Abstract
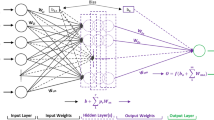
An ideally performed blasting operation enormously influences the mining overall cost. This aim can be achieved by proper prediction and attenuation of flyrock and backbreak. Poor performance of the empirical models has urged the application of new approaches. In this paper, an attempt has been made to develop a new neuro-genetic model for predicting flyrock and backbreak in Sungun copper mine, Iran. Recognition of the optimum model with this method as compared with the classic neural networks is faster and convenient. Genetic algorithm was utilized to optimize neural network parameters. Parameters such as number of neurons in hidden layer, learning rate, and momentum were considered in the model construction. The performance of the model was examined by statistical method in which absolutely higher efficiency of neuro-genetic modeling was proved. Sensitivity analysis showed that the most influential parameters on flyrock are stemming and powder factor, whereas for backbreak, stemming and charge per delay are the most effective parameters.
Abstract
تنفيذ عملية التفجير يؤثر بشكل كبير من الناحية المثالية تكاليف التعدين عموما. ويمكن تحقيق هذا الهدف عن طريق التنبؤ السليم وتخفيف flyrock وbackbreak. وحثت ضعف الأداء من نماذج تجريبية لتطبيق النهج الجديد. في هذه الورقة ، وقد بذلت محاولة لوضع نموذج جديد الاعصاب الوراثية للتنبؤ flyrock وbackbreak في منجم للنحاس Sungun وإيران. الاعتراف النموذج الأمثل مع هذا الأسلوب بالمقارنة مع الشبكة العصبية الكلاسيكي هو أسرع ومريحة. واستخدم الخوارزمية الجينية لتحسين المعلمات الشبكة العصبية. واعتبرت معلمات مثل عدد الخلايا العصبية في طبقة خفية ، معدل التعلم والزخم في بناء النموذج. تم فحص أداء نموذج من الأسلوب الإحصائي الذي ثبت كفاءة أعلى على الاطلاق من وضع نماذج الاعصاب الوراثية. حساسية التحليل أظهرت أن المعلمات الأكثر تأثيرا على flyrock هي النابعة ومسحوق للعامل في حين backbreak الناشئة والمسؤول عن تأخير في والمعلمات الأكثر فعالية.








Similar content being viewed by others
References
Baheer I (2000) Selection of methodology for modeling hysteresis behavior of soils using neural networks. Journal of Compuert Aided Civil Infrastructure Engineering 5(6):445–63
Bajpayee TS, Rehak TR, Mowrey GL, Ingram DK (2000) A summary of fatal accidents due to flyrock and lack of blast area security in surface mining, 1989–1999. Proceedings of the 27th annual conference on explosives and blasting technique, vol I. International Society of Explosives Engineers, Cleveland
Bhandari S (1997) Engineering rock blasting operations. A.A. Balkema, Rotterdam
Bornholdt S, Graudenz D (1992) General asymmetric neural networks and structure design by genetic algorithms. Neural Netw 5:327–334
De Jong KA (1975) Analysis of the behavior of a class of genetic adaptive systems. Ph.D. thesis. University of Michigan, Ann Arbor
Finol J, Guo YK, Dong Jing X (2001) A rule-based fuzzy model for the prediction of petro-physical rock parameters. J Petrol Sci Eng 29:97–113
Fletcher LR, D’Andrea DV (1986) Control of flyrock in blasting. Proceedings of the 12th annual conference on explosives and blasting technique. International Society of Explosives Engineers, Cleveland, pp 167–177
Fogel DB, Fogel LJ, Porto VW (1990) Evolving neural networks. Biol Cybern 63:487–493
Gate WC, Ortiz BLT, Florez RM (2005) Analysis of rock fall and blasting backbreak problems. Proceedings of the American rock mechanics conference 5:671–680
Gen M, Cheng R (2000) Genetic algorithms and engineering optimization. Ashikaga Institute of Technology, Ashikaga, Wiley-Interstice publication
Gokceoglu C, Zorlu K (2004) A fuzzy model to predict the uniaxial compressive strength and the modulus of elasticity of a problematic rock. Eng Appl Artif Intell 17:61–72
Goldberg DE (1989) Genetic algorithms in search, optimization and machine learning. Addison-Wesley, Reading
