Abstract
Introduction
We aimed to retrospectively analyze the therapeutic outcomes of using glucocorticoid combined with a vasodilator, breviscapine, versus glucocorticoid alone in patients with sudden sensorineural hearing loss (SSNHL) and to explore the impact on different audiometric curves.
Methods
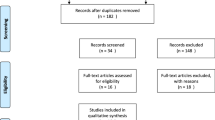
Data from 154 patients were collected between January 2017 and December 2018. Patients received treatments of either glucocorticoid combined with breviscapine (GC + Bre) or glucocorticoid alone (GC). These two groups were stratified into low frequencies SSNHL (LF-SSNHL), high frequencies SSNHL (HF-SSNHL), all frequencies SSNHL (AF-SSNHL), and total deafness SSNHL (TD-SSNHL) subgroups according to their corresponding audiograms. The hearing level was evaluated by pure tone audiometry, and hearing recovery was calculated by comparing the pure tone average (PTA) at pretreatment and 4 weeks after therapy.
Results
Hearing recovery was significantly greater for GC + Bre than GC-only treatment in the AF-SSNHL and TD-SSNHL subgroups (P < 0.05) and to a lesser extent in the LF-SSNHL and HF-SSNHL subgroups (P > 0.05). Logistic regression analysis also showed a favorable outcome for SSNHL in the GC + Bre group (odds ratio 2.848, P < 0.05).
Conclusion
Treating SSNHL using glucocorticoid combined with breviscapine could be more beneficial than using glucocorticoid alone, especially for patients with AF-SSNHL and TD-SSNHL.
Trial Registration Number
ChiCTR18000170072

Similar content being viewed by others
References
Chandrasekhar SS, Tsai Do BS, et al. Clinical practice guideline: sudden hearing loss (update). Otolaryngol Head Neck Surg. 2019;161(1_suppl):S1–S45.
Byl FM Jr. Sudden hearing loss: eight years' experience and suggested prognostic table. Laryngoscope. 1984;94(5 Pt 1):647–61.
Hughes GB, Freedman MA, Haberkamp TJ, Guay ME. Sudden sensorineural hearing loss. Otolaryngol Clin N Am. 1996;29(3):393–405.
Editorial Board of Chinese Journal of Otorhinolaryngology Head and Neck Surgery. The Otolaryngology Head and Neck Surgery Branch of Chinese Medical Association. Guideline of diagnosis and treatment of sudden deafness (2015). Chin J Otorhinolaryngol Head Neck Surg. 2015;50(6):443–7.
Chau JK, Lin JR, Atashband S, Irvine RA, Westerberg BD. Systematic review of the evidence for the etiology of adult sudden sensorineural hearing loss. Laryngoscope. 2010;120(5):1011–21.
Park KH, Lee CK, Lee JD, Park MK, Lee BD. Combination therapy with systemic steroids, an antiviral agent, anticoagulants, and stellate ganglion block for treatment of sudden sensorineural hearing loss. Korean J Audiol. 2012;16(2):71–4.
Bravenboer-de-Sousa M, Cazemier S, Stegeman I, Thomeer H. Use of vasodilators in idiopathic sudden sensorineural hearing loss: a systematic review. J Int Adv Otol. 2017;13(3):399–403.
Okada M, Hato N, Nishio SY, et al. The effect of initial treatment on hearing prognosis in idiopathic sudden sensorineural hearing loss: a nationwide survey in Japan. Acta Otolaryngol. 2017;137(sup565):S30–S3333.
Shim HS, Kim JS, Kim MG. Comparative analysis of the combined therapeutic effects of lipoprostaglandin E(1) on sudden idiopathic sensorineural hearing loss. J Audiol Otol. 2017;21(1):33–8.
Agarwal L, Pothier DD. Vasodilators and vasoactive substances for idiopathic sudden sensorineural hearing loss. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2009;4:CD003422.
Kanzaki J, Inoue Y, Ogawa K, et al. Effect of single-drug treatment on idiopathic sudden sensorineural hearing loss. Auris Nasus Larynx. 2003;30(2):123–7.
Lee HY, Kim JC, Choi MS, Chang DS, Kim AY, Cho CS. Therapeutic effect of combined steroid-lipoprostaglandin E1 for sudden hearing loss: a propensity score-matched analysis. Am J Otolaryngol. 2015;36(1):52–6.
Zhang RW, Zhang YL, Wang JS, Lin YY, Shang B (1988) Isolation and identification of flavonoids from shortscape fleabane (Erigeron breviscapus). Chin Trad Herb Drug. 1988;19(5):199–201.
Li XL, Li YQ, Yan WM, et al. A study of the cardioprotective effect of breviscapine during hypoxia of cardiomyocytes. Planta Med. 2004;70(11):1039–44.
Jia JH, Chen KP, Chen SX, Liu KZ, Fan TL, Chen YC. Breviscapine, a traditional Chinese medicine, alleviates myocardial ischaemia reperfusion injury in diabetic rats. Acta Cardiol. 2008;63(6):757–62.
Gao J, Chen G, He H, et al. Therapeutic effects of breviscapine in cardiovascular diseases: a review. Front Pharmacol. 2017;8:289.
Wei Y. Dengzhanxixin injection using character analysis in clinical based on real world HIS database. China J Chin Mater Med. 2012;37(18):2718–22.
