Abstract
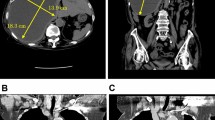
Infected hepatic cysts are very rare compared to simple liver cysts and abscesses. We treated a 77-year-old man with an infected hepatic cyst in the lateral segment caused by Edwardsiella tarda, which has not been previously reported as a pathogenic organism associated with infected hepatic cysts. Percutaneous drainage was temporarily effective, but infection recurred after the drainage tube was removed. We then inserted two drainage tubes into the cyst using an endoscopic ultrasonography (EUS)-guided technique, which was developed from EUS-guided fine needle aspiration (EUS-FNA). The internal drainage tube was a 7 Fr double pigtail stent, and the external tube was a 6 Fr nasobiliary drainage tube. Lavage through the external drainage tube was carried out for one week. The external drainage tube was discontinued when the patient’s condition improved significantly. Sixteen days after tube insertion, he was discharged with the internal tube draining the hepatic cyst into the stomach. Fifteen months after EUS-guided drainage, CT examination showed no recurrence of the hepatic cyst. EUS-guided drainage is an effective treatment for infected hepatic cysts.



Similar content being viewed by others
References
Schwed DA, Edoga JK, Stein LB. Biliary obstruction due to spontaneous hemorrhage into benign hepatic cyst. J Clin Gastroenterol. 1993;16:84–6.
Yamaguchi M, Kuzume M, Matsumoto T, et al. Spontaneous rupture of a nonparasitic liver cyst complicated by intracystic hemorrhage. J Gastroenterol. 1999;34:645–8.
Zanen AL, van Tilburg AJ. Bleeding into a liver cyst can be treated conservatively. Eur J Gastroenterol Hepatol. 1995;7:91–3.
Takahashi G, Yoshida H, Mamada Y, et al. Intracystic hemorrhage of a large simple hepatic cyst. J Nippon Med Sch. 2008;75:302–5.
Bourgeois N, Kinnaert P, Vereerstraeten P, et al. Infection of hepatic cysts following kidney transplantation in polycystic disease. World J Surg. 1983;7:629–31.
Telenti A, Torres VE, Gross JB Jr, et al. Hepatic cyst infection in autosomal dominant polycystic kidney disease. Mayo Clin Proc. 1990;65:933–42.
Grunfeld JP, Albouze G, Jungers P, et al. Liver changes and complications in adult polycystic kidney disease. Adv Nephrol Necker Hosp. 1985;14:1–20.
Abascal J, Moya M, Martin F. Infection of hepatic cysts in polycystic disease. World J Surg. 1984;8:424–5.
Gesundheit N, Kent DL, Fawcett HD, et al. Infected liver cyst in a patient with polycystic kidney disease. West J Med. 1982;136:246–9.
Yoshida H, Onda M, Tajiri T, et al. Infected hepatic cyst. Hepatogastroenterol. 2003;50:507–9.
Lin HP, Ho WH, Lee CC, et al. Infected simple hepatic cysts—3 cases report. J Intern Med Taiwan. 2009;20:373–7.
Mori E, Akai Y, Matsumoto T, et al. Hepatic cyst infection in a healthy older male. BMJ Case Rep. 2012;. doi:10.1136/bcr.04.2011.4136.
Quigley M, Joglekar VM, Keating J, et al. Fatal Clostridium perfringens infection of a liver cyst. J Infect. 2003;47:248–50.
Seewald S, Imazu H, Omar S, et al. EUS-guided drainage of hepatic abscess. Gastrointest Endosc. 2005;61:495–8.
Ang T, Seewald S, Teo E, et al. EUS-guided drainage of ruptured liver abscess. Endoscopy. 2009;41(Suppl 2):E21–2.
Noh SH, Park DH, Kim YR, et al. EUS-guided drainage of hepatic abscesses not accessible to percutaneous drainage. Gastrointest Endosc. 2010;71:1314–9.
Decker C, Varadarajulu S. EUS-guided drainage of an intra-abdominal abscess after liver transplantation. Gastrointest Endosc. 2011;73:1056–8.
