Abstract
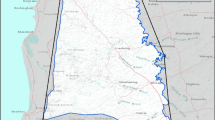
Lake Urmia, located in northwest Iran, contains a number of wetlands significantly affecting the environmental, social, and economic conditions of the region. The ecological condition of Lake Urmia has degraded during the past decade, due to climate change, human activities, and unsustainable management. The poor condition of the lake has also affected the surrounding wetlands. This study analyzes the land cover change of one of the wetlands in the southern part of Lake Urmia, known as Ghara-Gheshlagh wetland, in the period 1989–2015 using post-classification change detection and machine learning image classification. For this analysis, three Landsat images, acquired in 1989 (TM), 2001 (TM), and 2015 (Landsat-8), were used for the classification and change detection. Support vector machine learning algorithm, a supervised learning method, is employed, and images are classified into four main land cover classes namely “water,” ”barren,” “salty land,” and “agriculture and grassland.” Change detection was carried out for pairs of years 1989 to 2001 and 2001 until 2015. The results of this classification show that there is a sharp increase in the area of salt-saturated land as well as a decrease in the area of water resources. Overall classification accuracy obtained were high for the individual years: 1989 (91.48%), 2001 (90.63%), and 2015 (88.6%). Also, the Kappa coefficients for individual maps were high: 1989 (0.89), 2001 (0.8742), and 2015 (0.84). After that, the land cover change map of the study area is obtained between 1989 to 2001 and then 2001 to 2015. The results of this analysis suggest that more efforts should be taken to effectively manage water resources in the region and point to potential locations for focused management actions within the wetland area.









Similar content being viewed by others
References
Almutairi A, Warner TA (2010) Change detection accuracy and image properties: a study using simulated data. Remote Sens 2:1508–1529
Alphan H (2003) Land-use change and urbanization of Adana, Turkey. Land degradation Development 14:575–586
Alphan H, Doygun H, Unlukaplan YI (2009) Post-classification comparison of land cover using multitemporal Landsat and ASTER imagery: the case of Kahramanmaraş, Turkey. Environ Monit Assess 151:327–336
Anthony G, Greg H, Tshilidzi M (2007) Classification of images using support vector machines. arXiv preprint arXiv 0709:3967
Bhatta B, Saraswati S, Bandyopadhyay D (2010) Quantifying the degree-of-freedom, degree-of-sprawl, and degree-of-goodness of urban growth from remote sensing data. Appl Geogr 30:96–111
Coppin P, Jonckheere I, Nackaerts K, Muys B, Lambin E (2004) Review ArticleDigital change detection methods in ecosystem monitoring: a review. Int J Remote Sens 25:1565–1596
Cortes C, Vapnik V (1995) Support-vector networks. Mach Learn 20:273–297
Deng JS, Qiu LF, Wang K, Yang H, Shi YY (2011) An integrated analysis of urbanization-triggered cropland loss trajectory and implications for sustainable land management. Cities 28:127–137
Dewan AM, Yamaguchi Y (2009) Land use and land cover change in Greater Dhaka, Bangladesh: using remote sensing to promote sustainable urbanization. Appl Geogr 29:390–401
El-Hattab MM (2016) Applying post classification change detection technique to monitor an Egyptian coastal zone (Abu Qir Bay). Egyptian J Remote Sensing Space Sci 19:23–36
Foody GM, Mathur A (2004) A relative evaluation of multiclass image classification by support vector machines. Geoscience Remote Sensing, IEEE Transactions on 42:1335–1343
de Freitas MWD, Dos Santos JR, Alves DS (2013) Land-use and land-cover change processes in the Upper Uruguay Basin: linking environmental and socioeconomic variables. Landsc Ecol 28:311–327
Griffiths P, Hostert P, Gruebner O, Der Linden SV (2010) Mapping megacity growth with multi-sensor data. Remote Sens Environ 114:426–439
Howarth PJ, Wickware GM (1981) Procedures for change detection using Landsat digital data. Int J Remote Sens 2:277–291
