Abstract
Aim
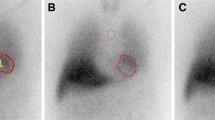
Purpose of this study was to assess the impact of mediastinal region of interest (ROI) definition on intra- and inter-observer variability in relation to collimator type.
Methods
Thirty-five subjects with CHF (80% men, mean age 66 ± 9 years, NYHA 2.4 ± 0.5, LVEF 29 ± 8.4%) were enrolled. 15 minutes and 4 hours post-injection (p.i.) of 123I-MIBG, planar images were sequentially acquired with low energy high energy (LEHR) and medium energy (ME) collimators. In the first analysis, observer-defined mediastinal ROI was used. In the second analysis, a predefined mediastinal ROI was used. Intra- and inter-observer variability of late H/M was assessed using Lin’s concordance coefficient (LCC).
Results
There was substantial agreement between all three observers using predefined mediastinum ROI. LCCs for LEHR were 0.98, 0.96, and 0.95, for ME 0.98, 0.97, and 0.97. However, observer-defined mediastinal ROI resulted in poor-moderate agreement. LCCs for LEHR were 0.82, 0.94, and 0.70, for ME 0.77, 0.91, and 0.80. Intra-observer analysis using predefined mediastinal ROI showed substantial agreement. LCC was 0.97 for LEHR and 0.96 for ME.
Conclusion
Predefined mediastinal ROI results in low intra- and inter-observer variability of late H/M and is, therefore, to be preferred over observer-defined mediastinal ROI. Intra- and inter-observer variability of late H/M is not influenced by collimator choice.



Similar content being viewed by others
References
Carrio I. Cardiac neurotransmission imaging. J Nucl Med 2001;42:1062-76.
Caldwell JH, Link JM, Levy WC, Poole JE, Stratton JR. Evidence for pre- to postsynaptic mismatch of the cardiac sympathetic nervous system in ischemic congestive heart failure. J Nucl Med 2008;49:234-41.
Kline RC, Swanson DP, Wieland DM, Thrall JH, Gross MD, Pitt B, et al. Myocardial imaging in man with I-123 meta-iodobenzylguanidine. J Nucl Med 1981;22:129-32.
Food and Drug Administration. Supplement approval for AndreView (Iobenguane I 123) Injection. http://www.accessdata.fda.gov/drugsatfda_docs/appletter/2013/022290Orig1s001ltr.pdf.
Paul M, Schafers M, Kies P, Acil T, Schafers K, Breithardt G, et al. Impact of sympathetic innervation on recurrent life-threatening arrhythmias in the follow-up of patients with idiopathic ventricular fibrillation. Eur J Nucl Med Mol Imaging 2006;33:866-70.
Boogers MJ, Borleffs CJW, Henneman MM, van Bommel RJ, van Ramshorst J, Boersma E, et al. Cardiac sympathetic denervation assessed with 123-iodine metaiodobenzylguanidine imaging predicts ventricular arrhythmias in implantable cardioverter-defibrillator patients. J Am Coll Cardiol 2010;55:2769-77.
Tamaki S, Yamada T, Okuyama Y, Morita T, Sanada S, Tsukamoto Y, et al. Cardiac iodine-123 metaiodobenzylguanidine imaging predicts sudden cardiac death independently of left ventricular ejection fraction in patients with chronic heart failure and left ventricular systolic dysfunction: Results from a comparative study with signal-averaged electrocardiogram, heart rate variability, and QT dispersion. J Am Coll Cardiol 2009;53:426-35.
Verberne HJ, Brewster LM, Somsen GA, van Eck-Smit BLF. Prognostic value of myocardial 123I-metaiodobenzylguanidine (MIBG) parameters in patients with heart failure: A systematic review. Eur Heart J 2008;29:1147-59.
