Abstract
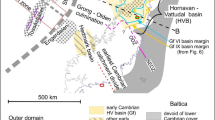
This paper describes the updated stratigraphy, structural framework and evolution, and hydrocarbon prospectivity of the Paleozoic, Mesozoic and Cenozoic basins of Yemen, depicted also on regional stratigraphic charts. The Paleozoic basins include (1) the Rub’ Al-Khali basin (southern flanks), bounded to the south by the Hadramawt arch (oriented approximately W–E) towards which the Paleozoic and Mesozoic sediments pinch out; (2) the San’a basin, encompassing Paleozoic through Upper Jurassic sediments; and (3) the southern offshore Suqatra (island) basin filled with Permo-Triassic sediments correlatable with that of the Karoo rift in Africa. The Mesozoic rift basins formed due to the breakup of Gondwana and separation of India/Madagascar from Africa–Arabia during the Late Jurassic/Early Cretaceous. The five Mesozoic sedimentary rift basins reflect in their orientation an inheritance from deep-seated, reactivated NW–SE trending Infracambrian Najd fault system. These basins formed sequentially from west to east–southeast, sub-parallel with rift orientations—NNW–SSE for the Siham-Ad-Dali’ basin in the west, NW–SE for the Sab’atayn and Balhaf basins and WNW–ESE for the Say’un-Masilah basin in the centre, and almost E–W for the Jiza’–Qamar basin located in the east of Yemen. The Sab’atayn and Say’un–Masilah basins are the only ones producing oil and gas so far. Petroleum reservoirs in both basins have been charged from Upper Jurassic Madbi shale. The main reservoirs in the Sab’atayn basin include sandstone units in the Sab’atayn Formation (Tithonian), the turbiditic sandstones of the Lam Member (Tithonian) and the Proterozoic fractured basement (upthrown fault block), while the main reservoirs in the Say’un–Masilah basin are sandstones of the Qishn Clastics Member (Hauterivian/Barremian) and the Ghayl Member (Berriasian/Valanginian), and Proterozoic fractured basement. The Cenozoic rift basins are related to the separation of Arabia from Africa by the opening of the Red Sea to the west and the Gulf of Aden to the south of Yemen during the Oligocene-Recent. These basins are filled with up to 3,000 m of sediments showing both lateral and vertical facies changes. The Cenozoic rift basins along the Gulf of Aden include the Mukalla–Sayhut, the Hawrah–Ahwar and the Aden–Abyan basins (all trending ENE–WSW), and have both offshore and onshore sectors as extensional faulting and regional subsidence affected the southern margin of Yemen episodically. Seafloor spreading in the Gulf of Aden dates back to the Early Miocene. Many of the offshore wells drilled in the Mukalla–Sayhut basin have encountered oil shows in the Cretaceous through Neogene layers. Sub-commercial discovery was identified in Sharmah-1 well in the fractured Middle Eocene limestone of the Habshiyah Formation. The Tihamah basin along the NNW–SSE trending Red Sea commenced in Late Oligocene, with oceanic crust formation in the earliest Pliocene. The Late Miocene stratigraphy of the Red Sea offshore Yemen is dominated by salt deformation. Oil and gas seeps are found in the Tihamah basin including the As-Salif peninsula and the onshore Tihamah plain; and oil and gas shows encountered in several onshore and offshore wells indicate the presence of proven source rocks in this basin.
