Abstract
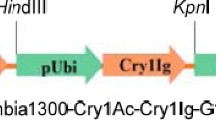
With the embryogenic calli of sugarcane variety ROC25 as the acceptors, a genetic transformation system mediated by Agrobacterium tumefaciens was established and the fusion insect-resistant gene (constructed by Amaranthus viridis L. agglutinin gene and soybean Kunitz tripsin inhibitor, AVAc-SKTI) transformed plants were acquired. The plant expression vector was constructed with the fused gene which was flanked on both sides of the MARs. The plant vectors were transformed into the embryogenic calli with the plant expression vector without MAR control. In the genetic transformation of sugarcane, the vector ligated with MARs in the same direction on both sides of the fused gene could increase the number of transgenic lines, which was 55.56% higher than that of the control. Moreover, the number of transgenic plants regenerated from each resistant callus increased by 26.43%. The AVAc-SKTI fusion insect-resistant gene transformed plants would improve the resistance of sugarcane plants to the attacks of borer (Diatraea saccharalis) and aphid (Ceratovacuna lanigera Zehnther).
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Allen GC, Hall GE Jr, Childs LC, Weissinger AK, Spiker S, Thompson WF (1993) Scaffold attachment regions increase reporter gene expression in stably transformed plant cells. Plant Cell 5(6): 603–613.
Allen GC, Hall Jr G, Michalowski S, Newman W, Spiker S, Weissinger AK, Thompson WF (1996) High-level transgene expression in plant cell: effects of a strong scaffold attachment region from tobacco. Plant Cell 8: 889–913.
Allen GC, Spiker S, Thompson WF (2000) Use of matrix attachment regions (MARs) to minimize transgene silencing. Plant Molecular Biology 43(2–3): 361–376.
Breyne P, Van Montagu M, Depicker A, Gheysen G (1992) Characterization of a plant scaffold attachment region in a DNA fragment that normalizes transgene expression in tobacco. Plant Cell 4(4): 463–471.
Gatehouse AMR, Shi Y, Powell KS (1993) Approaches to insect resistance using transgenic plants. Phil Trans R Soc Lond B 342: 279–286.
Gutierrez-Adan A, Pintado B (2000) Effect of flanking matrix attachment regions on expression of microinjected transgenes during preimplantation development of mouse embryos. Transgenic Research 9(2): 81–89.
Guo HN, Jia YT, Zhou YG, Zhang ZS, Ou-Yang Q, Jiang Y, Tian YC (2004) Effects of transgenic tobacco plants expressing ACA gene from Amaranthus caudatus on the population development of Myzus persicae. Acta Botanica Sinica 46(9): 1100–1105.
Han KH, Ma CP, Strauss SH (1997) Matrix attachment regions (MARs) enhance transformation frequency and transgene expression in poplar. Transgenic Research 6: 415–420.
Koide T, Ikenaka T (1973) Studies on soybean trypsin inhibitor. Eur J Biochemistry 32:417–431.
Kim SH, Hare S, Hase S, Ikenaka T, Toda H, Kitamura K, Kaizuma N (1985) Comparative study on amino sequence of Kunitz-type soybean trypsin inhibitor, Tia, Tib, Tic. J Biochemistry 98:435–448.
Lee TH, Kim SJ, Han YM, Yu DY, Lee CS, Choi YJ, Moon HB, Baik MG, Lee KK (1998) Matrix attachment region sequences enhanced the expression frequency of a whey acidic protein/human lactoferrin fusion gene in the mammary gland of transgenic mice. Molecular Cells 8(5): 530–536.
Rinderie SJ, Goldstein IJ, Remsen EE (1990) Physicochemical properties of amaranthin, the lectin from Amaranthus caudatus seeds. Biochemistry 29(46): 10555–10561.
Song SL, Kim CH, Baek SJ, Choi YD (1993) Nucleotide sequences of cDNAs encoding the precursors for soybean (Glycine max) Plant Physiology 101:1404–1402.
Yao W, Yu AL, Xu JS, Zhou H, Zhang MQ, Chen RK (2005) A simple and quick method for extracting sugarcane genomic DNA. J Agricul Biotechnol 13(1):121–122.
Zhou YG, Tian YC, Mang KQ (2001) Cloning of AHA gene from Amaranthus hypochondriacus and its aphid inhibition effect in transgenic tobacco plants. Chin J Biotechnol 17(1): 34–39.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Deng, ZN., Wei, YW., Lü, WL. et al. Fusion insect-resistant gene mediated by matrix attachment region (MAR) sequence in transgenic sugarcane. Sugar Tech 10, 87–90 (2008). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12355-008-0015-z
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12355-008-0015-z