Abstract
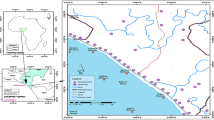
A lack of understanding exists of the origin and textural characteristics of Saudi Arabian Red Sea coastal sediments. This paper concerns the southern coastline of Jizan on the Saudi Red Sea. It is some 160 km long characterised by either narrow rocky headlands with intermittent pocket beaches or wide low-lying beaches dissected by wadis. Granulometric testing of samples from 135 locations showed that beach sand size was mainly very fine to medium grained (M z = 3.93 Ø), sorting ranged from 1.65 to 0.41 and skewness values from −051 to 0.39, being mainly negative; dune sands were medium to fine grained (M z = 1.13 Ø; average sorting 2.8), while skewness variations within dune samples indicated symmetrical to fine skewed values (б Ι = 0.55 to 0.89). Most foreshore samples were derived from wadis. Wadi mud levels can be high, e.g. Baysh (84%), and wadi Samrah (90%) with mean grain size ranging from very fine to medium sand (M z = 3.9 Ø), sorting being well to poor (0.45 to 1.52) due to sediment influxes. Sabkha had a wide range of sand/mud and significantly higher carbonate percentages than other environments. Sediment source differences and littoral reworking contributed to grain size variation. The carbonate content varied between 1.5 and 31.5% due to hinterland contributions, and spatial analysis showed increasing quantities of carbonate minerals towards the south. On the wider geographical front, findings from Jizan are similar to those of the Northern United Arab Emirates (UAE), including sabkhas, being composed of sand, skeletal carbonate, fine fluvial material and wind-blown silt and clay components of wadi origin. Further work on the northeastern Red Sea edge can hopefully confirm these findings.








Similar content being viewed by others
References
Abou Ouf MA, El Shater A (1992) Sedimentology and mineralogy of Jizan shelf sediments, Red Sea, Saudi Arabia. JKAU: Mar Sci 3:39–54
AbouOuf M, Durgaprasada Rao NVN, Tag RJ (1988) Benthic foraminifera from littoral sediments of Al Lith—Al Qunfidah coast, south eastern Red Sea. Indian Journal of Marine Sciences 17(3):217–221
Alcántara-Carrió J, Fernández-Bastero S, Alonso I (2010) Source area determination of aeolian sediments at Jandia Isthmus (Fuerteventura, Canary Islands). J Mar Syst 80(3):219–234
Al-Farraj A (2005) An evolutionary model for sabkha development on the north coast of the UAE. J Arid Environ 63(4):740–755
Alharbi OA, Philips MR, Williams AT, Bantan RA (2011) Landsat ETM applications: identifying geological and coastal landforms, SE Red Sea Coast, Saudi Arabia. In: Özhan E (Editor), Proceedings of the Tenth International Conference on the Mediterranean Coastal Environment, MEDCOAST 11 (Rhodes, Greece), pp 985–996
Alharbi OA, Phillips MR, Williams AT, Gheith AM, Bantan RA, Rasul NM (2012) Desalination impacts on the coastal environment: ash Shuqayq, Saudi Arabia. Sci Total Environ 421:163–172
Alhazmi OA (2006) Use of remote sensing applications for coastal landforms identification of Ash Shuqayq area, southeastern of the Red Sea coast. Msc, King Abdulaziz University, Saudi Arabia, Saudi Arabia
Al-Sayari SS, Zotl JG (1978) Quaternary period in Saudi Arabia. Springer, New York
Alsharhan A, ElSammak AA (2004) Grain-size analysis and characterization of sedimentary environment of the United Arab Emirates coastal area. J Coast Res 20:464–477
Al-Washmi HA, Gheith AM, Nabhan AI (2005) Geomorphological features, sediment distribution and transport along Ash Shuqayq-Al Huraydah coastal area, Southern Red Sea. Journal of the Faculty of Marine Science, King Abdulaziz University 16:57–80
Armstrong-Altrin JS, Nagarajan R, Lee YI, Zubillaga JJK, Saldaña LPC (2014) Geochemistry of sands along the San Nicolás and San Carlos beaches, Gulf of California, Mexico: implications for provenance and tectonic setting. Turk J Earth Sci 23(5):533–558
Bascom W (1964) Waves and beaches. Anchor Books, NY 267
Basyoni MH (1997) Sedimentological and hydrochemical characteristics of Al Lith sabkha, Saudi Arabia. Journal of King Abdulaziz University: Earth Science 9:75–86
Behairy AKA, Rao DNVN, El-Shater A (1991) A siliciclastic coastal sabkha, Red Sea coast, Saudi Arabia. Journal of the Faculty of Marine Science 2:65–77
Blott SJ, Pye K (2001) GRADISTAT: a grain size distribution and statistics package for the analysis of unconsolidated sediment. Earth Surf Process Landf 26(11):1237–1248
Bridge J, Demicco R (2008). Earth surface processes, landforms and sediment deposits: Cambridge University Press, New York
BSI (1975) Methods of test for soils for civil engineering purposes. British Standards Institution, B.S. 1377
Dean WE (1974) Determination of carbonate and organic matter in calcareous sediments and sedimentary rocks by loss on ignition: comparison with other methods. J Sediment Petrol 44:242–248
Dora GU, Kumar VS, Philip CS, Johnson G, Vinayaraj P, Gowthaman R (2011) Textural characteristics of foreshore sediments along Karnataka shoreline, west coast of India. International Journal of Sediment Research 26(3):364–377