Itoi T, Ang TL, Seewald S, et al. Endoscopic ultrasonography-guided drainage for tuberculous liver abscess drainage. Dig Endosc. 2011;23(Suppl 1):158–61.
Sato T, Imai M, Hayashi K et al. Giant Hepatic Cyst with Septal Structure: Diagnosis and Management: Intern J Hepatol. 2013; Article ID 981975.
Kourany M, Vasquez MA, Saenz R. Edwardsiellosis in man and animals in Panama: clinical and epidemiological characteristics. Am J Trop Med Hyg. 1977;26:1183–90.
Koshi G, Lalitha MK. Edwardsiella tarda in a variety of human infections. Indian J Med Res. 1976;64:1753–9.
Wilson JP, Waterer RR, Wofford JD, Chapman SW. Serious infections with Edwardsiella tarda. A case report and review of literature. Arch Intern Med. 1989;149:208–10.
Janda JM, Abbott SL. Infections associated with the genus Edwardesiella: the role of Edwardsiella tarda in human disease. Clin Infect Dis. 1993;17:742–8.
Jordan GW, Hadley WK. Human infection with Edwardsiella tarda. Ann Intern Med. 1969;70:283–8.
Wang IK, Kuo HL, Chen CL, et al. Extrainstestinal manifestations of Edwardsiella tarda infection. Int J Clin Pract. 2005;59:917–21.
Ota T, Nakano Y, Nishi M, et al. A case of liver abscess caused by Edwardsiella tarda. Intern Med. 2011;50:1439–42.
Ohara Y, Kikuchi O, Goto T, et al. Successful treatment of patient with sepsis and liver abscess caused by Edwardsiella tarda. Intern Med. 2012;51:2813–7.
Chung YF, Tan YM, Lui HF, et al. Management of pyogenic liver abscesses—percutaneous or open drainage? Singap Med J. 2007;48:1158–65.
Piraka C, Shah RJ, Fukami N, et al. EUS-guided transesophageal, transgastric, and transcolonic drainage of intra-abdominal fluid collections and abscesses. Gastrointest Endosc. 2009;70:786–92.
Seewald S, Thonke F, Ang TL, et al. One-step, simultaneous double-wire technique facilitates pancreatic pseudocyst and abscess drainage. Gastrointest Endosc. 2006;64:805–8.
Evans JA, Conway JD, Mishra G. A novel method for performing multiple wire insertions during endoscopic cyst gastrostomy. Gastrointest Endosc. 2010;71:612–4.
Baron TH, Harewood GC, Morgan DE, et al. Outcome differences after endoscopic drainage of pancreatic necrosis, acute pancreatic pseudocysts, and chronic pancreatic pseudocysts. Gastrointest Endosc. 2002;56:7–17.
Yamada N, Shinzawa H, Ukai K, et al. Treatment of symptomatic hepatic cysts by percutaneous instillation of minocycline hydrochloride. Dig Dis Sci. 1994;39:2503–9.
Yoshida H, Onda M, Tajiri T, et al. Long-term results of multiple minocycline hydrochloride injections for the treatment of symptomatic solitary hepatic cyst. J Gasreoenterol Hpatol. 2003;18:595–8.
Disclosures
Conflict of Interest:
Hiroki Taguchi, Tsutomu Tamai, Masatsugu Numata, Hitomi Maeda, Akihiko Ohshige, Hiromichi Iwaya, Shinichi Hashimoto, Shuji Kanmura, Hiroshi Fujita, Keita Funakawa, Akio Ido, and Hirohito Tsubouchi declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Human/Animal Rights:
All procedures followed were in accordance with the ethical standards of the responsible committee on human experimentation (institutional and national) and with the Helsinki Declaration of 1975, as revised in 2008(5).
Informed Consent:
Informed consent was obtained from all patients for being included in the study.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Taguchi, H., Tamai, T., Numata, M. et al. Endoscopic ultrasonography-guided transmural drainage of an infected hepatic cyst due to Edwardsiella tarda: a case report. Clin J Gastroenterol 7, 422–428 (2014). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12328-014-0520-4
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12328-014-0520-4



