Abstract
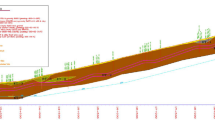
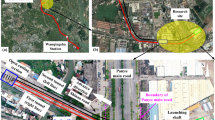
Nowadays, with the increasing population of large cities, the need to expand public transportation, especially metro systems, is greatly increasing in urban areas. Therefore, excavation of new tunnels near the existing ones or other excavations located nearby has become inevitable. Excavation of such tunnels in urban areas should be done by considering the effects of these tunnels on buildings and other urban structures. Significant factors affecting interaction between tunnels, as well as the characteristics of surface settlement, are the existence of mixed ground (soil-rock) at tunnel faces or fault zones in the direction of tunnel excavation which have not been clearly investigated by researchers. These parameters have a great effect on the amount of maximum surface settlement and shape of surface settlement curve. Although several studies aim to analyse the interaction between newly excavated and existing tunnels and its effects on surface settlements, this subject certainly needs further investigation. This study mainly focuses on the effects of the interaction between twin tunnels mainly opened in fault zones and mixed ground on the basis of surface settlement measurements by using Earth Pressure Balance Machine (EPBM). Both numerical and empirical methods are used in this study. Observed data are used to test the validity of the results obtained from three-dimensional numerical modelling. The results from numerical methods were in good agreement with the real data. The results of this study reveal that the amount of maximum surface settlement and shape of surface settlement curve are strongly related to spacing between tunnels, fault zone thickness and type of tunnel face material. The interaction factor is almost zero when spacing is larger than 4D (D is tunnel diameter). Independent of fault zone thickness, the effects of the fault on longitudinal surface settlement continue 25 m from both sides of the fault centre.











Similar content being viewed by others
References
Addenbrooke TI, Potts DM (2001) Twin tunnel interaction: surface and subsurface effects. Int J Geomech 1(2):249–271
Aksoy CO, Oğul K, Topal I, Ozer SC, Ozacar V, Posluk E (2012) Numerical modeling of non-deformable support in swelling and squeezing rock. Int J Rock Mech Min 52:61–70
Aksoy CO, Oğul K, Topal I, Poşluk E, Gicir A, Kucuk K, Uyar Aldas G (2014) Reducing deformation effect of tunnel with Non-Deformable Support System by Jointed Rock Mass Model. Tunn Undergr Sp Tech 40:218–227
Arioglu E (1992) Surface movements due to tunnelling activities in urban areas and minimization of building damages (in Turkish). Istanbul Technical University, Mining Engineering Department, Short Course
Ayson Drill Research and Build, A.S., 2005. Otogar–Bagcılar Station Geological-Geotechnical Report (in Turkish), July 2005.
Bagherzadeh A, Ferdosi B, Nakhaei J, Nasri MJ (2014) Numerical analysis of the support system in the transition zone of the Esfahan subway project. Arab J Geosci. doi:10.1007/s12517-014-1487-7
Chakeri, H., (2012), Investigation of Face Stability and Surface Settlement at Earth Pressure Balance (EPB) Tunneling Method, Ph.D. Thesis, Hacettepe University, Ankara, Turkey, 122 p.
Chakeri H, Hasanpour R, Hindistan MA, Unver B (2010) Analysis of interaction between tunnels in soft ground by 3D numerical modelling. Bull Eng Geol Environ J 70(3):439–448
Chakeri H, Ozcelik Y, Unver B (2013) Effects of important factors on surface settlement prediction for metro tunnel excavated by EPB. Tunn Undergr Sp Tech 36:14–23
Ercelebi SG, Copur H, Ocak I (2010) Surface settlement predictions for Istanbul Metro tunnels excavated by EPB-TBM. Environ Earth Sci 62:357–365
Ghaboussi J, Ranken RE (1976) Analysis of Interaction Between Two Parallel Tunnels, Department of Transportation, 129 p.
Ghaboussi J, Ranken RE (1977) Interaction between two parallel tunnels. Int J Numer Anal Met 1:75–103
Goshtasbi K, Elyasi A, Naeimipour A (2013) 3D numerical stability analysis of multi-lateral well junctions. Arab J Geosci 6:2981–2989
Hage Chehade F, Shahrour I (2008) Numerical analysis of the interaction between twin-tunnels: Influence of the relative position and construction procedure. Tunn Undergr Sp Tech 23:210–214
Hamza M, Ata A, Roussin A (1999) Ground movements due to construction of cut-and-cover structures and slurry shield tunnel of the Cairo Metro. Tunn Undergr Sp Tech 14(3):281–289
Herzog M (1985) Die Setsungsmulde Über Seicht Liegenden Tunneln. Berlin Bautechnik 11:375–377
Itasca (1997) Itasca consulting Group, Inc. FLAC3D (Fast Lagrangian Analysis of Continua in 3Dimensions), Version 2.10-224.
