Abstract
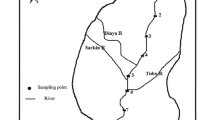
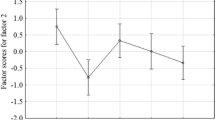
Rivers in Warri, Delta State of Nigeria are of particular importance in surface water pollution studies as they act as receptacles for effluents from oil industries, municipal sewage, agricultural and urban run-off. The water quality of these rivers is thus considerably changed. Results obtained from the analyses were correlated using Pearson’s correlation matrix, principal component analysis and pollution index. Positive correlations were observed for pH, conductivity, TDS, Cl−, Mg2+, \(\mathrm{NO}_{3}^{2-}\), COD, Cd and Ni2+. The pollution index, PI, for all the samples (1.11) is considered critical and indicates that the water samples from these rivers require treatment before use. Multivariate statistical and principal component analyses of the data showed three major components: PC1 with variance 6.42 representing 42.8% of the total variability, PC2 with variance 3.76 representing 25.10% of total variability, and PC3 with variance 2.13 representing 14.20% of the total variability. The first three principal components with eigenvalues greater than 1 represent 82.10% of the total variability, suggesting that three principal components adequately explain the variation in the data set. The results of the analyses when compared with World Health Organization (WHO) indicated that the rivers were polluted and so the water from such rivers is not safe for domestic use.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Akaninwor JO, Anosike EO, Egwu O (2007) Effect of Indomie industrial effluent discharge on microbial properties of new Calabar River. Sci Res Essays 2:1–5
Akpata TVI, Oyenekan JA, Nwankwo DI (1993) Impact of organic pollution on the Bactenal, Plankton and Benthic Population of Lagos lagoon, Nigeria. Int J Ecol Environ Sci 19:73–82
American Public Health Association (APHA) (1995) Standard method for examination of water and wastewater, 19th edn. FN SPON, Washington, pp 2–56
Anita MI, Ramkumar T, Venkatramanan S (2011) Application of statistical analysis for the hydrogeochemistry of saline groundwater in Kodiakarai, Tamilnadu. India J Coast Res, 1–11
Boyacioglu H, Boyacioglu H (2007) Water pollution sources assessment by multivariate statistical methods in the Tahtali Basin, Turkey. Environ Geol 54:275–282
Egereonu U, Dike R (2007) Evaluation of the pollution levels of Orashi rivers and Oguta Lake. J Chem Soc Nigeria 32:59–166
Garric J, Vindiman E, Ferand JF (1993) Ecotoxicology and waste water, some practical implications. Sci Total Environ (Suppl) 1085–1103
Horton RK (1965) An index system for rating water quality. J Water Pollut Control Fed 3:300–315
Kim JO, Mueller CW (1978) Introduction to factor analysis what it is and how to do it. Quantitative applications in the social sciences series. Sage, Newbury Park
Kobayashi H, Rittman BE (1982) Microbial removal of hazardous organic compounds. Environ Sci Technol 19(3):470–481
Lohani BN (1984) Recycling potentials of solid waste in Asia through organised scavenging. Conserv Recycl 74:181–190
Manahan SE (2005) Environmental chemistry, 8th edn. CRC Press, Boca Raton, pp 61–62, 179
Mohiuddin KM, Zakir HM, Otomo K, Sharmin S, Shikazono N (2001) Geochemical distribution of trace metal pollutants in water and sediments of downstream of an urban river. Int J Environ Sci Technol 7(1):17–28
Nduka JK, Orish EO, Ezenweke LO (2008) Some physicochemical parameters of potable water supply in Warri, Niger Delta area of Nigeria. Sci Res Essays 3(11):547–551
Nwankwo DI (1998) The influence of saw-mill wood wastes on Diatom population at Okobaba Lagos, Nigeria. J Bot 11:16–24
