Abstract
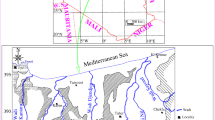
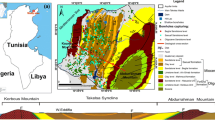
The Enfida aquifer system is of importance to the economic activity of the eastern center of Tunisia. The planning of a marina is likely to present a significant risk on groundwater. Classical physically based modeling is used to better understand salty water intrusion in the aquifers. The transport model (MT3DMS) is coupled with the groundwater model (Modflow). Model calibration was carried out over the period 1972–2005. Four scenarios were then simulated for a 50-year period, to assess the effects of both planned marina and future abstraction regime. We predict a rise in the groundwater salinity generated by the planned pumping infrastructure. The impact of the planned project will be observed only near the marina. However, limited measurements of transmissivity may affect the model’s results. Thus, the second part of the paper is aimed to assess the models output error due to the uncertainty in transmissivity, using a stochastic approach. Hundred realizations of a log-normal random transmissivity field had been performed. According to the most pessimistic realizations, the uncertainty may reach 49 % in the sector of an important pumping field. Accordingly, the calculated concentration may reach 6.5 g/l in 2055 instead of 3.2 g/l.













Similar content being viewed by others
References
Abarca E (2006) Seawater intrusion in complex geological environments. PhD Thesis, Technical University of Catalonia, Spain. 154p
Aboufirassi M, Marino MA (1984) Cokriging of aquifer transmissivity from field measurements of transmissivity and specific capacity. Math Geol 16(1):19–35
Ackerer P, Magnico P, More R (1994) Réflexions sur la modélisation de la propagation de polluants dans les hydrosystèmes souterrains. Revue des sciences de l'eau/J Water Sci 7(2):201–212
Ahmed S, de Marsily G (1987) Comparison of geostatistical methods for estimating transmissivity using data on transmissivity and specific capacity. Water Resour Res 23(9):1717–1737
Ahmed S, de Marsily G, Talbot A (1988) Combined use of hydraulic and electrical properties of an aquifer in a geostatistical estimation of transmissivity. Ground Water 26(1):78–86
Al-Bitar A, Ababou R (2005) Random field approach to seawater intrusion in heterogeneous coastal aquifers: unconditional simulations and statistical analysis. Geostat Environ Appl 233–248. doi:10.1007/3-540-26535-X_20
Anderson MP (1979) Using models to simulate the movement of contaminants through groundwater flow systems. Crit Rev Environ Controls 9(2):97–156
Anderson MP, Woessner WW (1992) Applied groundwater modeling. Academic, San Diego, 381p
Appleyard S (1995) The impact of urban development on recharge and groundwater quality in a coastal aquifer near Perth, Western Australia. Hydrogeol J 3(2):65–75. doi:10.1007/s100400050072
Bear J, Verruijt A (1987) Modeling groundwater flow and pollution. D. Reidel Publishing Company, New York, 414p
Bear J, Cheng AH-D (2009) Modeling groundwater flow and contaminant transport. Springer, Dordrecht, 834 p
Besbes M (1978) L'estimation des apports aux nappes souterraines. Un modèle d'infiltration efficace. Thèse Doc. es. Sc. Univ. Paris VI. 270p
Brovelli A, Carranza-Diaz O, Rossi L, Barry DA (2010) Design methodology accounting for the effects of porous medium heterogeneity on hydraulic residence time and biodegradation in horizontal subsurface flow constructed wetlands. Ecol Eng. doi:10.1016/j.ecoleng.2010.04.031
Carlson M, Lohse K, McIntosh J, McClain J (2011) Impacts of urbanization on groundwater quality and recharge in a semi-arid alluvial basin. J Hydrol 409:196–211. doi:10.1016/j.jhydrol.2011.08.020
Carrera J (1993) An overview of uncertainties in modeling groundwater solute transport. J Contam Hydrol 13:23–48
Changming L, Jingjie Y, Kendy E (2001) Groundwater exploitation and its impact on the environment in the North China plain. Water Int 26(2):265–272
Chiang WH, Kinzelbach W (2001) 3D-groundwater modeling with PMWIN a simulation system for modeling groundwater flow and pollution. Springer, Berlin, 346p