ملخص
الورقة تقوم بوصف الاستراتيجرافيا المحدثة للبنية والتطور التركيبي وكذا الآفاق الهيدروكربونية لأحواض الباليوزويك, الميزوزويك والكينوزويك في اليمن والموصوفة وبصورة إقليمية على العمود الاستراتيجرافي. أحواض الباليوزويك تحتوي على (1) حوض الربع الخالي (الحافة الجنوبية) والتي تحد من الجهة الجنوبية بواسطة قوس حضرموت والتي تتلاشى عليه رسوبيات الباليوزويك والميزوزويك (2) حوض صنعاء والذي يشمل رسوبيات الباليوزويك وحتى الجوراسي الأعلى (3) حوض الجزء الجنوبي الغربي المغمور من جزيرة سقطرى والممتلىء بترسيبات البرمو- ترياسيك والتي تقارن مع ترسيبات حوض الكارو في شرق أفريقيا. الأحواض الرسوبية للميزوزويك تشكلت نتيجة لتهشم قارة جوندوانا وانفصال الهند/مدغشقر من الجزيرة العربية/أفريقيا خلال الجوراسي العلوي/الكريتاسي الأسفل. الأحواض الخمسة للميزوزويك تشكلت على امتداد الصدوع المتواجدة في الأعماق والتي أعيد نشاطها ذات الاتجاه شمال/ غرب - جنوب/شرق والمعروفة بنظام صدوع نجد والتي تعود إلى حقب التحت كمبري. أحواض الميزوزويك تكونت بصورة شبه متوازية من الغرب إلى الشرق وحتى جنوب/شرق مع اتجاه الصدوع الرئيسية فحوض سهام - الضالع اتخذ الاتجاه شمال/شمال/غرب - جنوب/جنوب/شرق وحوض السبعتين على الاتجاه شمال /غرب - جنوب /شرق و حوض سيئون - المسيلة في الوسط اتخذ الاتجاه غرب/شمال/غرب - شرق/جنوب/شرق وحوض جزع - قمر والواقع في شرق اليمن يتخذ الاتجاه شرق/غرب. حوض السبعتين وحوض سيئون - المسيلة هما الحوضان اللذان يحتويان على النفط والغاز في الوقت الحالي, الصخور الخازنة تم تعبئتها من صخور الطفل لتشكيلة مضبي. الصخور الخازنة الرئيسية في حوض السبعتين تحتوي على الصخور الرملية لتشكيلة السبعتين والصخور الرملية لعضو اللام ذو العمر التيثوني وكذا صخور الأساس المتشققة ذات العمر البروتروزويك نتيجة لهبوط الطبقات بفعل التصدعات, بينما الصخور الخازنة الرئيسية في حوض سيئون - المسيلة عبارة عن الصخور الرملية لتشكيلة القشن ذات العمر الهاوترافيان/باراميان وعضو الغيل ذو العمر البرياسي/الفالانجيني وكذا في صخور الأساس المتشققة ذات العمر البروتروزويك. أحواض السينوزويك المتصدعة مرتبطة بانفصال الجزيرة العربية من أفريقيا من خلال انفتاح البحر الأحمر في الغرب وخليج عدن في الجنوب وذلك في حقب الأليجوسين حتى الحاضر. أحواض السينوزويك ملئت برسوبيات تتعدى سماكتها 3 ألاف متر وتتميز بتنوعها الصخري واختلاف الانتشار على المستوى الأفقي والرأسي. ألأحواض الانفلاقية لخليج عدن تحوي حوض المكلا - سيحوت وحوض حورة - أحور وحوض عدن - أبين وكلها تتجه شرق/شمال/شرق - غرب/جنوب/غرب وتنتشر في اليابسة والمغمورة نتيجة للفوالق الانفتاحية والهبوط الإقليمي والتي أثرت في الأجزاء الجنوبية لليمن بصورة دورية. الانفلاق المحيطي لخليج عدن يعود إلى بداية حقب الميوسين. الأبار الاستكشافية التي حفرت في حوض المكلا – سيحوت بينت دلالات بترولية في رسوبيات العصر الكريتاسي وحتى النيوجين, إضافة إلى الاكتشاف البترولي الغير تجاري في بئر شرمة في صخور الحجر الجيري المتشقق لتشكيلة الحبشية ذات العمرالأيوسين الأوسط. حوض تهامه ذات الاتجاه شمال/شمال/غرب-جنوب/جنوب/شرق والذي تكون في حقب الأليجوسين المتأخر أما القشرة المحيطية فيعود تشكيلها إلى حقب البليوسين. استراتيجرافيا الميوسين الأعلى في المنطقة المغمورة في البحر الأحمر تحتوي في الغالب على ترسيبات سميكة من الملح. دلالات الغاز والبترول والموجودة في جزيرة الصليف وكذلك الدلالات في العديد من الأبار الاستكشافية سواءً في اليابسة أو المغمورة تؤكد على وجود صخور مصدرية ناضجة في حوض تهامة.