Hsu C-W, Lin C-J (2002) A comparison of methods for multiclass support vector machines. Neural Networks, IEEE Transactions on 13:415–425
J. R. Jensen, Introductory digital image processing: a remote sensing perspective: Prentice-Hall Inc., 1996
Lambin EF, Geist HJ, Lepers E (2003) Dynamics of land-use and land-cover change in tropical regions. Annu Rev Environ Resour 28:205–241
Lu D, Mausel P, Brondizio E, Moran E (2004) Change detection techniques. Int J Remote Sens 25:2365–2401
M. E. Assessment (2005) Ecosystems and human well-being: wetlands and water. World Resources Institute, Washington, DC
Maimaitijiang M, Ghulam A, Sandoval JO, Maimaitiyiming M (2015) Drivers of land cover and land use changes in St. Louis metropolitan area over the past 40 years characterized by remote sensing and census population data. Int J Appl Earth Obs Geoinf 35:161–174
Melgani F, Bruzzone L (2004) Classification of hyperspectral remote sensing images with support vector machines. Geoscience Remote Sensing, IEEE Transactions on 42:1778–1790
Mountrakis G, Im J, Ogole C (2011) Support vector machines in remote sensing: a review. ISPRS J Photogramm Remote Sens 66:247–259
Peiman R (2011) Pre-classification and post-classification change-detection techniques to monitor land-cover and land-use change using multi-temporal Landsat imagery: a case study on Pisa Province in Italy. Int J Remote Sens 32:4365–4381
Riebsame WE, Meyer WB, Turner BL II (1994) Modeling land use and cover as part of global environmental change. Clim Chang 28:45–64
Singh A (1989) Review article digital change detection techniques using remotely-sensed data. Int J Remote Sens 10:989–1003
Squires GD, Friedman S, Saidat CE (2002) Experiencing residential segregation a contemporary study of Washington, DC. Urban Aff Rev 38:155–183
Su W, Gu C, Yang G, Chen S, Zhen F (2010) Measuring the impact of urban sprawl on natural landscape pattern of the western Taihu Lake watershed, China. Landsc Urban Plan 95:61–67
Tan M, Li X, Xie H, Lu C (2005) Urban land expansion and arable land loss in China—a case study of Beijing–Tianjin–Hebei region. Land Use Policy 22:187–196
Tu J (2013) Spatial variations in the relationships between land use and water quality across an urbanization gradient in the watersheds of northern Georgia, USA. Environ Manag 51:1–17
V. Vapnik, The nature of statistical learning theory Springer Sci Business Media, 2013
Wampler P (2011) Pick sanitation over vaccination in Haiti. Nature 470:175–175
Wampler PJ, Sisson AJ (2011) Spring flow, bacterial contamination, and water resources in rural Haiti. Environ Earth Sci 62:1619–1628
Wu H, Ye L-P, Shi W-Z, Clarke KC (2014) Assessing the effects of land use spatial structure on urban heat islands using HJ-1B remote sensing imagery in Wuhan, China. Int J Appl Earth Obs Geoinf 32:67–78
Wu C, Du B, Cui X, Zhang L (2017) A post-classification change detection method based on iterative slow feature analysis and Bayesian soft fusion. Remote Sens Environ 199:241–255
Xian G, Crane M (2005) Assessments of urban growth in the Tampa Bay watershed using remote sensing data. Remote Sens Environ 97:203–215
Xian G, Crane M (2006) An analysis of urban thermal characteristics and associated land cover in Tampa Bay and Las Vegas using Landsat satellite data. Remote Sens Environ 104:147–156
Zarghami M (2011) Effective watershed management; case study of Urmia Lake, Iran. Lake Reservoir Management 27:87–94
Zhang B-P, Yao Y-H, Cheng W-M, Zhou C, Lu Z, Chen X et al (2002) Human-induced changes to biodiversity and alpine pastureland in the Bayanbulak region of the East Tienshan Mountains. Mt Res Dev 22:383–389
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Ojaghi, S., Farnood Ahmadi, F., Ebadi, H. et al. Wetland cover change detection using multi-temporal remotely sensed data. Arab J Geosci 10, 470 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12517-017-3239-y
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12517-017-3239-y