Abstract
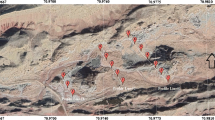
Sinkhole collapse is one of the main limitations on the development of karst areas, especially where bedrock is covered by unconsolidated material. Studies of sinkhole formation have shown that sinkholes are likely to develop in cutter (enlarged joint) zones as a result of subterranean erosion by flowing groundwater. Electrical resistivity imaging or tomography (RESTOM) is well suited to mapping sinkholes because of the ability of the technique for detecting resistive features and discriminating subtle resistivity variations. Two-dimensional electrical resistivity tomography surveys were conducted at two sinkhole sites near Cheria city where limestone is covered by about 10 m of clayey soils. A Wenner transect was conducted between the two sinkholes. The electrode spacing was 2 m. The length of transect is about 80 m. The survey results suggest that RESTOM is an ideal geophysical tool to aid in the detection and monitoring of sinkholes and other subsurface cavities.
ملخص
الانهيارات الناتجة عن الفجوات الصخرية هي واحدة من أهم العوامل المؤثرة في تنمية المناطق الكارستية ، وخصوصا عندما يكون الأساس الصخري مغطى بتربة غير معززة.
أظهرت الدراسات لتشكيل مثل هده الانهيارات أنه من المرجح أن تتطور في شكل القاطع نتيجة لتآكلت ناتجة عن تدفق المياه الجوفية.
تعتبر المقاومية الكهربائية أو التصوير المقطعي (RESTOM) مناسبة تماما لرسم الخرائط الصخرية بسبب قدرة هده التقنية للكشف عن ميزات المقاومية و اختلافات المقاومية الخفية. أجريت عملية المسح المقطعي بطريقة المقاومية الكهربائية ثنائية الأبعاد في موقعين بالقرب من مدينة الشريعة حيث أن الطبقات الجيولوجية والمكونة أساسا من الحجر الجيري مغطاة بحوالي 10 أمتار من التربة الطينية.
أجري مقطع جيوفيزيائى بطريقة Wenner بين اثنين من الفجوات الصخرية حيث كان التباعد بين كل قطب 2م و طول المقطع حوالي 80 متر.
وتشير نتائج دراسات المسح عن طريق التصوير المقطعي RESTOM أنها أداة جيوفيزيائية مثالية للمساعدة في كشف ورصد الفجوات الصخرية وغيرها من التجاويف تحت سطح الأرض.






Similar content being viewed by others
References
Al-Amoush and Abou Karaki (1997) Practical quantification of the anisotropy factor in electrical resistivity measurements, application on water exploration in Jordan, MSc. Thesis, University of Jordan
Annan AP, Cosway SW, Redman JD (1991) Water table detection with ground-penetrating radar. In: Soc. Explor. Geophys (Annual International Meeting Program with Abstracts), pp 494–497
Baali F (2001). Eude hydrogéologique hydrochimique de la région karstique de Chéria N–E Algérien. Magister Univ Annaba Algérie, p. 100
Baali F, Rouabhia A, Kherici N, Djabri L, Bouchaou L, Hani A (2007) Qualité des eaux souterraines et risque de pollution en milieu semi aride. Cas de la cuvette de Chéria. NE algérien. Journal of Estudios Geologicos. Vol. 63. CSIC, Spain
Ballard RF (1983) Cavity detection and delineation research. Report 5, Electromagnetic (radar) techniques applied to cavity detection. Technical Report GL, 83–1, p 90
Barker R, Moore J (1998) The application of time-lapse electrical tomography in groundwater studies. Lead Edge 17(10):1454–1458
Beck BF (1991) On calculating the risk of sinkhole collapse. In: Kastning EH, Kastning KM (eds) Proc Appalachian Karst Symp, Radford, Virginia, 23–26 March 1991. National Speleological Society, Huntsville, Alabama, pp 231–236
Benson RC, Kaufmann RD, Yuhr LB, Martin D (1998) Assessment, prediction and remediation of karst conditions on I-70, Frederick, Maryland, 49th Highway Geology Symposium, Precott, Arizona, Sept. 10–14, 1998. Arizona Department of Transportation, Material Group, Arizona Geological Survey, pp 313–325
Bishop I, Styles P, Emsley SJ, Ferguson NS (1997) The detection of cavities using the microgravity technique: case histories from mining and karstic environments. Geol Soc Eng Geol Spec Publ 12:153–166