Similar content being viewed by others
References
Ahlbrandt TS (2002) Madbi Amran/Qishn Total Petroleum System of the Ma’Rib–Al Jawf/Shabwah, and Masila–Jeza Basins, Yemen. USGS Bull 2202-G:1–28
As-Saruri ML (1999) Lithostrtigraphie der Tertiaer-Sedimente der Republik Jemen. Schriftenr Geol Wiss H 10:1–131
As-Saruri ML, Beydoun ZR (1998) Lithostratigraphic subdivision of the outcropping late Cenozoic Shihr Group, Republic of Yemen. Zeitschr Geol Wiss 26(5/6):705–724
As-Saruri ML, Wiefel H (1998) The lithological–structural provinces of the basement in the central region of southwestern Arabian Peninsula. Zeitschr Geol Wiss 26(5–6):731–741
Beydoun ZR (1964) The stratigraphy and structure of the eastern Aden Protectorate. In: Overseas Geol. and Mineral Resources, Bull Supp 5, HMSO, London, 1–107
Beydoun ZR (1966) Eastern Aden Protectorate and part of Dhufar. USGS Prof Pap 560-H:1–49
Beydoun ZR (1989) The hydrocarbon prospects of the Red Sea–Gulf of Aden: a review. J Petrol Geol 12:125–144
Beydoun ZR (1991) Arabian plate hydrocarbon geology and potential. A plate tectonic approach. AAPG Stud Geol 33:1–77
Beydoun ZR, As-Saruri ML (1998) Phanerozoic depositional basins and inter-basinal highs of Yemen: their structural framework and sedimentary cover. Zeitschr Geol Wiss 26(5/6):517–529
Beydoun ZR, Bichan HR (1970) Geology of Socotra Island, Gulf of Aden. Q J Geol Soc Lond 125:413–446
Beydoun ZR, Greenwood JEGW (1968) Aden protectorate and Dhofar. In: Dubertret L (ed) Lexique Stratigraphique International III, fasic, 10b2 CNRS. Asie, Paris, pp 1–128
Beydoun ZR, Sikander AH (1992) The Red Sea–Gulf of Aden, re-assessment of hydrocarbon potential. Mar Pet Geol 9:474–485
Beydoun ZR, As-Saruri ML, Baraba RS (1996) Sedimentary basins of the Republic of Yemen: their structural evolution and geological characteristics. Rev Inst Fr Pétrol 51(6):763–775
Beydoun ZR, As-Saruri ML, El-Nakhal H, Al-Ganad IN, Baraba RS, Nani AO, Al-Aawah MH (1998) International lexicon of stratigraphy, Republic of Yemen. VIII, Asia, fasc, 10b2. IUGS Publ 34:1–245
Bosellini A (1989) The continental margin of Somalia: their structural evolution and sequence stratigraphy. Mem Sci Geol XLI:373–458
Bosence DWJ (1997) Mesozoic rift basins of Yemen. Mar Pet Geol 14(6):611–616
Bosworth W, Huchon P, McClay K (2005) The Red Sea and Gulf of Aden basins. J Afr Earth Sci 43:334–378
Bott WF, Smith BA, Oakes G, Sikander AH, Ibrahim AI (1992) The tectonic framework and regional hydrocarbon prospectivity of the Gulf of Aden. J Petrol Geol 15:211–243
Bott WF, Richardson SM, Harbury NA, Johns C, Scott D, Samuel MA, Granmer FS, Smith BA, Hollar WD (1994) Remote Socotra and ancillary islands: recent field investigation of Paleozoic and Mesozoic outcrops and their relationship to speculative petroleum system. GEO/94, Proc 1:216–233
Brannan J, Gerdes KD, Newth IR (1997) Tectono-stratigraphic development of the Qamar basin, Eastern Yemen. Mar Pet Geol 14(6):701–730
Brannan J, Sahota G, Gerdes KD, Berry JAL (1999) Geological evolution of the central Marib–Shabwah basin, Yemen. GeoArabia 4(1):9–34
Brise ACR, Bott WF, Morrison J, Samuel MA (1997) The Mesozoic and early tertiary tectonic evolution of the Socotra area, eastern Gulf of Aden, Yemen. Mar Pet Geol 14(6):675–684
Burser BH, Bosence DWJ (1998) Sedimentation and tectonics of rift basins: Red Sea−Gulf of Aden. Chapman and Hall, London
Camp VE, Roobol MJ (1989) The Arabian continental alkali basalt province: part I. Evolution of Harrat Rahat, Kingdom of Saudi Arabia. Geol Soc Am Bull 101:71–95
