Abstract
Introduction
Atrial septal defect (ASD) is one of the most common congenital heart diseases in children. P-wave dispersion has been reported to be associated with non-homogeneous propagation of sinus impulses. The heterogeneity of atrial conduction time may predispose the atria to arrhythmias. The aim of this study was to determine the impact of surgical repair on P-wave indices in children with isolated secundum ASD.
Methods
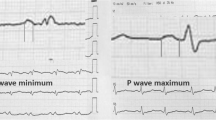
Children with isolated secundum ASD undergoing surgical repair (n=50; mean age, 7.0±3.0 years) and healthy controls (n=51; mean age, 7.6±2.7 years) were compared. Maximum P-wave duration (Pmax), shortest duration (Pmin) and P-wave dispersion (Pd) were measured using 12-lead surface electrocardiography.
Results
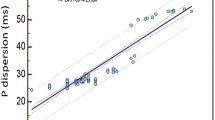
Mean Pmax was found to be significantly higher in children with ASD compared with controls (95.2±10.8 vs 84.1±9.2 msec; P<0.001), and Pd before surgery was significantly higher compared with controls (47.4±12.0 vs 38.8±9.7 msec; P<0.001). Both P-wave indices were significantly decreased within the first year after surgical closure — the values decreased to those comparable to healthy controls (Pmax, 86.2±9.7 msec; Pd, 39.8±10.7 msec; P>0.05).
Conclusion
Surgical closure of ASD in children decreases Pmax and P-wave conduction time. We speculate that earlier closure of the defect may play an important role in avoiding permanent changes in the atrial myocardium and atrial fibrillation in adulthood.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Samánek M, Slavík Z, Zborilová B, Hrobonová V, Vorísková M, Skovránek J. Prevalence, treatment, and outcome of heart disease in live-born children: a prospective analysis of 91,823 live-born children. Pediatr Cardiol. 1989;10:205–211.
Ruschhaupt DG, Khoury L, Thilenius OG, Replogle RL, Arcilla RA. Electrophysiologic abnormalities of children with ostium secundum atrial septal defect. Am J Cardiol. 1984;53:1643–1647.
Murphy JG, Gersh BJ, McGoon MD, et al. Long-term outcome after surgical repair of isolated atrial septal defect. Follow-up at 27 to 32 years. N Engl J Med. 1990;323:1645–1650.
Hashiba K, Tanigawa M, Fukatani M, et al. Electrophysiologic properties of atrial muscle in paroxysmal atrial fibrillation. Am J Cardiol. 1989;64:20J–23J.
Dilaveris PE, Gialafos EJ, Sideris SK, et al. Simple electrocardiographic markers for the prediction of paroxysmal idiopathic atrial fibrillation. Am Heart J. 1998;135:733–738.
Tezcan UK, Amasyali B, Can I, et al. Increased P-wave dispersion and maximum P-wave duration after hemodialysis. Ann Noninvasive Electrocardiol. 2004;9:34–38.
Dogan A, Acar G, Gedikli O, et al. A comparison of P-wave duration and dispersion in patients with short-term and long-term atrial fibrillation. J Electrocardiol. 2003;36:251–255.
Tsikouris JP, Kluger J, Song J, White CM. Changes in P-wave dispersion and P-wave duration after open heart surgery are associated with the peak incidence of atrial fibrillation. Heart Lung. 2001;30:466–471.
Kose S, Aytemir K, Sade E, et al. Detection of patients with hypertrophic cardiomyopathy at risk for paroxysmal atrial fibrillation during sinus rhythm by P-wave dispersion. Clin Cardiol. 2003;26:431–434.
Ho TF, Chia EL, Yip WC, Chan KY. Analysis of P-wave and P dispersion in children with secundum atrial septal defect. Ann Noninvasive Electrocardiol. 2001;6:305–309.
Guray U, Guray Y, Mecit B, Yilmaz MB, Sasmaz H, Korkmaz S. Maximum P-wave duration and P-wave dispersion in adult patients with secundum atrial septal defect: the impact of surgical repair. Ann Noninvasive Electrocardiol. 2004;9:136–141.
Sahn DJ, DeMaria A, Kisslo J, Weyman A. Recommendations regarding quantitation in M-mode echocardiography: results of a survey of echocardiographic measurements. Circulation. 1978;58:1072–1083.
Schiller NB, Shah PM, Crawford M, et al. Recommendations for quantitation of the left ventricle by two-dimensional echocardiography. American Society of Echocardiography Committee on Standards, Subcommittee on Quantitation of Two-Dimensional Echocardiograms. J Am Soc Echocardiogr. 1989;2:358–367.
Berger F, Vogel M, Kramer A, et al. Incidence of atrial flutter/fibrillation in adults with atrial septal defect before and after surgery. Ann Thorac Surg. 1999;68:75–78.
Oliver JM, Gallego P, Gonzalez A, Benito F, Mesa JM, Sobrino JA. Predisposing conditions for atrial fibrillation in atrial septal defect with and without operative closure. Am J Cardiol. 2002;89:39–43.
Porter CJ, Feldt RH, Edwards WD, Scward JB, Schaff HV. Atrial septal defects. In: Allen HD, Gutgesell HP, Clark EB, Driscoll DJ, eds. Moss and Adams’ Heart Disease in Infants, Children, and Adolescents: Including the Fetus and Young Adult. Philadelphia: Lippincott Williams & Wilkins; 2001:603–617.
Gatzoulis MA, Freeman MA, Siu SC, Webb GD, Harris L. Atrial arrhythimia after surgical closure of atrial septal defects in adults. N Engl J Med. 1999;340:839–846.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Yavuz, T., Nisli, K., Oner, N. et al. The effects of surgical repair on P-wave dispersion in children with secundum atrial septal defect. Adv Therapy 25, 795–800 (2008). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12325-008-0081-3
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12325-008-0081-3