Abstract
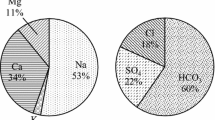
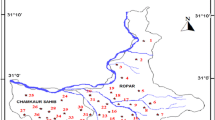
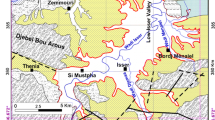
A hydrogeochemical study was conducted on the groundwater of south Al Madinah Al Munawarah City, Saudi Arabia, to assess the quality of groundwater for drinking and irrigation uses. Groundwater samples have been collected and analyzed for major and some trace constituents from the study area. The nitrate concentration in most groundwater samples of the study area exceeded the safe limits for drinking purposes, whereas the concentrations of phosphate, boron, and trace constituents were below the maximum permissible limit for drinking purposes; Cr in two samples showed high content over the recommended limits of drinking purposes. Uncontrolled abstraction of groundwater in Abar Al Mashi area caused many environmental problems including water resource depletion and contamination. Correlations between chloride and major ions were positive and may be attributed to impact of agricultural activities on groundwater chemistry. Groundwater of the study area was classified into six water types. The chemical water types of groundwater in the study area contain CaHCO3 in the eastern and southeastern parts and NaCl in western and northwestern parts, reflecting different land use characteristics and pollution sources. Piper diagram showed that almost all the samples fall in one zone, indicating similar chemical signature. Groundwater can be used safely for drinking with special treatments to eliminate the effect of increased concentrations of total dissolved solids, nitrate, and chromium. The groundwater of the study area can be used safely for irrigation on clay soil; however, specific crops should be selected according to their salt tolerance.







Similar content being viewed by others
References
Abderrahman WA (2006) Water management in ArRiyadh. Int J Water Resour Dev 22(2):281
Abderrahman WA, Dabbagh AE, Edgell HS, Shahlam AB (1988) Evaluation of groundwater resources in aquifer systems of three regions in Saudi Arabia. 6th IWRA World Wat Congr on Wat Resour 1–11 Ottawa
Al Sayari SS, Zötl JG (1978) Quaternary period in Saudi Arabia. Springer, New York
Al-Bassam AM (1998) Determination of hydrochemical processes and classification of hydrochemical facies for Sakakah aquifer, northeastern Saudi Arabia. J Afr Earth Sci 27(1):27–38
Al-Bassam AM, Al-Rumikhani YA (2003) Integrated hydrochemical method of water quality assessment for irrigation in arid areas: application to the Jilh aquifer, Saudi Arabia. J Afr Earth Sci 36:345–356
Al-Bassam AM, Hussein MT, Sharaf MA (2003) Areal distribution of the dissolved major and minor ions in the Sakaka aquifer, Saudi Arabia. Ann Geol Surv Egypt 32:453–466
Allael-Din MN, Madany IM, Al-Tayaran A, Al-Jubair AH, Gomaa A (1993) Quality of water from some wells in Saudi Arabia. Water Air Soil Pollut 66(1–2):135–143
Al-Sefry SA, Sen Z (2006) Groundwater rise problem and risk evaluation in major cities of arid lands—Jeddah case in Kingdom of Saudi Arabia. Water Resour Manag 20:91–108
Al-Shaibani AM (2008) Hydrogeology and hydrochemistry of a shallow alluvial aquifer, western Saudi Arabia. Hydrogeol J 16:155–165
Al-Shaibani A, Lloyd JW, Abokhodair AA, Alahmari A (2007) Hydrogeological and quantitative groundwater assessment of the basaltic aquifer, northern Harrat Rahat, Saudi Arabia. Arab Gulf J Sci Res 25(1/2):39–49
Alyamani M (2000) Salinity problem of groundwater in the Wadi Tharad basin, Saudi Arabia. GeoJournal 48:291–297
American Public Health Association (APHA) (1998) Standard methods for the examination of water and wastewater, 20th edn. APHA-AWWA-WET, Washington, DC
Bamousa AO, Matar SS, Daoudi M, Al-Doaan MI (2012) Structural and geomorphic features accommodating groundwater of Al-Madinah City, Saudi Arabia. Arab J Geosci. doi:10.1007/s12517-012-0574-x
Bayumi TH (2008) Impact of natural and human activities on the groundwater quality in the southern part of Al-Madinah Al-Munawarah, Saudi Arabia. Ann Geol Surv Egypt 35(1):557–578
Bazuhair AS, Wood WW (1996) Chloride mass-balance method for estimating ground water recharge in arid areas: examples from western Saudi Arabia. J Hydrol 186:153–159
Bokhari AY, Khan MZA (1992) Deterministic modeling of Al-Madinah Al-Munawarah groundwater quality using Lumped parameter approach. J King Abdulaziz Univ: Earth Sci 5:89–107
Carney M (1991) European drinking water standards. J Am Wat Works Ass (AWWA) 83:48–55
Dabbagh AE, Höِtzl H, Zöِtl JG (1988) Karst features of the Arabian platform and their influence on aquifers. Proceedings of the IAH 21st Congress, Karst Hydrogeology and Karst Environment Protection. XXI, Guilin, China, Geolog Pub House Beijing, China 1988:452–460
Daesslé LW, Mendoza-Espinosa LG, Camacho-Ibar VF, Rozier W, Morton O, Van Dorst L, Lugo-Ibarra KC, Quintanilla-Montoya AL, Rodríguez-Pinal A (2006) The hydrogeochemistry of a heavily used aquifer in the Mexican wine-producing Guadalupe Valley, Baja California. Environ Geol 51:151–159
De Jong RL, Yazicigil H, Al-Layla RI (1989) Scenario planning for water resources: Saudi Arabian case study. Water Int 14:6–12