Butler DK (1984) Microgravimetric and gravity gradient techniques for detection of subsurface cavities. Geophysics 49(7):1084–1096
Burger HR (1992) Exploration geophysics of the shallow subsurface. Prentice-Hall, Englewood Cliffs, NJ, 489
Chaffai H, Baali F, Djabri L, Rouabhia Aek (2003) Facteurs influençant le chimisme des eaux dans une zone semi-aride: Cas des aquifères d'El Ma El Abiod, Tébessa, Hammamet et Chéria. ICOWAP-Sep 2003. Colloque Oasis, Eau et population, Biskra Algérie, pp 339–344
Colley GC (1963) The detection of caves by gravity measurements. Geophys Prospect XI:1–9
Cook JC (1965) Seismic mapping of underground cavities using reflection amplitudes. Geophysics 30(4):527–538
Cook KL, Van NRG (1954) Interpretation of resistivity data over filled sinks. Geophys Prospect 21:716–723
Dahlin T (1996) 2D resistivity surveying for environmental and engineering applications. First Break 14:275–284
Dahlin T, Loke M (1998) Resolution of 2-D Wenner resistivity imaging as assessed by numerical modelling. J Appl Geophys 38:237–249
Deceuster J, Delgranche J, Kaufmann O (2006) 2D cross-borehole resistivity tomographies below foundations as a tool to design proper remedial actions in covered karst. J Appl Geophys 60:68–86
Gaud J (1977) Etude géologique et hydrogéologique du plateau de Chéria Wilaya de Tébessa. Rapport interne N.° 2. A.N.R.H de Tébessa (Agence Nationale des ressources hydriques), p 96
Google Maps (2009) TerraMetrics, Cnes/Spot Image, GeoEye, Données cartographiques © 2009 Europa Technologies
Griffiths DH, Barker RD (1993) Two-dimensional resistivity imaging and modeling in areas of complex geology. J Appl Geophys 29:211–226
La Moreaux PE, Wilson BM, Memon BA (1984) Guide to the hydrology of carbonate rocks. UNESCO, France
Loke M, Barker R (1996) Rapid least-squares inversion of apparent resistivity pseudosection by a quasi-Newton method. Geophys Prospect 44:131–152
Mathé V, Léveque F, Mathé PE, Chevallier C, Pons Y (2006) Soil anomaly mapping using a caesium magnetometer: limits in the low magnetic amplitude case. J Appl Geophys 58:202–217
Rybakov M, Goldshmidt V, Fleischer L, Rotstein Y (2001) Cave detection and 4-D monitoring: a microgravity case history near the Dead Sea. The Leading Edge (Soc Explor Geophys) 20(8):896–900
Rybakov M, Rotstein Y, Shirman B, Al-Zoubi A (2005) Cave detection near the Dead Sea-a micromagnetic feasibility study. The Leading Edge (Soc Explor Geophys) 24(6):585–590
Sasaki Y, Matsuo K (1993) Surface-to-tunnel resistivity tomography at the Kamaishi Mine. Butsuri-Tansa 46:128–133
Spies B, Ellis R (1995) Cross-borehole resistivity tomography of a pilot sale, in-situ vitrification test. Geophysics 60:886–898
Telford WM, Geldart LP, Sheriff RE (1990) Applied geophysics, 2nd edn. Cambridge University Press, New York
Van Schoor M, Duvenhage D (2000) Comparison of crosshole radio imaging and electrical resistivity tomography for mapping out disseminated sulphide mineralisation at a surface test site in Mpumalanga, South Africa. Explor Geophys 30:3–4
Vila JM (1980) La chaîne alpine de l’Algérie orientale et des confins Algéro-Tunisiens. Thèse de Doctorat- es-sciences, Université Pierre et Marie curie, Paris VI
Williams PW (1985) Subcutaneous hydrology and the development of doline and cockpit karst. Z Geomorphol NF 29(4):463–482
Zhou W, Beck BF, Adams AL (2002) Effective electrode array in mapping karst hazards in electrical resistivity tomography. Environ Geol 42:922–928
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Fehdi, C., Baali, F., Boubaya, D. et al. Detection of sinkholes using 2D electrical resistivity imaging in the Cheria Basin (north–east of Algeria). Arab J Geosci 4, 181–187 (2011). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12517-009-0117-2
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12517-009-0117-2