Abstract
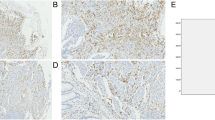
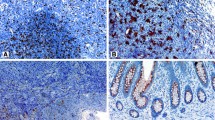
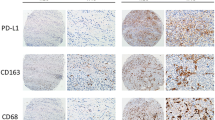
The scavenger receptor, CD163, is a macrophage-specific marker. Recent studies have shown that CD163 expression in breast and rectal cancer cells is associated with poor prognosis. This study was conducted to evaluate the relationship between CD163 expression as a macrophage trait in cancer cells, and macrophage infiltration and its clinical significance in colorectal cancer. Immunostaining of CD163 and macrophage infiltration were evaluated in paraffin-embedded specimens, earlier analyzed for CD31, D2-40 and S-phase fraction, from primary tumors and normal colorectal mucosa of 75 patients with colorectal carcinoma. The outcomes were analyzed in relation to clinical-pathological data. CD163 expression was positive in cancer cells in 20 % of colorectal cancer patients and was related to advanced tumor stages (P = 0.008) and unfavorable prognosis (p = 0.001). High macrophage infiltration was related to shorter survival and positive CD163 expression in tumor cells. The prognostic impact of macrophage infiltration was independent of tumor stage and CD163 expression in cancer cells (p = 0.034). The expression of macrophage phenotype in colorectal cancer cells is associated with macrophage density in tumor stroma and lower survival rates. Macrophage infiltration has an independent prognostic impact on mortality in colorectal cancer. In accordance with previous experimental studies, these findings provide new insights into the role of macrophages in colorectal cancer.




Similar content being viewed by others
References
Mantovani A, Sozzani S, Locati M, Allavena P, Sica A (2002) Macrophage Polarization: Tumor-Associated Macrophages as a Paradigm for Polarized M2 Mononuclear Phagocytes. Trends Immunol 23(11):549–555
Lin EY, Pollard JW (2007) Tumor-Associated Macrophages Press the Angiogenic Switch in Breast Cancer. Cancer Res 67(11):5064–5066
Sica A, Schioppa T, Mantovani A, Allavena P (2006) Tumour-Associated Macrophages are a Distinct M2 Polarised Population Promoting Tumour Progression: Potential Targets of Anti-Cancer Therapy. Eur J Cancer 42(6):717–727
Cecconi O, Calorini L, Mannini A, Mugnai G, Ruggieri S (1997) Enhancement of Lung-Colonizing Potential of Murine Tumor Cell Lines co-Cultivated With Activated Macrophages. Clin Exp Metastasis 15(2):94–101
Oosterling SJ, van der Bij GJ, Meijer GA, Tuk CW, van Garderen E, van Rooijen N, Meijer S, van der Sijp JR, Beelen RH, van Egmond M (2005) Macrophages Direct Tumour Histology and Clinical Outcome in a Colon Cancer Model. J Pathol 207(2):147–155. doi:10.1002/path.1830
Miselis NR, Wu ZJ, Van Rooijen N, Kane AB (2008) Targeting Tumor-Associated Macrophages in an Orthotopic Murine Model of Diffuse Malignant Mesothelioma. Mol Cancer Ther 4:788–799. doi:10.1158/1535-7163.MCT-07-0579
Bingle L, Brown NJ, Lewis CE (2002) The Role of Tumour-Associated Macrophages in Tumour Progression: Implications for new Anticancer Therapies. J Pathol 196(3):254–265. doi:10.1002/path.1027 [pii]
Tan SY, Fan Y, Luo HS, Shen ZX, Guo Y, Zhao LJ (2005) Prognostic Significance of Cell Infiltrations of Immunosurveillance in Colorectal Cancer. World J Gastroenterol 11(8):1210–1214
Lackner C, Jukic Z, Tsybrovskyy O, Jatzko G, Wette V, Hoefler G, Klimpfinger M, Denk H, Zatloukal K (2004) Prognostic Relevance of Tumour-Associated Macrophages and von Willebrand Factor-Positive Microvessels in Colorectal Cancer. Virchows Arch 445(2):160–167. doi:10.1007/s00428-004-1051-z
