Abstract
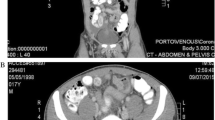
Perforation of Meckel’s diverticulum with enteroliths is a rare complication. Here, we report a case of perforation of Meckel’s diverticulum with enteroliths, which could be accurately diagnosed by the preoperative computed tomography (CT). A 46-year-old man with acute onset of severe abdominal pain, and a localized muscle guarding in the right hypochondrium, had a solitary stone detected in the right abdomen by the radiography. The abdominal CT revealed a saclike outpouching of the small intestine, containing air/fluid levels and an enterolith, with surrounding free air and mesenteric inflammatory change in the right paraumbilical area. He was diagnosed as the perforation of Meckel's diverticulum with enterolith, and the emergency operation was indicated. The perforated Meckel’s diverticulum was identified approximately 90 cm proximal to the ileocecal valve. The diverticulum was transected at the base, and removed. The patient’s postoperative course was uneventful. This case strongly suggested the ability of CT enterography to accurately diagnose pathologies involving the small intestine, such as the perforation of Meckel’s diverticulum, which open premises for its use in the diagnosis of acute abdomen preoperatively.




Similar content being viewed by others
References
Sager J, Kumar V, Shah DK. Meckel’s diverticulum: a systemic review. J R Soc Med. 2006;99:501–5.
Kloss BT, Broton CE, Sullivan AM. Perforated Meckel diverticulum. Int J Emerg Med. 2010;3:455–7.
Higginson AP, Hall RI. Meckel’s diverticulitis due to an obstructing enterolith: ultrasound and CT appearances. Clin Radiol. 2001;56:593–5.
Arnold JF, Pellicane JV. Meckel’s diverticulum: a ten-year experience. Am Surg. 1997;63:354–5.
Yagci G, Cetiner S, Tufan T. Perforation of Meckel’s diverticulum by a chicken bone, a rare complication: report of a case. Surg Today. 2004;34:606–8.
Loh D. Perforated Meckel’s diverticulum caused by faecolith. ANZ J Surg. 2008;78:518–9.
Oya S, Miyata K, Yuasa N, Takeuchi E, Goto Y, Miyake H, et al. A case of perforated Meckel’s diverticulum with true enterolith. Jpn J Gastroenterol Surg. 2009;42:561–565 (in Japanese with English abstract).
Lai HC. Intestinal obstruction due to Meckel’s Enterolith. Pediatr Neonatol. 2010;51:139–40.
Pantongrag-Brown L, Levine MS, Buetow PC, Buck JL, Elsayed AM. Meckel’s enteroliths: clinical, radiologic, and pathologic findings. Am J Roentgenol. 1996;167:1447–50.
Sharma G, Benson CK. Enteroliths in Meckel’s diverticulum: report of a case and review of the literature. Can J Surg. 1970;13:54–8.
Barr H. Calculi in Meckel’s diverticulum. Br J Surg. 1984;71:478–9.
Athey GN. Unusual demonstration of a Meckel’s diverticulum containing enterolith. Br J Radiol. 1980;53:365–8.
Fa-Si-Oen PR, Roumen RM, Croiset van Uchelen FA. Complications and management of Meckel’s diverticulum: a review. Eur J Surg. 1999;165:674–8.
Mackey WC, Dineen P. A fifty year experience with Meckel’s diverticulum. Surg Gynecol Obstet. 1983;156:56–64.
Fich A, Talley NJ, Shorter RG, Phillips SF. Does Helicobacter pylori colonize the gastric mucosa of Meckel’s diverticulum? Mayo Clin Proc. 1990;65:187–91.
Hill P, Rode J. Helicobacter pylori in ectopic gastric mucosa in Meckel’s diverticulum. Pathology. 1998;30:7–9.
Kusumoto H, Yoshida M, Takahashi I, Anai H, Maehara Y, Sugimachi K. Complications and diagnosis of Meckel’s diverticulum in 776 patients. Am J Surg. 1992;164:382–3.
Malik AA, Shams-ul-Bari, Wani KA, Khaja AR. Meckel’s divertculum-revisited. Saudi J Gastroenterol. 2010;16:3–7.
Rossi P, Gourtsoyiannis N, Bezzi M, Raptopoulos V, Massa R, Capanna G, Pedicini V, Coe M. Meckel’s diverticulum: imaging diagnosis. AJR. 1996;166:567–73.
Elsayes KM, Menias CO, Harvin HJ, Francis IR. Imaging manifestations of Meckel’s diverticulum. AJR. 2007;189:81–8.
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Nishikawa, T., Takei, Y., Tsuno, N.H. et al. Perforation of Meckel’s diverticulum with enteroliths. Clin J Gastroenterol 5, 298–301 (2012). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12328-012-0313-6
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12328-012-0313-6