Abstract
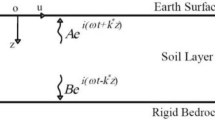
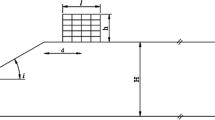
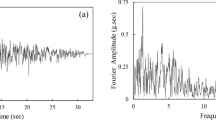
Evaluation of the ground response is one of the most common and important seismic geotechnical issues. Ground response analysis is used for predicting ground motions and response spectra and is developed to determine the dynamic stress and strain of soil. They are used for geotechnical risk assessment (types of instabilities) calculating the forces that can cause instability resulting from earthquakes and earth retaining structures. In this study, the effect of surface topography has been studied on seismic site response. The influence of different land surface geometries has been studied under real acceleration and earthquakes. Therefore, parameters such as the height and the angle of slope, the distance of earthquake fault, and the material properties have been selected for the seismic response evaluation. The results show that when the height and angle of slope increase, the maximum acceleration on the slope crest becomes greater than elsewhere on the surface for both stiff and soft soils. Moreover, the amplification factor always decreases when the maximum acceleration of the input motion record increases.














Similar content being viewed by others
References
Assimaki D, Kausel E (2002) An equivalent linear algorithm with frequency- and pressure-dependent moduli and damping for the seismic analysis of deep sites. Soil Dyn Earthq Eng 22(9–12):959–965
Bararpour M (2012) “Effect of surface topography on seismic site response”, Babol Noshirvani University in Iran, M.Sc. thesis, P 43
Bararpour M, Janalizade A, Shakeri A et al. (2012) Two-dimensional analysis of the sites dynamic effects of slope and valley, the first international & third national conference on Dams & Hydropower, Tehran, Iran
Bouchon M (1973) Effect of topography on surface motion. Bull Seismoll Soc Am 63(2):615–632
Bouckovalas G, Papadimitriou A (2005) Numerical evaluation of slope topography effects on seismic ground motion. Soil Dyn Earthq Eng 25:547–558
Choobbasti AJ, Farrokhzad F, Barari A (2009) Prediction of slope stability using artificial neural network (case study, Nobad, Mazandaran, Iran). Arab J of Geosci 2(4):311–319
Chopra AK (1996) Dynamic of structures theory and application to earthquake engineering. University of California at Berkeley. 361–368
Das Braja M (1993) Principles of soil dynamics, PWS-KENT publishing company
Davis LL, West LR (1973) Observed effects of topography on ground motion. Bull Seismol Soc Am 63(1):283–298
Di Fiore V (2010) “Seismic site amplification induced by topographic irregularity: results of a numerical analysis on 2D synthetic models”. Eng Geol. ENGEO- 03078
Gao Y, Zhang N (2013) Scattering of cylindrical SH waves induced by a symmetrical V-shaped canyon: near-source topographic effects. Geophys J Int 193(2):874–885
Gao Y, Zhang N, Li D, Liu H, Cai Y, Wu Y (2012) Effects of topographic amplification induced by a U-shaped canyon on seismic waves. Bull Seismol Soc Am 102(4):1748–1763
Gatmiri B, Nguyen K (2007) Evaluation of seismic ground motion induced by topographic irregularity. Soil Dyn Earthq Eng 27(2):183–188
Geli L, Bard PY, Jullien B (1988) The effect of topography on earthquake ground motion: a review and new results. Bull Seismoll Soc Am 78(1):42–63
GEO-SLOPE International Ltd (2004) Quake/w for finite element dynamic analysis. Calgary, Alberta, Canada
Havenith HB et al (2003) Initiation of earthquake-induced slope failure: influence of topographical and other site specific amplification effects. J Seismol 7:397–412
Hu Y-X, Liu S-C, Dong W et al. (1996) Earthquake Engineering, E & FN Spon, an imprint of Chapman & Hall, 2-6 Boundary Row, London SE1 8HN, UK
Janalizade A, Saadati M, Tavakoli HR (2012) Seismic response of pile foundation in liquefiable soil: parametric study. Arab J Geosci Springer 5(6):1307–1315
Kamalian M, Gatmiri B, Sohrabi-Bidar A, Khalaj A (2007) Amplification pattern of 2D semi-sine-shaped valleys subjected to vertically propagating incident waves. Commun Numer Methods Eng 23:871–887
Kim MK, Lee JS, Kim MK (2003) Two-dimensional seismic response analysis of basin effects. KSCE J Civ Eng 7(1):33–39
Kramer SL (1996) Geotechnical earthquake engineering. Prentice Hall, Upper Saddle River
Leenders N (2000) Three-dimensional dynamic modeling of earthquake tremors, Delft Memoirs of the centre of Engineering geology in the Netherlands, No. 200, M.Sc. thesis, TU Delft. 64
Loria CS (2003) Numerical assessment of influence of the earthquakes on irregular topographies- analysis of Colombia, 1999 and El Salvador, 2001 earthquakes, ITC 2003, M.Sc. thesis, 1–141
Paolucci R (2002) Amplification of earthquake ground motion by steep topographic irregularities. Earthq Eng Struct Dyn 31(10):1831–1853
Raamachandran J (2000) Boundary and finite elements. Alpha Science International Ltd., Oxford
Sanchez-Sesma FJ, Campillo M (1993) Topographic effects for incident P, SV, and Rayleigh waves. Tectonophysics 218(1-3):113–125
Semblat JF, Duval AM, Dangla P (2000) Numerical analysis of seismic amplification in Nice (France) and comparisons with experiments. Soil Dyn Earthq Eng 19:347–362
Takenaka H, Furumura T, Fujiwara H et al. (1998) Recent developments in numerical methods for ground motion simulation, the effects of surface geology on seismic motion, recent progress and new horizon on ESG study, Irikura, Kudo, Okada & Sasatani (eds); Balkema, Rotterdam, ISBN 90 5809 030 2, Vol. 1, PP. 91-101
The National Academies press (2003) Preventing earthquake disasters: the grand challenge in earthquake engineering: a research agenda for the network for Earthquake Engineering Simulation (NEES)
Zhang N, Gao Y, Yang J, Xu C (2015) An analytical solution to the scattering of cylindrical SH waves by a partially filled semi-circular alluvial valley: near-source site effects. Earthq Eng Eng Vib 14(2):189–201
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Bararpour, M., Janalizade, A. & Tavakoli, H.R. The effect of 2D slope and valley on seismic site response. Arab J Geosci 9, 93 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12517-015-2039-5
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12517-015-2039-5