Dvorak HF (1986) Tumors: Wounds That do not healSimilarities Between Tumor Stroma Generation and Wound Healing. N Engl J Med 315(26):1650–1659
Murdoch C, Lewis CE (2005) Macrophage Migration and Gene Expression in Response to Tumor Hypoxia. Int j of cancer J int du cancer 117(5):701–708. doi:10.1002/ijc.21422
Chen JJ, Yao PL, Yuan A, Hong TM, Shun CT, Kuo ML, Lee YC, Yang PC (2003) Up-Regulation of Tumor Interleukin-8 Expression by Infiltrating Macrophages: Its Correlation With Tumor Angiogenesis and Patient Survival in non-Small Cell Lung Cancer. Clin Cancer Res 9(2):729–737
Sundar SS, Ganesan TS (2007) Role of Lymphangiogenesis in Cancer. J Clin Oncol 25(27):4298–4307. doi:10.1200/JCO.2006.07.1092
Vassilopoulos G, Russell DW (2003) Cell Fusion: An Alternative to Stem Cell Plasticity and its Therapeutic Implications. Curr Opin Genet Dev 13(5):480–485
Alvarez-Dolado M, Pardal R, Garcia-Verdugo JM, Fike JR, Lee HO, Pfeffer K, Lois C, Morrison SJ, Alvarez-Buylla A (2003) Fusion of Bone-Marrow-Derived Cells With Purkinje Neurons, Cardiomyocytes and Hepatocytes. Nature 425(6961):968–973
Nygren JM, Jovinge S, Breitbach M, Sawen P, Roll W, Hescheler J, Taneera J, Fleischmann BK, Jacobsen SE (2004) Bone Marrow-Derived Hematopoietic Cells Generate Cardiomyocytes at a low Frequency Through Cell Fusion, but not Transdifferentiation. Nat Med 10(5):494–501
Chakraborty AK, de Freitas SJ, Espreafico EM, Pawelek JM (2001) Human Monocyte x Mouse Melanoma Fusion Hybrids Express Human Gene. Gene 275(1):103–106
Chakraborty AK, Pawelek J (2007) Beta1,6-Branched Oligosaccharides Regulate Melanin Content and Motility in Macrophage-Melanoma Fusion Hybrids. Melanoma Res 17(1):9–16
Chakraborty AK, Sodi S, Rachkovsky M, Kolesnikova N, Platt JT, Bolognia JL, Pawelek JM (2000) A Spontaneous Murine Melanoma Lung Metastasis Comprised of Host x Tumor Hybrids. Cancer Res 60(9):2512–2519
Pawelek JM (2008) Cancer-Cell Fusion With Migratory Bone-Marrow-Derived Cells as an Explanation for Metastasis: new Therapeutic Paradigms. Future Oncol 4(4):449–452
Pawelek JM, Chakraborty AK (2008) Fusion of Tumour Cells With Bone Marrow-Derived Cells: A Unifying Explanation for Metastasis. Nat Rev Cancer 8(5):377–386
Powell AE, Anderson EC, Davies PS, Silk AD, Pelz C, Impey S, Wong MH (2011) Fusion between Intestinal epithelial cells and macrophages in a cancer context results in nuclear reprogramming. Cancer Res 71 (4):1497–1505. doi:0008–5472.CAN-10-3223 [pii]10.1158/0008-5472.CAN-10-3223
Silk AD, Gast CE, Davies PS, Fakhari FD, Vanderbeek GE, Mori M, Wong MH (2013) Fusion Between Hematopoietic and Epithelial Cells in Adult Human Intestine. PLoS One 8(1):e55572. doi:10.1371/journal.pone.0055572
Chakraborty A, Lazova R, Davies S, Backvall H, Ponten F, Brash D, Pawelek J (2004) Donor DNA in a Renal Cell Carcinoma Metastasis from a Bone Marrow Transplant Recipient. Bone Marrow Transplant 34(2):183–186. doi:10.1038/sj.bmt.17045471704547 [pii]
Yilmaz Y, Lazova R, Qumsiyeh M, Cooper D, Pawelek J (2005) Donor Y Chromosome in Renal Carcinoma Cells of a Female BMT Recipient: Visualization of Putative BMT-Tumor Hybrids by FISH. Bone Marrow Transplant 35(10):1021–1024
Nguyen TT, Schwartz EJ, West RB, Warnke RA, Arber DA, Natkunam Y (2005) Expression of CD163 (Hemoglobin Scavenger Receptor) in Normal Tissues, Lymphomas, Carcinomas, and Sarcomas is Largely Restricted to the Monocyte/Macrophage Lineage. Am J Surg Pathol 29(5):617–624