Grima A, Verhoef PNW (1999) Forecasting rock trencher performance using fuzzy logic. Int J Rock Mech Min Sci 36(4):413–432
Haupt RL, Haupt SE (2004) Practical Genetic Algorithms, 2nd edn. Wiley, Hoboken
Hegazy T, Moselhi O, Fazio P (1994) Developing practical neural network applications using back-propagation. Microcomput Civ Eng 9:145–159
Heisterman J (1989) Parallel algorithms for learning in neural networks with evolution strategy. Parallel Comput 12
Heisterman J (1990) Learning in neural nets by genetic algorithms. Proceeding of Parallel Processing in Neural Systems and Computers (ICNC). Elsevier, Amsterdam, pp 165–168
Holland J (1975) Adaptation in natural and artificial systems. University of Michigan Press, Ann Arbor
Holmeberg R, Persson G (1976) The effect of stemming on the distance of throw of flyrock in connection with hole diameters. Swedish Detonic Research Foundation, Stockholm: Report DS 1
Hustrulid W (1999) Blasting principles for open pit mining, vol 1. A.A. Balkema, Rotterdam
Institute of Makers of Explosives (IME) (1997) Glossary of commercial explosives industry terms. Safety publication, no. 12. Institute of Makers of Explosives, Washington.
Jenkins SS (1981) Adjusting blast design for best results. A.A. Balkema, Pit and Quarry, Rotterdam
Jong YH, Lee CI (2004) Influence of geological conditions on the powder factor for tunnel blasting. Int J Rock Mech Min Sci 41:533–538
Kahraman S, Altun H, Tezekici BS, Fener M (2006) Sawability prediction of carbonate rocks from shear strength parameters using artificial neural networks. Int J Rock Mech Min Sci 43:157–164
Khandelwal M, Singh TN (2006) Evaluation of blast-induced ground vibration predictors. Soil Dyn Earthquake Eng 27:116–125
Kinato H (1990) Empirical studies on the speed of Convergence of Neural Network Training using Genetic Algorithms. In 8th national conference on artificial intelligence, vol II. AAAI, MIT Press, pp 798–795
Koike K, Matsuda S (2003) Characterizing content distributions of impurities in a limestone mine using a feed forward neural network. Nat Resour Res 12(3):209–222
Konya CJ et al (2003) Rock blasting and overbreak control. National Highway Institute, FHWA-HI-92-001, USA
Konya CJ, Walter EJ (1991) Rock blasting and overbreak control. FHWA Report- FHWA-HI-92-001
Kopp JW (1994) Observation of flyrock at several mines and quarries. Proceeding of 20th conference on explosives and blasting technique, Austin, Texas, pp 75–81
Ladegaard-Pedersen A, Persson A (1973) Flyrock in blasting II, experimental investigation. Swedish Detonic Research Foundation, Stockholm: Report DS 13
Langefors U, Kishlstrom B (1963) The modern technique of rock blasting. Wiley, New York
Lopez JC, Lopez JE (1995) Drilling and blasting of rocks. A.A. Balkema, Rotterdam
Lundborg N (1974) The hazards of flyrock in rock blasting. Swedish Detonic Research Foundation, Stockholm: Reports DS 12
Lundborg N (1981) Risk for flyrock when blasting. Swedish Council for Building Research, Stockholm: BFR Report R 29
Marshall SJ, Harrison RF (1991) Optimization and training of feed forward neural networks by GAs. Proceeding of IEE 2nd International Conference on Artificial Neural Networks, pp 39–43
Meulenkamp F, Alveraz G (1999) Application of neural networks for the prediction of the unconfined compressive strength (UCS) from Equotip hardness. Int J Rock Mech Min Sci 36:29–39
Michalewicz Z (1996) Genetic algorithms + Data structures = Evolution programs. Springer, Heidelberg
Miller G, Todd P, Hedge S (1989) Designing neural networks using genetic algorithms. Proceeding of the 3rd International Joint Conference on Genetic Algorithms, pp 379–384
Monjezi M, Dehghani H (2008) Evaluation of effect of blasting pattern parameters on backbreak using neural networks. Int J Rock Mech Min Sci 45:1446–1453
Monjezi M, Dehghani H, Samimi Namin F (2007) Application of TOPSIS method in controlling flyrock in blasting operations. Proceedings of the 7th international science conference SGEM, Sofia, Bulgaria, pp 41–49
