Abstract
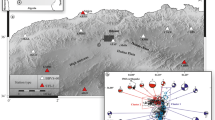
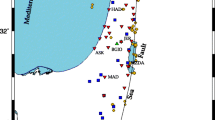
Gulf of Aqaba is recognized as an active seismic zone where many destructive earthquakes have occurred. The estimation of source parameters and coda Q attenuation are the main target of this work. Fifty digital seismic events in eight short-period seismic stations with magnitude 2.5–5.2 are used. Most of these events occurred at hypocentral depths in the range of 7–20 km, indicating that the activity was restricted in the upper crust. Seismic moment, M o, source radius, r, and stress drop, Δσ, are estimated from P- and S-wave spectra using the Brune’s seismic source model. The average seismic moment generated by the whole sequence of events was estimated to be 4.6E + 22 dyne/cm. The earthquakes with higher stress drop occur at 10-km depth. The scaling relation between the seismic moment and the stress drop indicates a tendency of increasing seismic moment with stress drop. The seismic moment increases with increasing the source radius. Coda waves are sensitive to changes in the subsurface due to the wide scattering effects generating these waves. Single scattering model of local earthquakes is used to the coda Q calculation. The coda with lapse times 10, 20, and 30 s at six central frequencies 1.5, 3, 6, 12, 18, 24 Hz are calculated. The Q c values are frequency dependent in the range 1–25 Hz, and are approximated by a least squares fit to the power law [\( {Q_c}(f) = {Q_o}{(f/{f_o})^\eta } \)]. The average of Q c values increases from 53 ± 10 at 1.5 Hz to 700 ± 120 at 24 Hz. The average of Q o values ranges from 13 ± 1 at 1.5 Hz to 39 ± 4 at 24 Hz. The frequency exponent parameter η ranges between 1.3 ± 0.008 and 0.9 ± 0.001.
يعتبر خليج العقيه من المناطق ذات النشاط الزلزالى الكبير حيث تحدث فيه كثير من الزلازل المدمره. ولقد كان الهدف الرئيسى لهذا البحث هو استنتاج معاملات المصدر ومعامل اضمحلال موجات الكودا. استخدم فى هذا البحث 50 زلزال مسجل فى 8 محطات زلازل قصيره المدى بقوه تتراح بين 2.5 -5.2. معظم هذه الزلاول تقع على اعماق تتراوح من 7 الى 30 كم. تم حساب العزم السيزمى وطول الفالق تغيير الاجهاد باستخدام نموذج برون السيزمى لكلا من الطيف الزلزالى للموجات الاوليه والثانويه. تم استنتاج الاتى متوسط العزم السيزمى لكل الزلازل 22+4.6 داين/سم والزلازل ذات الاجهاد العالى تحدث على عمق 10 كم. العلاقه بين العزم السيزمى ومعامل تغيير الاجهاد علاقه طرديه (ازدياد بين العزم السيزمى مع ازدياد معامل تغيير الاجهاد). يزداد العزم السيزمى مع ازدياد طول الفالق. موجات الكودا حساسه للتغيرات التحت سطحيه لتأثير التشتت الذى ينتج من هذه الموجات. استخدم نموذج التشتت الفردى للزلازل المحليه لحساب معامل الإضمحلال لموجات الكودا. حسب معامل الإضمحلال لموجات الكودا للازمنه 10 , 20 و30 ثانيه لست ترددات 1.5; 3; 6; 12; 18 و 24 هرتز. قيم متوسط معامل الكودا عند 30 ثانيه تتراوح بين 53±10 للتردد 1.5 هرتر الى 700±120 للتردد 24 هرتز. وتتراوح من 13±1 عند تردد 1.5 الى 39±4 عند تردد 24 هرتز.