Domenico PA, Schwartz FW (1998) Physical and chemical hydrogeology, 2nd edn. Wiley, New York
El Maghraby MM (2004) Salinization of groundwater at the Quba area, Al Madinah Al Munawarah, Saudi Arabia. Proceed of the 6th Int Conf On Geochem Alex Univ Egypt 15–16 September (2004) 309–318
Environmental Protection Agency (EPA) (2004) 2004 Edition of the drinking water standards and health advisories. EPA 822-R-04-004 Office of Water US EPA Washington DC
Gastmans D, Chang HK, Hutcheon I (2010) Groundwater geochemical evolution in the northern portion of the Guarani Aquifer System (Brazil) and its relationship to diagenetic features. Appl Geochem 25:16–33
George M, Shorbaji H (1987) Explanatory notes to the hydrogeologic and hydrochemical maps of the Al Madinah quadrangle. Sheet 24D KDS Open-file rep BRGM-OF-07-23 Ministry of Petroleum and Mineral Resources KSA
Hussain G, Sadiq M (1991) Metal chemistry of irrigation and drainage waters of Al-Hassa Oasis of Saudi Arabia and its effects on soil properties. Water Air Soil Pollut 57–58:773–783
Johnson PR (1983) A preliminary lithofacies map of the Saudi Arabian Shield: an interpretation of the lithofacies and lithostratigraphy of the late Proterozoic layered rocks of Saudi Arabia: Saudi Arabian Deputy Ministry of Mineral Resources Jiddah. Technical Rep RF-TR-03-2, 72
Krapac IG, Dey WS, Roy WR, Smyth CA, Storment E, Sargent SL, Steele JD (2002) Impacts of swine manure pits on groundwater quality. Environ Pollut 120:475–492
LeBlanc DR (1984) Sewage plume in a sand and gravel aquifer, Cape Cod, Massachusetts. US Geological Survey water-supply paper 2218, USA
Lloyd JW, Heathcote JA (1985) Natural inorganic hydrochemistry in relation to groundwater. Oxford University Press, New York
Lloyd JW, Pirn RH (1990) The hydrogeology and groundwater resources development of the Cambro-Ordovician sandstone aquifer in Saudi Arabia and Jordan. J Hydrol 121:1–20
Matsah MI, Hossain D (1993) Ground conditions in Al-Madinah Al-Munawarah, Saudi Arabia. J King Abdulaziz Univ: Earth Sci 6:47–77
Ministry of Petroleum and Mineral Resources KSA (1987) Hydrogeologic map of the Al Madinah quadrangle. Sheet 24D KSA
Notodarmojo S, Ho GE, Scott WD, Davis GB (1991) Modeling phosphorus transport in soils and groundwater with two-consecutive reactions. Water Res 25:1205–1216
Parkhurst DL, Appelo AAJ (1999) User’s guide to PHREEQC (V 2)—a computer program for speciation, batch-reaction, one-dimensional transport, and inverse geochemical modeling. US Geol Surv Wat-Resour Inv 99–4259:312
Pellaton C (1981) Explanatory noted to the geologic map of the Al-Madinah Quadrangle. Sheet 24D KSA Geolog Map GM-52C DGMR Govt KSA
Pieke JG (1985) Groundwater resources and development in the central region of the Arabian Gulf. IAH- Memoires of the 18th congress Hydrogeology in the service of Man 18/2 Cambridge (IAHS) 46–55
Piper AM (1944) A graphic procedure in the geochemical interpretation of water analyses. Am Geophys Un Transac 25:914–923
Saudi Standards, Metrology and Quality Organization (SASO) (1984) Saudi standards, metrology and quality organization. Iss 409/84 Riyadh KSA
Schoeller H (1962) Geochemie des eaux souterraines. Rev de I’ Inst Francais du Petrole 10:230–244
Sowayan AM, Allayla R (1989) Origin of the saline groundwater in wadi Ar-Rimah, Saudi Arabia. Gr Water 27:481–490
Subyani AM (2004) Use of chloride-mass balance and environmental isotopes for evaluation of groundwater recharge in the alluvial aquifer Wadi Tharad western Saudi Arabia. Environ Geol 46:741–749
Tijani J (1994) Hydrochemical assessment of groundwater in Moro area Kwara State Nigeria. Environ Geol 24:94–202
Trauth R, Xanthopoulos C (1997) Nonpoint pollution of groundwater in urban areas. Water Res 31:2711–2718
Wilcox LV (1955) Classification and use of irrigation waters. US Dep Agric Circ 969:19
Wood WW, Sandford WE (1995) Chemical and isotopic method for quantifying ground-water recharge in a regional, semiarid environment. Gr Water 33(3):458–486
World Health Organization (WHO) (2011) Guidelines for drinking-water quality, 4th edn. Geneva 541 [electronic resource]
Zanini L, Robertson WD, Ptacek CJ, Schiff SL, Mayer T (1998) Phosphorous characterization in sediments impacted by septic effluent at four sites in central Canada. J Contam Hydrol 33:405–429
Acknowledgments
The authors are grateful to anonymous reviewers. The present study was supported by the Deanship of Scientific Research, Taibah University, Saudi Arabia (research number 431/688). The authors are grateful to staff members of Chemistry Department, Faculty of Science at Taibah University for their assistance to analyze the water samples.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Khashogji, M.S., El Maghraby, M.M.S. Evaluation of groundwater resources for drinking and agricultural purposes, Abar Al Mashi area, south Al Madinah Al Munawarah City, Saudi Arabia. Arab J Geosci 6, 3929–3942 (2013). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12517-012-0649-8
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12517-012-0649-8