Monjezi M, Rezaei M, Yazdian A (2010) Prediction of backbreak in open-pit blasting using fuzzy set theory. Expert Syst Appl 37:2637–2643
Montana D, Davis C (1989) Training feed forward neural networks using genetic algorithms. Technical Report, BBN Systems and Technologies Inc, Cambridge
Neaupane KM, Adhikari NR (2006) Prediction of tunneling-induced ground movement with the multi-layer perceptron. International Journal of Tunneling and Underground Space Technology 21:151–159
Nie X, Zhang Q (1994) Prediction of rock mechanical behavior by artificial neural network: a comparison with traditional method. IV CSMR, Integral Approach to Applied Rock Mechanics. Santiago, Chile
Rehak TR, Bajpayee TS, Mowrey GL, Ingram DK (2001) Flyrock issues in blasting. Proceedings of the 27th Annual Conference on Explosives and Blasting Technique, vol. I. International Society of Explosives Engineers, Cleveland, pp 165–175
Roth J (1979) A model for the determination of flyrock range as a function of shot conditions. US Bureau of Mines contract J0387242, Management Science Associates, Los Altos
Rustan PA (1993) Minimum distance between charged boreholes for safe detonation. In: Rossamanith (ed) Rock fragmentation by blasting, FRAGBLAST-4
Sarma KS (1994) Models for assessing the blasting performance of explosives. Ph.D. thesis. University of Queensland, Brisbane.
Schiffmann WH, Joost M, Werner R (1993) Application of genetic algorithms to the construction of topologies for multilayer perceptrons. Proceeding of the international joint conference on neural networks and genetic algorithms, Innsbruk, pp 675–682
Scoble MJ, Lizotte YC, Paventi M, Mohanty BB (1997) Measurement of blast damage. Min Eng 49:103–108
Shea CW, Clark D (1998) Avoiding tragedy: lessons to be learned from a flyrock fatality. Coal Age 2:51–54
Singh TN, Singh V (2005) An intelligent approach to prediction and control ground vibration in mines. Geotech Geol Eng 23:249–262
Sivanandam SN, Deepa SN (2008) Introduction to genetic algorithms. Springer, Heidelberg
Tawadrous AS (2006) Evaluation of artificial neural networks as a reliable tool in blast design. Proceedings of the 32nd annual conference on explosives and blasting techniques. International Society of Explosives Engineers, Dallas
Tawadrous AS, Katsabanis PD (2006) Prediction of surface crown pillar stability using artificial neural networks. Int J Numer Anal Methods Geomech 31:917–31
Van Rooij AJF, Jain LC, Johnson RP (1996) Neural network training using genetic algorithms. World Scientific Publishing Co. Pvt, Ltd, Singapore
Vonk E, Jain LC, Johnson RP (1997) Automatic generation of neural network architecture using evolutionary computation. World Scientific Publishing Co. Pvt. Ltd, Singapore
Whitely D, Bogart C (1990) Genetic algorithms and neural networks: optimizing connections and connectivity. Parallel Comput 14:347–361
White DW (1993) GANNet: a genetic algorithm for searching topology and weight spaces in neural network design. Dissertation at the University of Maryland
Whitely D, Hanson T (1989) Optimizing neural networks using faster, more accurate genetic search. Proceeding of the 3rd international conference on Genetic Algorithms, San Mateo, pp 391–396
Workman JL, Calder PN (1994) Flyrock prediction and control in surface mine blasting. Proceeding of the 20th conference on Explosives and Blasting Technique, Austin, Texas, pp 59–74
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Monjezi, M., Amini Khoshalan, H. & Yazdian Varjani, A. Prediction of flyrock and backbreak in open pit blasting operation: a neuro-genetic approach. Arab J Geosci 5, 441–448 (2012). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12517-010-0185-3
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12517-010-0185-3