Degrad Dev 13:495513
El-Swaify SA (1997) Factors affecting soil erosion hazards and conservation needs for tropical steeplands. Soil Technol 11(1):3–16
Golekar RB, Baride MV, Patil SN, Adil SH (2015) Altimetric and hypsometric analysis for soil and water conservation: a case study of Anjani and Jhiri river basin, Northern Maharashtra, India. Earth Sci Res J 19(1):51–58
Hurtrez JE, Lucazean F, Lave J, Avouac JP (1999) Investigation of the relationship between basin morphology, tectonic uplift and denudation from the study of an active fold belt in Siwalik hills (Central Nepal). J Geophys Res 104:779–796
Langbein WB (1947) Topographic characteristics of drainage basins. US Geol. Survey, Water Supply Paper, 968C, 125–155
Ozkaymak C, Sozbilir H (2012) Tectonic geomorphology of the Spildağı high ranges, western Anatolia. Geomorphology 173–174:128–140. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.geomorph.2012.06.003
Perez-Pena JV, Azanon JM, Azor A (2009) CalHypso: an ArcGIS extension to calculate hypsometric curves and their statistical moments applications to drainage basin analysis SE Spain. Comput Geosci 35:1214–1223
Raj R, Maurya DM, Chamyal LS (1999) Tectonic geomorphology of the Mahi river basin, Western India. J Geol Soc India 54:387–398
Ritter DF, Kochel RC, Miller IR (2002) Process geomorphology. McGraw Hill, Boston
Schumn SA (1956) Evolution of drainage systems and slopes in badlands at Perth Amboy, New Jersey. Geol Soc Am Bull 67(5):597–646
Stoddart DR (1969) Ecology and morphology of recent coral reefs. Biol Rev 44(4):433–498
Strahler AN (1952) Hypsometric (area-altitude) analysis of erosional topology. Geol Soc Am Bull 63(11):1117–1142
Tiwari AK, Risse LM, Nearing MA (2000) Evaluation of WEPP and its comparison with USLE and RUSLE. Trans ASAE 43(5):1129–1135
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Walia, S., Singh, S., Loshali, D.C. et al. Hypsometric analysis of the micro-watersheds with different management practices located on Shivalik foothills. Arab J Geosci 11, 276 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12517-018-3637-9
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12517-018-3637-9