Liu X, Yao L, Sun D, et al. Effect of breviscapine injection on clinical parameters in diabetic nephropathy: a meta-analysis of randomized controlled trials. Exp Ther Med. 2016;12(3):1383–97.
Siegel LG. The treatment of idiopathic sudden sensorineural hearing loss. Otolaryngol Clin N Am. 1975;8(2):467–73.
Koc A, Sanisoglu O. Sudden sensorineural hearing loss: literature survey on recent studies. J Otolaryngol. 2003;32(5):308–13.
Lawrence R, Thevasagayam R. Controversies in the management of sudden sensorineural hearing loss: an evidence-based review. Clin Otolaryngol. 2015;40(3):176–82.
Wilson WR, Byl FM, Laird N. The efficacy of steroids in the treatment of idiopathic sudden hearing loss. A double-blind clinical study. Arch Otolaryngol. 1980;106(12):772–6.
Lou JZ, Rui B. Effect of breviscapine combined with octreotide on the inflammatory reaction and vasoactive substances in patients with severe acute pancreatitis. J Hainan Med Univ. 2017:47–50.
Guo C, Zhu Y, Weng Y, et al. Therapeutic time window and underlying therapeutic mechanism of breviscapine injection against cerebral ischemia/reperfusion injury in rats. J Ethnopharmacol. 2014;151(1):660–6.
Furchgott RF. Role of endothelium in responses of vascular smooth muscle. Circ Res. 1983;53(5):557–73.
Rapoport RM, Draznin MB, Murad F. Endothelium-dependent relaxation in rat aorta may be mediated through cyclic GMP-dependent protein phosphorylation. Nature. 1983;306(5939):174–6.
Hua ZG, Xiao W, Li W, Xie Z. Effects of breviscapine on isolated thoracic aorta rings of rats. Acad J Guangdong Coll Pharm. 1997:680–683.
Ohinata Y, Makimoto K, Kawakami M, Haginomori S, Araki M, Takahashi H. Blood viscosity and plasma viscosity in patients with sudden deafness. Acta Otolaryngol. 1994;114(6):601–7.
Lin L, Hua L, Cai HY, Yang WM. Effects of scutellarin on vascular endothelial growth factor and protein kinase Cε expression in human umbilical vein endothelial cells after ischemia-reperfusion injury. J Clin Rehabilit Tissue Eng Res. 2011:3723–3727.
Berjis N, Moeinimehr M, Hashemi SM, Hashemi SM, Bakhtiari EK, Nasiri S. Endothelial dysfunction in patients with sudden sensorineural hearing loss. Adv Biomed Res. 2016;5:5.
Chappey O, Wautier MP, Boval B, Wautier JL. Endothelial cells in culture: an experimental model for the study of vascular dysfunctions. Cell Biol Toxicol. 1996;12(4–6):199–205.
Zhang H, Wang XY, Liu Y, et al. Effects of dengzhan xixin injection on inflammatory cytokine production in rat cardiac microvascular cells induced by tumor necrosis factor. Chin Pharma J. 2009;44(23):1791–5.
Song Y, Zhang HM, Jian-Jian MA, Chang-Ling LI. Effects of scutellarein on thrombosis and hemorheology in rats. Chin J New Drugs. 2011;20(15):1446–9.
Acknowledgements
Acknowledgements
We thank the participants of the study.
Funding
This research was funded by the National Natural Science Foundation of China (No. 81771015) and the Shanghai Municipal Education Commission/Gaofeng Clinical Medicine Grant Support (No. 20152526) to Yanmei Feng.
Authorship
All named authors meet the International Committee of Medical Journal Editors (ICMJE) criteria for authorship for this article, take responsibility for the integrity of the work as a whole, and have given their approval for this version to be published.
Authorship Contributions
Zhong Zheng wrote the manuscript. Ying Shen, Liang Xia analysed data. Hongmin Wu, Huiqun Zhou, Xulan Tang, Lili Meng, Hui Wang, Yaqin Wu collected data. Haibo Shi, Shankai Yin gave suggestions on the data acquisition and analysis. Yanmei Feng and Zhengnong Chen designed and supervised the research. All authors reviewed the manuscript.
Disclosures
Zhong Zheng, Ying Shen, Liang Xia, Hongmin Wu, Huiqun Zhou, Xulan Tang, Lili Meng, Hui Wang, Yaqin Wu, Haibo Shi, Shankai Yin, Yanmei Feng and Zhengnong Chen have nothing to disclose. The funders had no role in the design of the study; in the collection, analyses, or interpretation of data; in the writing of the manuscript, or in the decision to publish the results.
Compliance with Ethics Guidelines
The study protocol was approved and implemented according to the ethical standards of the Shanghai Jiaotong University Affiliated Sixth People’s Hospital ethics committee. Information of patients was anonymized and deidentified prior to analysis. The progress was conducted in accordance with the spirit of the Helsinki Declaration. All participants provided written informed consent for their inclusion in the database and the use of their data for research purposes.
Data Availability
The datasets generated during and/or analyzed during the current study are available from the corresponding author on reasonable request.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding authors
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Zheng, Z., Shen, Y., Xia, L. et al. Glucocorticoid and Breviscapine Combination Therapy Versus Glucocorticoid Alone on Sudden Sensorineural Hearing Loss in Patients with Different Audiometric Curves. Adv Ther 37, 4959–4968 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12325-020-01513-9
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12325-020-01513-9