Camp VE, Roobol M, Hooper PR (1991) The Arabian continental alkali basalt province: part II. Evolution of Harrats Khaybar, Ithnayn, and Kura. Kingdom of Saudi Arabia. Geol Soc Am Bull 103:363–391
Camp VE, Roobol MJ, Hooper PR (1992) The Arabian continental alkali basalt province: Part III. Evolution of Harrats Kishb. Kingdom of Saudi Arabia. Geol Soc Am Bull 104:379–396
Cannon RT, Simiyu Sambi WMN, Karanja FA (1981) The proto-Indian ocean and a probable Paleozoic Mesozoic triradial rift system in east Africa. Earth Planet Sci Lett 52:419–426
Christmann P, Al-Janad I, Labbe JF, Lambert A, Letalent J, Al-Muflihi Y, Shamsan MA (1984) Evaluation of mineral resource potential 1983–1984 field season: northeast area of Yemen Arab Republic, Northeast project. Report of BRGM 84 RDM062PA BRGM, BP 6069-45060 Orleans Cedex, France
Coleman RG (1993) Geologic evolution of the Red Sea. Oxford monographs on geology and geophysics no. 24. Oxford University Press, New York, pp 1–186
Coney P, Jones DL, Monger JWH (1980) Cordilleran suspect terranes. Nature 2988:329–333
Courtillot V (1980) Opening of the Gulf of Aden and Afar by progressive tearing. Phys Earth Planet Inter 21:343–350
Csato I (2005) Extensional tectonics and salt structure, Marib-Shabwa Basin, Yemen. AAPG Annual Convention, Dallas, pp 1–6
Csato I, Habib A, Kocz I, Kovacs Z, Milota K (2001) Play concepts of oil exploration in Yemen. Oil Gas J 99(23):68–74
Davison L, Al-Kadasi M, Al-Khirbash S, Al-Subbary AK, Baker J, Blakey S, Bosence DWJ, Dart C, Heaton R, McClay K, Menzies M, Nichols G, Owen L, Yelland A (1994) Geological evolution of the southeastern Red Sea Rift margin, Republic of Yemen. Geol Soc Am Bull 106:449–456
Davison L, Bosence DWJ, Alsop GI, Al-Aawah MH (1996) Deformation and sedimentation around active Miocene salt diapers on the Tihama plain, northwest Yemen. In: Alsop GI, Blundell DJ (eds) Salt tectonics. Geol Soc Spec Publ 100:23–39
Davison I, Tatnell MR, Owen LA, Jenkins G, Baker J (1998) Tectonic geomorphology and rates of crustal processes along the Red Sea margin, north-west Yemen. In: Purser BH, Bosence DWJ (eds) Sedimentation and tectonics in rift Basins: Red Sea−Gulf of Aden. Chapman and Hall, London, pp 595–612
Delfour J (1981) Geologic tectonic and metallogenic evolution of the northern part of the Arabian Shield (Kingdom of Saudi Arabia). Bull Bur Rech Geol Min Fr 2 Ser 2(1/2):1–19
Dyer RA, Husseini MI (1991) The western Rub’ Al-Khali Infracambrian graben system. Proc SPE Middle East Oil Show, Nov. 1991, Bahrain, pp 505–512 (SPE 21396)
Ellis RA, Kerr HM, Cornwall CP, Williams DO (1996) A tectono-stratigraphic framework for Yemen and its implications for hydrocarbon potential. Petrol Geosci 2:29–42
Fantozzi PL, Sgavetti M (1998) Tectonic and sedimentary evolution of the Gulf of Aden continental margins: new structural and stratigraphic data from Somalia and Yemen. In: Burser BH, Bosence DWJ (eds) Sedimentation and tectonics of rift basins, Red Sea−Gulf of Aden. Chapman & Hall, London, pp 56–76
Fournier M, Huchon Ph, Khanbari Kh, Leroy S (2007) Segmentation and along-strike asymmetry of the passive margin in Socotra, eastern Gulf of Aden: are they controlled by detachment faults? Geochem Geophys Geosyst 8(3):Q03007. doi:10.1029/2006GC001526
Fournier M, Chamot-Rooke N, Petit C et al (2010) Arabia–Somalia plate kinematics, evolution of the Aden–Owen–Carlsberg triple junction, and opening of the Gulf of Aden. J Geophys Res 115:B04102. doi:10.1029/2008 JB006257
Geukens F (1960) Contribution a la geologie du Yemen. Meme Inst Geol Louvain 21:122–179
Geukens F (1966) Yemen: geology of the Arabian Peninsula. USGS Prof Pap 560-B:1–23
