Abstract
Introduction
The aim of this study is to investigate the additive intraocular pressure (IOP)-lowering effects and safety of the selective Rho kinase inhibitor, 0.4% ripasudil, in patients with glaucoma not adequately controlled by other maximal tolerated medical therapies.
Methods
We retrospectively reviewed 92 glaucoma patients who received ripasudil as an additive glaucoma treatment. In spite of receiving prior maximal tolerated medical therapies, all patients had uncontrolled glaucoma before receiving ripasudil. IOP was recorded at all follow-up dates.
Results
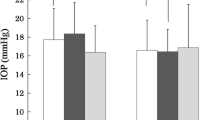
The study population consisted of 43 primary open-angle glaucoma (POAG), 28 normal-tension glaucoma (NTG), ten secondary glaucoma, seven exfoliation glaucoma, and four developmental glaucoma patients. After ripasudil administration, there was a significant decrease in the IOP. The mean pre-administration IOP and % IOP reduction at the last follow-up were 19.7 ± 4.9 mmHg and 6.5 ± 17.0% for POAG, 15.5 ± 2.0 mmHg and 2.3 ± 10.4% for NTG, 22.8 ± 8.3 mmHg and 19.1 ± 13.5% for secondary glaucoma, 22.5 ± 4.4 mmHg and 2.1 ± 14.5% for exfoliation glaucoma, and 20.2 ± 8.9 mmHg and 11.4 ± 23.1% for developmental glaucoma, respectively. Side effects led to ripasudil discontinuation in 13 patients, with five exhibiting an allergic reaction, six developing blepharitis, and two having a burning sensation.
Conclusions
Use of ripasudil as an adjunctive therapy resulted in lowering of the IOP. Ripasudil was well tolerated.
Funding
Grant-in-Aid for Scientific Research from the Ministry of Education, Culture, Sports, Science, and Technology of Japan (26462689).




Similar content being viewed by others
References
Weinreb RN, Khaw PT. Primary open-angle glaucoma. Lancet. 2004;363:1711–20.
Kass MA, Heuer DK, Higginbotham EJ, et al. The Ocular Hypertension Treatment Study: a randomized trial determines that topical ocular hypotensive medication delays or prevents the onset of primary open-angle glaucoma. Arch Ophthalmol. 2002;120:701–13.
Honjo M, Tanihara H, Inatani M, et al. Effects of Rho-associated protein kinase inhibitor, Y-27632, on intraocular pressure outflow facility. Invest Ophthalmol Vis Sci. 2001;42:137–44.
Tokushige H, Inatani M, Nemoto S, et al. Effects of topical administration of Y-39983, a selective rho-associated protein kinase inhibitor, on ocular tissues in rabbits and monkeys. Invest Ophthalmol Vis Sci. 2007;48:3216–22.
Isobe T, Mizuno K, Kaneko Y, Ohta M, Koide T, Tanabe S. Effects of K-115, a Rho-kinase inhibitor on aqueous humor dynamics in rabbits. Curr Eye Res. 2014;39:813–22.
Tanihara H, Inoue T, Yamamoto T, Kuwayama Y, Abe H, Araie M, K-115 Clinical Study Group. Phase I clinical trials of a selective Rho kinase inhibitor K-115. JAMA Ophthalmol. 2013;131:1288–95.
Tanihara H, Inoue T, Yamamoto T, Kuwayama Y, Abe H, Araie M, K-115 Clinical Study Group. Phase 2 randomized clinical study of a rho kinase inhibitor, K-115, in primary open-angle glaucoma and ocular hypertension. Am J Ophthalmol. 2013;156:731–6.
Tanihara H, Inoue T, Yamamoto T, Kuwayama Y, Abe H, Araie M, K-115 Clinical Study Group. Intra-ocular pressure-lowering effects of a Rho kinase inhibitor, ripasudil (K-115), over 24 hours in primary open-angle glaucoma and ocular hypertension: a randomized, open-label, crossover study. Acta Ophthalmol. 2015;93:e254–60.
Tanihara H, Inoue T, Yamamoto T, et al. Additive intraocular pressure-lowering effects of the rho kinase inhibitor ripasudil (K-115) combined with timolol or latanoprost. JAMA Ophthalmol. 2015;133:755–61.
Hodapp E, Parrish RK II, Anderson DR. Clinical detection in glaucoma. St. Louis: Mosby; 1993. p. 52–61.
Tanihara H, Inoue T, Yamamoto T, et al. One-year clinical evaluation of 0.4% ripasudil (K-115) in patients with open-angle glaucoma and ocular hypertension. Acta Ophthalmol. 2016;94:e26–34.
Acknowledgments
Sponsorship and article processing charges for this study were funded by a Grant-in-Aid for Scientific Research from the Ministry of Education, Culture, Sports, Science, and Technology of Japan (26462689).
All named authors meet the International Committee of Medical Journal Editors (ICMJE) criteria for authorship for this manuscript, take responsibility for the integrity of the work as a whole, and have given final approval to the version to be published.
Data collection and analysis of this manuscript was provided by Dr. Shino Sato.
Writing of this manuscript was provided by Dr. Kazuyuki Hirooka.
Editing assistance of this manuscript was provided by Dr. Eri Nitta, Dr. Kaori Ukegawa and Dr. Akitaka Tsujikawa.
Disclosures
Shino Sato, Kazuyuki Hirooka, Eri Nitta, Kaori Ukegawa, and Akitaka Tsujikawa have nothing to disclose.
Compliance with Ethics Guidelines
All procedures followed were in accordance with the ethical standards of the responsible committee on human experimentation and with the Helsinki Declaration of 1964, as revised in 2013. Informed consent was obtained from all patients for being included in the study.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Enhanced content
To view enhanced content for this article go to http://www.medengine.com/Redeem/74E4F0604FDDABAE.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Sato, S., Hirooka, K., Nitta, E. et al. Additive Intraocular Pressure Lowering Effects of the Rho Kinase Inhibitor, Ripasudil in Glaucoma Patients Not Able to Obtain Adequate Control After Other Maximal Tolerated Medical Therapy. Adv Ther 33, 1628–1634 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12325-016-0389-3
Received:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12325-016-0389-3