Flotats A, Carrio I, Agostini D, Guludec D, Marcassa C, Schafers M, et al. Proposal for standardization of 123I-metaiodobenzylguanidine (MIBG) cardiac sympathetic imaging by the EANM Cardiovascular Committee and the European Council of Nuclear Cardiology. Eur J Nucl Med Mol Imaging 2010;37:1802-12.
Somsen GA, Verberne HJ, Fleury E, Righetti A. Normal values and within-subject variability of cardiac I-123 MIBG scintigraphy in healthy individuals: Implications for clinical studies. J Nucl Cardiol 2004;11:126-33.
Veltman CE, Boogers MJ, Meinardi JE, Al Younis I, Dibbets-Schneider P, van der Wall EE, et al. Reproducibility of planar 123I-meta-iodobenzylguanidine (MIBG) myocardial scintigraphy in patients with heart failure. Eur J Nucl Med Mol Imaging 2012;39:1599-608.
McMurray JJ, Adamopoulos S, Anker SD, Auricchio A, Bohm M, Dickstein K, et al. ESC guidelines for the diagnosis and treatment of acute and chronic heart failure 2012: The Task Force for the Diagnosis and Treatment of Acute and Chronic Heart Failure 2012 of the European Society of Cardiology. Developed in collaboration with the Heart Failure Association (HFA) of the ESC. Eur Heart J 2012;33:1787-847.
McBride GB. A proposal for strength-of-agreement criteria for Lin’s concordance correlation coefficient. NIWA Client Report: HAM 2005-062; 2005
Jacobson AF, Senior R, Cerqueira MD, Wong ND, Thomas GS, Lopez VA, et al. Myocardial iodine-123 meta-iodobenzylguanidine imaging and cardiac events in heart failure: Results of the prospective ADMIRE-HF (AdreView Myocardial Imaging for Risk Evaluation in Heart Failure) study. J Am Coll Cardiol 2010;55:2212-21.
Merlet P, Benvenuti C, Moyse D, Pouillart F, Dubois-Rand JL, Duval AM, et al. Prognostic value of MIBG imaging in idiopathic dilated cardiomyopathy. J Nucl Med 1999;40:917-23.
Verberne HJ, Habraken J, Eck-Smit BLF, Agostini D, Jacobson AF. Variations in 123I-metaiodobenzylguanidine (MIBG) late heart mediastinal ratios in chronic heart failure: A need for standardisation and validation. Eur J Nucl Med Mol Imaging 2008;35:547-53.
Agostini D, Carrio I, Verberne HJ. How to use myocardial 123I-MIBG scintigraphy in chronic heart failure. Eur J Nucl Med Mol Imaging 2009;36:555-9.
Verberne HJ, Somsen GA, Povinec P, Eck-Smit BLF, Jacobson AF. Impact of mediastinal, liver and lung 123I-metaiodobenzylguanidine (123I-MIBG) washout on calculated 123I-MIBG myocardial washout. Eur J Nucl Med Mol Imaging 2009;36:1322-8.
Dobbeleir AA, Hambye AS, Franken PR. Influence of high-energy photons on the spectrum of iodine-123 with low- and medium-energy collimators: consequences for imaging with 123I-labelled compounds in clinical practice. Eur J Nucl Med 1999;26:655-8.
Fletcher AM, Motherwell DW, Small AD, McCurrach GM, Goodfield NE, Petrie MC, et al. I-123 MIBG cardiac uptake measurements: limitations of collimator choice and scatter correction in the clinical context. Nucl Med Commun 2010;31:629-36.
Acknowledgment
None of the authors has been supported by a grant.
Disclosure
The authors have indicated that they have no financial conflict of interest.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Verschure, D.O., Bongers, V., Hagen, P.J. et al. Impact of a predefined mediastinal ROI on inter-observer variability of planar 123I-MIBG heart-to-mediastinum ratio. J. Nucl. Cardiol. 21, 605–613 (2014). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12350-014-9854-z
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12350-014-9854-z