Ghebreab W (1998) Tectonics of the Red Sea assessed. Earth Sci Rev 45:1–44
Greenwood JEGW, Bleackley D (1967) Aden protectorate. Geol Surv Prof Pap 560-C:1–96, Washington
Greenwood WR, Anderson RE, Fleck RJ, Roberts RJ (1980) Precambrian geologic history and plate tectonic evolution of the Arabian Shield. Bulletin 24, Ministry of Oil and Mineral Resources, Jiddah, Saudi Arabia, pp 1–35
Greenwood WR, Stoeser DB, Fleck RJ, Stacey JS (1982) Late Proterozoic island arc complexes and tectonic belt in the southern part of the Arabian Shield. Kingdom of Saudi Arabia, Ministry of Oil and Mineral Resources, Open file Rep. USGS-OF-02-8
GSMEB (Geological Survey and Mineral Exploration Board) (1994) Geology and mineral resources of Yemen. Ministry of Oil and Mineral Resources, San’a, pp 1–128
Haitham FM, Nani ASO (1990) The Gulf of Aden rift: hydrocarbon potential of the Arabian sector. J Petrol Geol 13:211–220
Heaton RC, Jackson MPA, Bamahmoud M, Nani ASO (1996) Superposed Neogene extension, contraction and salt canopy emplacement in the Yemeni Red Sea. In: Jackson MPA, Roberts DG, Snelson S (eds.) Salt tectonic: a global perspective for exploration. AAPG Mem 65:333–351
Huchon P, Khanbari Kh (2003) Rotation of the syn-rift stress field of the northern Gulf of Aden margin, Yemen. Tectonophysics 364:147–166
Hughes GW, Beydoun ZR (1992) The Red Sea–Gulf of Aden: biostratigraphy, lithostratigraphy and palaeoenvironments. J Petrol Geol 15(2):135–156
Hughes GW, Varoll O, Beydoun ZR (1991) Evidence for Middle Oligocene rifting of the Gulf of Aden and for Late Oligocene rifting of the southern Red Sea. Mar Pet Geol 8:354–358
Husseini MI (1989) Tectonic and depositional model of Late Precambrian–Cambrian of Arabian and adjoining plates. AAPG Bull 73:1117–1131
Isaev EN (1987) Structural–geophysical model of the basement complex of the Gulf of Aden–Red Sea region. Tectonophysics 143:181–192
Isaev EN, Samoilyuk VV, Isaev IV Chuprov AI (1984) Anomalous magnetic field of the P.D.R.Yemen: Explanatory notes to the map of 1:500.000 and 1:1.000.000 scales. Unpublished report, Moscow MOM, San’a
Johnson PR, Vranas GJ (1984) The origin and development of the Proterozoic rocks of the Arabian Shield: an analysis of terranes and mineral environments. Saudi Arabian Deputy Ministry of Mineral Resources, Open File Report Rf-OF-04-32
Jungwirth J, As-Saruri ML (1990) Structural evolution of the platform cover of the southern Arabian Peninsula. Zeitschr Geol Wiss 18(6):505–514
King WA, Mills BR, Scoot G, Abdillah AA (2003) The Masilah Fields, Republic of Yemen. In: Halbouty MT (eds) Giant oil and gas fields of the decade 1990–1999. AAPG Spec Publ 17:1–24
Kruck W, Thiele J (1983) Late Paleozoic glacial deposits in the Yemen Arab Republic. Geol Jahrb B 46:3–29
Lamare P (1930) Nature et extension des depots secondaires dans L Arabie, I Ethiopie et les pays Somalia. Mem Soc Geol Fr s 6, fasc 3–4, 14:49–68
Leckie DA, Rumpel T (2003) Tide-influenced sedimentation in a rift basin—Cretaceous Qishn Formation, Masila Block, Yemen: a billion barrel oil field. AAPG Bull 87(6):987–1013
Leroy S et al (2004) From rifting to spreading in the eastern Gulf of Aden: a geophysical survey of a young oceanic basin from margin to margin. Terra Nova 16:185–192
Lindquist SJ (1999) The Red Sea Basin Province: Sud-Nubia and Magna Petroleum Systems. US Geol Surv Open-File Rep OF99-50-A
Little OH (1925) The geography and geology of Mukalla (South Arabia). Geol Surv Egypt, Cairo, pp 1–250
Manighetti I, Tapponnier P, Gillot PY, Jacques E, Courtillot V, Armijo R, Ruegg JC, King G (1998) Propagation of rifting along the Arabia–Somalia plate boundary into Afar. J Geophys Res 103:4947–4974