Eisema D (1981) Supply and deposition of suspended matter in the North Sea. Special Publication of the International Association of Sedimentologists 5:415–428
El-Sayed MI (1999) Tidal flat rocks and sediments along the eastern coast of the United Arab Emirates. Carbonates Evaporites 14(1):106–120
Frank WM, Friedman GM (1973) Continental-shelf sediments off New Jersey. Journal of Sedimentary Research 43(1):224–237
Folk RL (1974) Petrology of sedimentary rock. Hemphill Publication Company, Texas
Folk RL (1980) Petrology of sedimentary rocks. Hemphill Publication Company, Texas
Folk RL, Ward W (1957) Brazos river bar: a study in the significance of grain size parameters. J Sediment Petrol 27:3–26
Gheith AM (1999) Mineralogy and diagenesis of coastal sabkha sediments of the hypersaline lagoons on the eastern coast of the Red Sea, Saudi Arabia. Arabian Gulf Journal of Scientific Research 17(2):199–219
Gheith AM (2000a) Sedimentary reflection of the coastal processes on the shore zone sediments along the eastern Red Sea coast, Saudi Arabia. Zeitschrift fur. Geomorphologie 44(4):449–468
Gheith AM (2000b) Use of surface features of quartz grains as indicators of various modern sedimentary environments along the eastern coastal plain of the Red Sea, Saudi Arabia. Arab Gulf Journal of Scientific Research 18(3):165–172
Kamaruzzaman BY, Shazili NAM, Lokman H (2002) Particle size distribution in the bottom sediments of the Kemaman River estuarine system, Terengganu, Malaysia. Pertanika Journal of Tropical Agricultural Science 25(2):149–155
Liu X, Vandenberghe J, An Z, Li Y, Jin Z, Dong J, Sun Y (2016) Grain size of Lake Qinghai sediments: implications for riverine input and Holocene monsoon variability. Palaeogeogr Palaeoclimatol Palaeoecol 449:41–51
Madah F, Mayerle R, Bruss G, Bento J (2015) Characteristics of tides in the Red Sea region, a numerical model study. Open Journal of Marine Science 5(02):193
Manual SP (1984) US Army engineer waterways experiment station. US Government Printing Office, Washington 2
Mohamed MAE, Madkour HA, El-Saman MI (2011) Impact of anthropogenic activities and natural inputs on oceanographic characteristics of water and geochemistry of surface sediments in different sites along the Egyptian Red Sea coast. Afr J Environ Sci Technol 5(7):494–511
Morcos SA (1970) Physical and chemical oceanography of the Red Sea. Oceanography Marine Biology Annual Review 8:73–202
Okeyode IC, Jibiri NN (2013) Excess lifetime cancer risks associated with the use of sediments from Ogun River, Nigeria as building material. Research Journal of Physics 7(j):1–8 7, 1-8
Pan B, Pang H, Zhang D, Guan Q, Wang L, Li F, Guan W, Cai A, Sun X (2015) Sediment grain-size characteristics and its source implication in the Ningxia–Inner Mongolia sections on the upper reaches of the Yellow River. Geomorphology 246:255–262
Patzert WC (1974) Wind-induced reversal in Red Sea circulation. Deep-Sea Res 21:109–121
Rao DNVN, Behairy AKA (1986) Nature and composition of shore-zone sediments between Jeddah and Yanbu, Eastern Red Sea. Mar Geol 70:287–305
Rasul N (1992) Late quaternary to present day coarse-grained sedimentation of the Indus fluvial-marine system. PhD, University of Wales, UK
Sabrouti MAE (1983) Texture and mineralogy of the surface sediments of ShrmObhur, west Red Sea coast of Saudi Arabia. Mar Geol 53(1–2):103–116
Skolasińska K (2014) Inquiry of levee formation by grain size analysis—a case study from the Warta River (central Poland). Catena 122:103–110
Solohub JT, Klovan JE (1970) Evaluation of grain-size parameters in lacustrine environments. J Sediment Petrol 40(1):81–101
Tag RJ, Abu Ouf M, El Shater A (1990a) Textural characteristics of coastal sediment between Wadi Al-Fagh and Wadi Al Qunfudah. Southeastern Red Sea. Arabian Gulf Journal of Scientific Research 8(2):33–47
Tag RJ, Abu Ouf M, El Shater A (1990b) The nature and occurrence of heavy minerals in the recent sediments of Al-Lith Al QunfudahCoast of Saudi Arabian Red Sea. Indian Journal of Marine Science 19:265–168
Thomas T, Phillips MR, Williams AT, Jenkins RE (2012) Medium timescale behaviour of adjacent embayedd beaches; influence of low energy forcing. Appl Geogr 32:265–280
Udden JA (1914) Mechanical composition of clastic sediments. Geological Society of America Bulletin25(1):655–744
UNEP/PERSGA (1997) Assessment of land-based sources and activities affecting the marine environment in the Red Sea and Gulf of Aden. Regional organisation for the conservation of the environment of the Red Sea and Gulf of Aden. UNEP Regional Seas Reports and Studies
Wentworth CK (1922) A scale of grade and class terms for clastic sediments. The Journal of Geology 30(5):377–392
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Alharbi, O.A., Williams, A.T., Phillips, M.R. et al. Textural characteristics of sediments along the southern Red Sea coastal areas, Saudi Arabia. Arab J Geosci 9, 735 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12517-016-2741-y
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12517-016-2741-y