Chiles JP, Delfiner P (1999) Geostatistics: modeling spatial uncertainty. Wiley, New York, 695p
Cinnirella S, Buttafuoco G, Pirrone N (2005) Stochastic analysis to assess the spatial distribution of groundwater nitrate concentrations in the Po catchment. Environ Pollut 133:569–580
Clark I, Harper WV (2000) Practical geostatistics 2000. Ecosse North America, Columbus, 342p
Cornaton F (2004) Deterministic models of groundwater age, life expectancy and transit time distributions in advective-dispersive systems. PhD thesis, Fac. Sc. Univ. Neuchâtel. 147p
Delhomme JP (1976) Application de la théorie des variables régionalisées dans les sciences de l’eau. Docteur-Ingénieur thesis, Ecole des Mines de Paris, Univ. Paris VI. 130p
DGP « Direction Générale de la Privatisation » (2006) Mission d’étude et d’assistance au projet de réalisation, de financement et d’exploitation d’un port en eaux profondes sous forme de concession. Ref. EuropeAid/119858/D/SV/TN. Rapport de la mission 3. Rapport sur les études d’impact sur l’environnement. Premier Ministère. Tunisie. 17p
Dreybrodt W, Romanov D, Kaufmann G (2009) Evolution of isolated caves in porous limestone by mixing of phreatic water and surface water at the water table of unconfined aquifers: a model approach. J Hydrol 376:200–208. doi:10.1016/j.jhydrol.2009.07.027
El Batti (1974) Hydrogéologie de la plaine d’Enfida. Doc. 3ème cycle thesis. Univ. Scientifique et médicale de Grenoble. 122p
Ferraris L, Gabellani S, Rebora N, Provenzale A (2002) A comparison of stochastic models for spatial rainfall downscaling. Water Resour Res 39:1368–1384
Freeze RA (1975) A stochastic-conceptual analysis of one-dimensional groundwater flow in non uniform homogeneous media. Water Resour Res 11(5):725–741. doi:10.1029/WR011i005p00725
Frenzel H (1995) A field generator based on Mejia’s algorithm. Institut für fuer Umwelt-physik. University of Heidelberg, Germany
Fried JJ (1975) Groundwater pollution. Elsevier, Amsterdam, 330p
Fried JJ (1981) Groundwater pollution mathematical modeling: improvement or stagnation? Sci Total Environ 21:283–298
Harbaugh AW, Banta ER, Hill MC, McDonald MG (2000) Modflow-2000, the U.S. geological survey modular ground-water model: user guide to modularization concepts and the groundwater flow Process. US Geological Survey, Reston, 121p
Horriche F, Zammouri M (2008) Etude sur modèles mathématiques de la plaine d’Enfida: construction, calage et exploitation des modèles d’écoulement et de transport de soluté. Mission d’expertise : Etude hydrogéologique de la zone d’implantation du port en eaux profondes dans la région d’Enfida. A.P.A.L, Ministère Env. Dévelop. Durable, Tunise. 117p
Isaak E, Srivastava R (1989) An introduction to applied geostatistics. Oxford University Press, New York, 592p
Journel A, Huijbregts CJ (1978) Mining geostatistics. Academic, New York, 600p
Kerrou J (2008) Deterministic and probabilistic numerical modeling towards sustainable groundwater management. Application to seawater intrusion in the Korba aquifer (Tunisia). PhD thesis. Univ. Neuchâtel. Switzerland. 181p
Kitanidis PK (2000) Introduction to geostatistics. Application in hydrogeology. Cambridge University Press, Cambridge, 249p
Konikow LF (2011) The secret to successful solute-transport modeling. Ground Water 49(2):144–159
Lerner DN (2002) Identifying and quantifying urban recharge: a review. Hydrogeol J 10(1):143–152. doi:10.1007/s10040-001-0177-1
Manaa M (1989) Etude hydrogéologique préliminaire du Sahel de Sousse. Direction des Ressources en Eau. Arrondissement de Sousse. Ministère de l’Agriculture, Tunisie
Manaa M, Chaieb H, Amri R (1996) Etude par modèle hydrogéologique de la nappe alluviale de l’oued El Khairat. DGRE. Ministère de l’Agriculture, Tunisie
de Martonne E (1942) Nouvelle carte mondiale de l’indice d’aridité. Annale de géographie 288:241–250
Matheron G (1970) La théorie des variables régionalisées et ses applications., Les Cahiers du centre de Géostatistique 5. Ecole Nationale Supérieure des Mines de Paris. 212p