Mattash MA, Balogh K (1994) K–Ar radiometric age data on Cenozoic volcanics and their associated intrusion from Yemen. Acta Mineral Petrogr Szeged 35:83–92
McClusky S, et al (2010) Kinematics of the southern Red Sea–Afar triple junction and implications for plate dynamics. Geophys Res Lett 37, LO5310, 5, doi:10.1029/2009GL041127
Paul SK (1990) People’s Democratic Republic of Yemen: a future oil province. In: Brooke J (ed) Classic petroleum provinces. Geol Soc Spec Publ 50:329–339
Putnam PE, Kendall G, Winter DA (1997) Estuarine deposits of the Upper Qishn Formation (Lower Cretaceous), Masila region, Yemen. AAPG Bull 81(8):1306–1329
Redfern P, Jones JA (1995) The interior rifts of the Yemen: analysis of basin structure and stratigraphy in a regional plate tectonic context. Basin Res 7:337–356
Richardson SM, Bott WF, Smith BA, Hollar WD, Birmingham PM (1994) Offshore Socotra, Republic of Yemen: potential for a new hydrocarbon province. GEO/94, Proceedings II:811–823
Richardson SM, Bott WF, Smith BA, Hollar WD, Birmingham PM (1995) A new hydrocarbon ‘plays’ area offshore Socotra Island, Republic of Yemen. J Petrol Geol 18:5–28
Saint-Marc P (1978) Arabian Peninsula. In: Moullade M, Nairn AED (eds) The Phanerozoic geology of the world, part II. The Mesozoic, Elsevier Sci Publ Comp Amsterdam, pp 435–462
Samuel MA, Harbury NA, Bott WF, Thabet A (1997) Fields observation from Socotran platform: their interpretation and correlation to Southern Oman. Mar Pet Geol 14(6):661–73
Schramm et al (1986) Geological survey and mineral prospecting in the Habaan–Mukalla area, Final Report, Geol. Forschung und Erkundung, Halle, Germany, Department of geological Survey and Mineral Exploration, Aden, Unpublished report, Vols. 1–5
Sykes RM, Abu Risheh AK (1989) Exploration of deep Paleozoic and Precambrian plays in the Sultanate of Oman. In: OAPEC/ADNOC Seminar on Deep Formations in the Arab Countries: Hydrocarbon potential and exploration techniques. Abu Dabi, Proceedings Country Reports and Gas Studies, E71–E113
Trad F, Masse P, Walgenwitz F, Gruneisen P (1991) The volcanic passive margin in the vicinity of Aden, Yemen. Bull Cent Rech Explor-Prod Elf-Aquitaine 15:1–9
von Wissmann H (1932) Übersicht über Aufbau und Oberflächen-Gestaltung Arabiens. Zeitschr Erkunde. Berlin 9(10):335–357
von Wissmann H, Ratjens K, Kossmat F (1942) Beiträge zur Tektonik Arabiens. Geol Rundsch 33(4–6):221–353
Watchorn F, Nicols GJ, Bosence DWJ (1998) Rift related sedimentation and stratigraphy, southern Yemen (Gulf of Aden). In: Purser BH, Bosence DWJ (eds) Sedimentation and tectonics of rift basins: Red Sea–Gulf of Aden. Chapman & Hall, London, pp 165–189
Whitehouse MJ, Windley BF, Stoeser DB, Al-Khirbash S, Ba-Bttat MAO, Haider A (2001) Precambrian basement character of Yemen and correlations with Saudi Arabia and Somalia. Precambrian Res 105:357–369
Windley BF, Whitehouse MJ, Ba-Bttat MAO (1996) Early Precambrian gneiss terranes and Pan-African Island arcs in Yemen: crustal accretion of the eastern Arabian Shield. Geology 24(2):131–143
Acknowledgements
The authors are grateful to anonymous reviewers and to Dr. François Roure for helpful comments that improved this paper.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
As-Saruri, M.A., Sorkhabi, R. & Baraba, R. Sedimentary basins of Yemen: their tectonic development and lithostratigraphic cover. Arab J Geosci 3, 515–527 (2010). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12517-010-0189-z
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12517-010-0189-z