Olobaniyi SB, Owoyemi FB (2006) Chemical Facies of groundwater in the Deltaic Plain Sands Aquifer of Warri, Western Niger Delta, Nigeria. Afr J Sci Technol 7(1):73–81
Otukunefor TV, Obiukwu CO (2005) Impact of Refinery Influent on Physicochemical properties of water body on Niger Delta. J Appl Ecol Environ Res 3:61–72
Panda UC, Sundaray SK, Rath P, Nayak BB, Bhatta D (2006) Application of factor and cluster analysis for characterization of river and estuarine water systems—a case study: Mahandi river (India). J Hydrol 331:434–446
Phiri O, Mumba P, Moyo BHZ, Kadewa W (2005) Assessment of the impact of industrial effluents on water quality of receiving rivers in urban areas of Malawi. Int J Environ Sci Technol 2(3):237–244
Pradhan UK, Shirodkar PV, Shahu BK (2009) Physicochemical characteristic of the coastal water off Devi estuary, Orissa and evaluation of its seasonal changes using chemometric techniques. Curr Sci 96(9):1203–1209
Praus P (2005) Water quality assessment using SVD-based principal component analysis of hydrological data. Water SA 31(4):417–422
Rim-Rukeh A, Ikhifa OG, Okokoyo AP (2006) Effects of agricultural activities on the water quality of Orogodo river, Agbor Nigeria. J Appl Sci Res 2(5):256–259
Sekabira K, Oryem Origa H, Basamba TA, Mutumba G, Kakudidi E (2010) Heavy metal assessment and water quality values in urban stream and rain water. Int J Environ Sci Technol 7(4):759–770
Sheikh MA, Noah NM, Tsuha K, Oomori T (2007) Occurrence of tributylin compounds and characteristics of heavy metals. Int J Environ Sci Technol E1:49–60
Shrestha S, Kazama F (2007) Assessment of surface water quality using multivariate statistical techniques: a case study of the Fuji river basin, Japan. Environ Model Softw 22(4):464–475
Tubonimi JKI, Omubo A, Herbert OS (2010) Assessment of water quality along Amadi creek in Port Harcourt, Nigeria. Sci Afr 19(1):153–165
World Health Organization (WHO) (1998) Guidelines for drinking water quality, 2nd edn. WHO, Geneva, p 188. ISBN:9241545143
Wunderlin DA, Días MP, AméMaría V, Pesce SF, Hued AC, Bistoni MÁ (2001) Pattern recognition techniques for the evaluation of spatial and temporal variations in water quality. A case study: Suquia river basin (Cordoba–Argentina). Water Res 35(12):2881–2894
Xiaoyun F, Baoshan C, Hui Z, Zhiming Z, Honggang Z (2010) Assessment of river water quality in Pearl River Delta using multivariate statistical techniques. In: International society for environmental information sciences 2010 annual conference (ISEIS) procedia environmental sciences, vol 2, pp 1220–1234
Yisa J, Jimoh T (2010) Analytical studies on water quality index of river Landzu. Am J Appl Sci 7(4):453–458
Zvinowanda CM, Okonkwo JO, Shabalala PN, Agyei NM (2009) A novel adsorbent for heavy metal remediation in aqueous environment. Int J Environ Sci Technol 6(3):425–434
Zhang Q, Zhongwu L, Guangming Z, Jianbing L, Yong F, Qingshui Y, Yamei W, Fangyi Y (2009) Assessment of surface water quality using multivariate statistical techniques in red soil hilly region: a case study of Xiangjiang watershed. China Environ Monit Assess 152:123–131
Zhou F, Guo HC, Liu Y, Jiang YM (2007) Chemometrics data analysis of marine water quality and source identification in Southern Hong Kong. Mar Pollut Bull 54(6):745–756
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Onojake, M.C., Ukerun, S.O. & Iwuoha, G. A Statistical Approach for Evaluation of the Effects of Industrial and Municipal Wastes on Warri Rivers, Niger Delta, Nigeria. Water Qual Expo Health 3, 91–99 (2011). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12403-011-0046-7
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12403-011-0046-7