Abstract
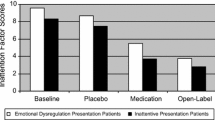
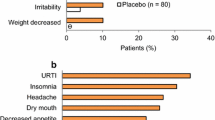
A three-year open-label study of atomoxetine in adults with ADHD followed two multicenter, double-blind trials. In the double-blind trials, female gender and higher levels of emotional symptoms were associated with better outcome. Following a 4-week placebo washout period, 384 (of 536) subjects continued into the open-label study. 61% of subjects entering this open-label study remained after 6 months at an average dose of 100 mg/day. Subjects who had previously responded to double-blind atomoxetine achieved maximum response after 8 weeks of open-label medication, but others continued to improve for 36 weeks. Women improved more (7.7 ± 6.4) than men (6.1 ± 6.4) on the Wender–Reimherr Adult Attention Deficit Disorder Scale (WRAADDS) (P = .007) and the Conners’ Adult ADHD Rating Scale (P = .03). Subjects with emotional dysregulation improved more than others on the WRAADDS (P = .001). Responders ultimately improved approximately 60% in attentional, hyperactive/impulsive, and emotional symptoms. Thirty-nine percent of atomoxetine double-blind non-responders became responders during open-label treatment.

Similar content being viewed by others
References
Adler LA, Spencer TJ, Milton DR et al (2005) Long-term, open-label study of the safety and efficacy of atomoxetine in adults with attention-deficit/hyperactivity disorder: an interim analysis. J Clin Psychiatry 66:294–299
Adler LA, Spencer TJ, Williams DW, et al (2008) Long-term, open-label safety and efficacy of atomoxetine in adults with ADHD: final report of a 4-year study. J Atten Disord 248–253
Adler LA, Spencer T, Brown TE et al (2009) Once-daily atomoxetine for adult attention-deficit/hyperactivity disorder: a 6-month, double-blind trial. J Clin Psychopharmacol 29:44–50
Biederman J, Spencer TJ (1999) Attention-deficit/hyperactivity disorder (ADHD) as a noradrenergic disorder. Biol Psychiatry 46:1234–1242
Biederman J, Spencer TJ, Wilens TE et al (2005) Long-term safety and effectiveness of mixed amphetamine salts extended release in adults with ADHD. CNS Spectr 10(Suppl 20):16–25
Biederman J, Ball SW, Monuteaux MC et al (2008) New insights into the comorbidity between ADHD and major depression in adolescent and young adult females. J Am Acad Child Adolesc Psychiatry 47:426–434
Conners CK, Erhardt D, Sparrow E (1999) Conners’ adult ADHD rating scales (CAARS). Multi-Health Systems Inc, North Tonawanda
Faraone SV, Biederman J (1998) Neurobiology of attention-deficit hyperactivity disorder. Biol Psychiatry 44:951–958
Marchant BK, Reimherr FW, Halls C et al (2010) OROS methylphenidate in the treatment of adults with ADHD: a 6-month, open-label, follow-up study. Ann Clin Psychiatry 22:196–204
Michelson D, Allen AJ, Busner J et al (2002) Once-daily atomoxetine treatment for children and adolescents with attention-deficit/hyperactivity disorder: a randomized, placebo-controlled study. Am J Psychiatry 159:1896–1901
Michelson D, Adler L, Spencer T et al (2003) Atomoxetine in adults with ADHD: two randomized, placebo-controlled studies. Biol Psychiatry 53:112–120
Quinn PO (2008) Attention-deficit/hyperactivity disorder and its comorbidities in women and girls: an evolving picture. Curr Psychiatry Rep 10(5):419–423
Rasmussen K, Levander S (2009) Untreated ADHD in adults: are there sex differences in symptoms, comorbidity, and impairment? J Atten Disord 12(4):353–360
Reimherr FW, Marchant BK, Strong RE et al (2005) Emotional dysregulation in adult ADHD and response to atomoxetine. Biol Psychiatry 58:125–131
Reimherr FW, Williams ED, Strong RE et al (2007) A double-blind, placebo-controlled, crossover study of osmotic release oral system methylphenidate in adults with ADHD with assessment of oppositional and emotional dimensions of the disorder. J Clin Psychiatry 68(1):93–101
Robison RJ, Reimherr FW, Marchant BK et al (2008) Gender differences in 2 clinical trials of adults with attention-deficit/hyperactivity disorder: a retrospective data analysis. J Clin Psychiatry 69:213–221
Rösler M, Fischer R, Ammer R et al (2009) A randomised, placebo-controlled, 24-week, study of low-dose extended-release methylphenidate in adults with attention-deficit/hyperactivity disorder. Eur Arch Psychiatry Clin Neurosci 259:120–129
Rösler M, Retz W, Fischer R et al (2010) Twenty-four-week treatment with extended release methylphenidate improved emotional symptoms in adult ADHD. World J Biol Psychiatry 11:709–718
Weisler RH, Biederman J, Spencer TJ et al (2005) Long-term cardiovascular effects of mixed amphetamine salts extended release in adults with ADHD. CNS Spectr 12(Suppl 20):35–43
Weisler R, Young J, Mattingly G et al (2009) Long-term safety and effectiveness of lisdexamfetamine dimesylate in adults with attention-deficit/hyperactivity disorder. CNS Spectr 14:573–585
Wender PH (1995) Attention-deficit hyperactivity disorder in adults. Oxford University Press, New York
Wender PH, Reimherr FW, Marchant BK et al (2011) One year trial of methylphenidate in adult ADHD. J Atten Disord 15:36–45
Acknowledgments
The initial trial was funded by Eli Lilly and Co., although this reanalysis was not.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Marchant, B.K., Reimherr, F.W., Halls, C. et al. Long-term open-label response to atomoxetine in adult ADHD: influence of sex, emotional dysregulation, and double-blind response to atomoxetine. ADHD Atten Def Hyp Disord 3, 237–244 (2011). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12402-011-0054-2
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12402-011-0054-2