Matheron G, de Marsily G (1980) Is transport in porous media always diffusive? A counter-example. Water Resour Res 16(5):901–917. doi:10.1029/WR016i005p00901
McAllister TL, Overton MF, Brill ED (1996) Cumulative impact of marinas on estuarine water quality. Environ Manag 20(3):385–396. doi:10.1007/BF01203846
Mejia JM, Rodriguez-Iturbe I (1974) On the synthesis of random field sampling from the spectrum: an application to the generation of hydrologic spatial processes. Water Resour Res 10(4):705–711. doi:10.1029/WR010i004p00705
Naji A, Cheng AHD, Ouazar D (1998) Analytical stochastic solutions of saltwater/freshwater interface in coastal aquifers. Stoch Hydrol Hydraul 12:413–430
Nazoumou Y (2002) Impact des barrages sur l’alimentation des nappes souterraines de Kairouan. Doc. thesis ENIT, Univ. El Manar, Tunis. 221p
Odo BO (2008) Etude de la sensibilité des modèles de l’écoulement et du transport de soluté dans la plaine d’Enfida. Mém. Fin d’études. ESIER, Medjez el Bab. Tunisie. 115p
Razack M, Huntley D (1991) Assessing transmissivity from specific capacity in a large and heterogeneous alluvial aquifer. Ground Water 29(6):856–861
Razack M, Lasm T (2006) Geostatistical estimation of the transmissivity in a highly fractured metamorphic and crystalline aquifer (Man-Danane Region, Western Ivory Coast). J Hydrol 325:164–178
Renard P (2008) La fin des certitudes? Bulletin d’Hydrogéologie 22, 23–42. Centre d’Hydrogéologie, Univ. Neuchâtel. Ed. Peter Lang
Rentier C (2003) Méthode stochastique de délimitation des zones de protection autour des captages d’eau—Conditionnement par des mesures de conductivité hydraulique K, de hauteur piézométrique h et de résistivité électrique ρ, Doc. Thesis, Univ. Liège. 215p
Robinson C, Brovelli A, Barry DA, Li L (2009) Tidal influence on BTEX biodegradation in sandy coastal aquifers. Adv Water Resour 32:16–28. doi:10.1016/j.advwatres.2008.09.008
Rodriguez-Iturbe I, Marani M, D’Odorico P, Rinaldo A (1998) On space–time scaling of cumulated rainfall fields. Water Resour Res 34(12):3461–3469
Simmons CS (1982) A stochastic-convective transport representation in dispersion in one-dimensional porous media systems. Water Resour Res 18(4):1193–1214
SCET (2007) Etude de gestion des eaux de ruissellement dans la région Centre-Est (Salloum-Hergla). Phase II : Avant projet sommaire, O.N.A.S., Ministère Env. Dévelop. Durable, Tunisie
Schiedek T, Beier M, Ebhardt G (2007) An integrative method to quantify contaminant fluxes in the groundwater of urban areas. J Soils Sediments 7(4):261–269. doi:10.1065/jss2007.04.221
Theodossiou N, Latinopoulos P (2006) Evaluation and optimisation of groundwater observation networks using the Kriging methodology. Environ Model Softw 21:991–1000
Zammouri M, Ounaies S, Jarraya-Horriche F (2006) Modélisation de la recharge artificielle par lâchers dans le lit d’un cours d’eau. Cas de la plaine d’Enfida (Tunisie). Las aguas subterraineas en los paise mediterraneos. Instituto Geologico y Minero de Espana. Serie : Hidrogeologica y Aguas Subterraneas, N°17, 407–412
Zheng C, Wang PP (1999) A modular three-dimensional multispecies transport model for simulation of advection, dispersion and chemical reactions of contaminants in groundwater systems; documentation and user’s guide. In: SERDP-99-1. Contract report, US Army Engineer Research and Development Center, Vicksburg, MS. 169p
Zhou Y, Van Geer FC (1992) KALMOD, a stochastic-deterministic model for simulating groundwater flow with Kalman filtering. Hydrol Sci J 37(4):375–389
Acknowledgments
Financial support for this research was provided by “Agence de Protection et d’Aménagement du Territoire” (APAL). The authors wish to acknowledge Dr. H. Ben Moussa (APAL) and Dr. F. Maalal (CRDA Monastir) for their valuable help in the data gathering.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Zammouri, M., Jarraya-Horriche, F., Odo, B.O. et al. Assessment of the effect of a planned marina on groundwater quality in Enfida plain (Tunisia). Arab J Geosci 7, 1187–1203 (2014). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12517-012-0814-0
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12517-012-0814-0