Similar content being viewed by others
References
Abdel-Fattah AK, Hussein HM, Ibrahim EM, Abu El Atta AS (1997) Fault plane solutions of the 1993 and 1995 Gulf of Aqaba earthquakes and their tectonic implications. Ann Geofisica XL 6:1555–1564
Abdel-fattah Ali K, Hussein HM, El-Hady Sh (2006) Another look at the 1993 and 1995 Gulf of Aqaba earthquakes from the analysis of teleseismic waveforms. Acta Geophys 54(3):260–279
Aki K (1980) Attenuation and scattering of shear waves in the lithosphere. J Geophys Res 85:6496–6504
Aki K, Chouet B (1975) Origin of coda waves: source, attenuation and scattering effects. J Geophys Res 80:3322–3342
Badawy A (1996) Seismicity and kinematic evolution of the Sinai plate, L. Eötvös University, Budapest, Ph.D. thesis, pp 115
Badawy (1999) Historical seismicity of Egypt. Acta Geodaeteica Geophys Hung 34(1–2):119–135
Badawy (2005) Seismicity of Egypt. Seismol Res Lett 76(2):149–160
Barton N (2007) Rock quality, seismic velocity, attenuation and anisotropy. Taylor & Francis Group, pp 729
Ben-Avraham Z (1985) Structural framework of the Gulf of Elat (Aqaba), northern Red Sea. J Geophys Res 90:703–726
Berthelot F (1986) Etude thermique du Golfe de Suez dans son context géodynamique. Thése Univ Pierre et Marie Curie, Paris, p 200
Boore DM, Boatwright J (1984) Average body wave radiation coefficients. Bull Sei Soc Am 74(5):1615–1620
Boatwright J (1985) Characteristics of aftershock sequence of the Borah peak, Idaho earthquake determined from digital recording of the events. Bull Sei Soc Am 75:1265–1284
Brune JN (1970) Tectonic stress and the spectra of seismic shear waves from earthquakes. J Geophys Res 75:4997–5009
Campillo M, Margerin L, Aki K (1998) Seismology. In: Reseach Groupp POAN (ed) New asps of electromagnetic and acoustic wave diffusions. Springer, New York, pp 87–89
Courtillot V, Armijo R, Tapponnier P (1987) The Sinai triple junction revisited. Tectonophysics 14:151–168
Dainty AM, Duckworth RM, Tie A (1987) Attenuation and back scattering from local coda. Bull Sei Soc Am 77:1728–1747
Deif A, Abou Elenean K, El Hadidy M, Tealeb A, Mohamed A (2009) Probabilistic seismic hazard maps for Sinai Peninsula, Egypt
Frankel A (1991) Mechanisms of seismic attenuation in the crust: scattering and anelasticity in New York, South Africa, and Southern California. J Geophys Res 96:6269–6289
Garfunkel Z (1988) The pre-quaternary geology of Israel. In: Yom-Tov Y, Tchernov E (eds) Monographiae biologicae. Dr. W. Junk Publishers, The Zoogeography of Israel, pp 627–634
Horowitz A (1987) Palynological evidence for the age and rate of sedimentation along the Dead Sea Rift, and structural implications. Tectonophysics 141:107–115
Kebeasy RM (1990) Seismicity. In Geology of Egypt, ed. R. Said, 51–59 Rotterdam: Balkema
Le Pichon X, Gaulier JM (1988) The rotation of Arabia and the Levant fault system. Tectonophysics 153:271–294
Maamoun M (1978) Helwan seismic magnitude scale. Academy of scientific research and technology, Helwan Institute of Astronomy and Geophysics, Bulletin No. 169
Margerin L, Campillo M, Shapiro N, Van Tiggelen BB (1999) Residence time of diffuse waves in the crust as a physical interpretation of coda Q; application to a seismogram recorded in Mexico. Geophys J 138:343–352
Masuda T, Takagi A (1978) Source parameters estimations for small earthquakes, Sci. Rep. Tohoku Univ., Ser. 5, Geophysics, v25
Meissner R (1989) Rupture, creep, lamellae and crocodile: happening in the continental crust. Terra Nova 1:17–28
Sato H, Fehler MC (1998) Seismic wave propagation and scattering in the heterogeneous Earth, modern acoustics and signal processing. AIP Press, Springer, New York, Inc
Singh DD, Aladino G, Bragato PL (2001) Coda Q c attenuation and source parameter analysis in Friuli (NE Italy) and its vicinity. Pure Appl Geophys 158:1737–1761
Steckler MS, Ten Brink US (1986) Lithospheric strength variations as a control on new plate boundaries: examples from the northern Red Sea region. Earth PlanetSci Lett 79:120–132
Woodgold CRD (1994) Coda Q in the Charlevoix, Quebec, region: lapse-time dependence and spatial and temporal comparisons. Bull Seism Soc Am 84:1123–1131
Acknowledgments
We want to express our deep thanks to Prof. Dr.\ M. M. Dessokey for his valuable discussions, advice and encouragement. We want to thank our colleagues in Helwan Seismological Center, for their help and providing data, necessary for this work. Deep thanks to Mr. Mahmoud Samy for his efforts in providing us the software used in this work.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Morsy, M.A., El Hady, S. & El-Meneam, E.A. Source parameters of some recent earthquakes in the Gulf of Aqaba, Egypt. Arab J Geosci 5, 943–952 (2012). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12517-010-0206-2
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12517-010-0206-2