Karakus, M., Ozsan, A., Basarir, H. (2007), Finite element analysis for the twin metro tunnel constructed in Ankara Clay-Turkey, Bulletin of Engineering Geology and the Environment, Vol. 66, pp. 71–79
Kawata, T., Ohtsuka, M., (1993), Observational construction of large scaled twin road tunnels with minimum interval, Reith JL (ed) Infrastructures Souterraines de Transports, Balkema, Roterdam.
Kim CY, Bae GJ, Hong SW, Park CH, Moon HK, Shin HS (2001) Neural network based prediction of ground surface settlements due to tunnelling. Compt Rendus Geosci 28(6–7):517–547
Liu, H.Y., Small, J.C., Carter, J.P., Williams, D.J. (2009), Effects of tunneling on existing support systems of perpendicularly crossing tunnels, Computer Geotechnics, Vol. 36(5), pp. 880–894
Mahmutoglu Y (2010) Surface subsidence induced by twin subway tunnelling in soft ground conditions in Istanbul. Bull Eng Geol Environ. 70:115–131
Mair RJ (1983) Geotechnical aspects of soft-ground tunnelling. Proc. Conf. on Construction Problems in Soft Soils, N.T.I., Singapore
Martos, F., (1958). Concerning an Approximate equation of the subsidence Trough and Its Time Factors. International Strata Control Congress, Leipzig, pp. 191–205
Mroueh H, Shahrour I (2002) Three-dimensional finite element analysis of the interaction between tunnelling and pile foundations. Int J Numer Anal Met 26:217–230
O’Reilly MP, New BM (1985) Settlements above tunnels in the United Kingdom. Proceedings of Tunneling 82, Bringhton, pp. 173-181.
Ocak I (2009) Environmental effects of tunnel excavation in soft and shallow ground with EPBM: the case of Istanbul. Environ Earth Sci 59:347–352
Peck RB (1969) Deep excavations and tunnelling in soft ground. Proc. 7th International Conference on Soil Mechanics and Foundation Engineering, State of the Art Volume, pp. 225–290.
Perri, G. (1994), Analytical solution for tunneling-induced ground movement in clays, Tunneling and Underground Space Technology, pp. 249–261.
Safari OH, Pirasteh S, Pradhan B, Amid H (2013) Geohazards analysis of Pisa tunnel in a fractured incompetent rocks in Zagros Mountains, Iran. Arab J Geosci 6:1101–1112
Saitoh, A., Gomi, K., Shiraishi, T. (1994), Influence forecast and field measurement of a tunnel excavation crossing right above existing tunnels, Salam A (ed) Tunneling and Ground Conditions, Balkema, Roterdan, pp. 83–90
Schmidt, B., (1969). A method of estimating surface settlement above tunnels constructed in soft ground. Can. Geotechnol. J. 20, 11–22
Siahmansouri A, Gholamnejad J, Fatehi Marji M (2014) A hybridized numerical and regression method for estimating the minimum rock pillar width of twin circular tunnels. Arab J Geosci 7:1059–1066
Shahrour, I., Mroueh, H. (1997), Three-dimensional non-linear analysis of a closely twin tunnels, Sixth International Symposium on Numerical Models in Geomechanics (NUMOG VI), Vol. 2, Montreal, QC, Canada, pp. 481–487
Soliman, E., Duddeck, H., Ahrens, H. (1993), Two and three dimensional analysis of closely spaced double tube tunnels, Tunnel Underground Space Technology, Vol. 8(1), pp. 13–18
Talebinejad A, Chakeri H, Moosavi M, Özçelik Y, Ünver B, Hindistan M.A (2014) Investigation of surface and subsurface displacements due to multiple tunnels excavation in urban area. Arab J Geoscie. doi:10.1007/s12517-013-1056-5
Verma AK, Bajpai RK, Singh TN, Narayan PK, Dutt A (2011) 3D instability analysis of an underground geological repository—an Indian case study. Arab J Geosci 4:1173–1188
Wang L, Ravichandran N, Hsein Juang N (2012) Bayesian updating of KJHH model for prediction of maximum ground settlement in braced excavations using centrifuge data. Compt Rendus Geosci 44:1–8
Yamaguchi, I., Yamazaki, I., Kiritani, K. (1998), Study of ground-tunnel interactions of four shield tunnels driven in close proximity, in relation to design and constructions of parallel shield tunnels, Tunneling Underground Space Technology, Vol. 13(3), pp. 289–304
Yasitli NE (2014) Numerical modeling of surface settlements at the transition zone excavated by New Austrian tunneling method and umbrella arch method in weak rock. Arab J Geosci 6:2699–2708
Yu and Akagi (2003) must be given as Yu and Akagi (2003) (from Chakeri, 2012)
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Chakeri, H., Ozcelik, Y. & Unver, B. Investigation of ground surface settlement in twin tunnels driven with EPBM in urban area. Arab J Geosci 8, 7655–7666 (2015). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12517-014-1722-2
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12517-014-1722-2