Shabo I, Stal O, Olsson H, Dore S, Svanvik J (2008) Breast Cancer Expression of CD163, a Macrophage Scavenger Receptor, is Related to Early Distant Recurrence and Reduced Patient Survival. Int j of cancer J int du cancer 123(4):780–786
Shabo I, Olsson H, Sun XF, Svanvik J (2009) Expression of the Macrophage Antigen CD163 in Rectal Cancer Cells is Associated With Early Local Recurrence and Reduced Survival Time. Int j of cancer J int du cancer. doi:10.1002/ijc.24506
Larizza L, Schirrmacher V, Pfluger E (1984) Acquisition of High Metastatic Capacity After in Vitro Fusion of a Nonmetastatic Tumor Line With a Bone Marrow-Derived Macrophage. J Exp Med 160(5):1579–1584
Larsson LI, Bjerregaard B, Wulf-Andersen L, Talts JF (2007) Syncytin and Cancer Cell Fusions. ScientificWorldJournal 7:1193–1197. doi:10.1100/tsw.2007.212
Pawelek J, Chakraborty A, Lazova R, Yilmaz Y, Cooper D, Brash D, Handerson T (2006) Co-Opting Macrophage Traits in Cancer Progression: A Consequence of Tumor Cell Fusion? Contrib Microbiol 13:138–155
Pawelek JM (2005) Tumour-Cell Fusion as a Source of Myeloid Traits in Cancer. Lancet Oncol 6(12):988–993
Chakraborty AK, Pawelek J, Ikeda Y, Miyoshi E, Kolesnikova N, Funasaka Y, Ichihashi M, Taniguchi N (2001) Fusion Hybrids With Macrophage and Melanoma Cells up-Regulate N-Acetylglucosaminyltransferase V, beta1-6 Branching, and Metastasis. Cell Growth Differ 12(12):623–630
Droste A, Sorg C, Hogger P (1999) Shedding of CD163, a Novel Regulatory Mechanism for a Member of the Scavenger Receptor Cysteine-Rich Family. Biochem Biophys Res Commun 256(1):110–113
Hogger P, Dreier J, Droste A, Buck F, Sorg C (1998) Identification of the Integral Membrane Protein RM3/1 on Human Monocytes as a Glucocorticoid-Inducible Member of the Scavenger Receptor Cysteine-Rich Family (CD163). J Immunol 161(4):1883–1890
Schluter C, Duchrow M, Wohlenberg C, Becker MH, Key G, Flad HD, Gerdes J (1993) The Cell Proliferation-Associated Antigen of Antibody Ki-67: A Very Large, Ubiquitous Nuclear Protein With Numerous Repeated Elements, Representing a new Kind of Cell Cycle-Maintaining Proteins. J Cell Biol 123(3):513–522
Li SH, Li CF, Sung MT, Eng HL, Hsiung CY, Huang WW, Lin CN, Yu SC, Huang HY (2007) Skp2 is an Independent Prognosticator of Gallbladder Carcinoma Among p27 (Kip1)-Interacting Cell Cycle Regulators: An Immunohistochemical Study of 62 Cases by Tissue Microarray. Mod Pathol 20(4):497–507. doi:10.1038/modpathol.3800762
Roy S, Chu A, Trojanowski JQ, Zhang PJ (2005) D2-40, a Novel Monoclonal Antibody Against the M2A Antigen as a Marker to Distinguish Hemangioblastomas from Renal Cell Carcinomas. Acta Neuropathol 109(5):497–502. doi:10.1007/s00401-005-0999-3
Sharma S, Sharma MC, Sarkar C (2005) Morphology of Angiogenesis in Human Cancer: A Conceptual Overview, Histoprognostic Perspective and Significance of Neoangiogenesis. Histopathology 46(5):481–489. doi:10.1111/j.1365-2559.2005.02142.x
Adell G, Zhang H, Jansson A, Sun XF, Stal O, Nordenskjold B (2001) Decreased Tumor Cell Proliferation as an Indicator of the Effect of Preoperative Radiotherapy of Rectal Cancer. Int J Radiat Oncol Biol Phys 50(3):659–663
Gao J, Knutsen A, Arbman G, Carstensen J, Franlund B, Sun XF (2009) Clinical and Biological Significance of Angiogenesis and Lymphangiogenesis in Colorectal Cancer. Dig Liver Dis 41(2):116–122. doi:10.1016/j.dld.2008.07.315
Kundel HL, Polansky M (2003) Measurement of Observer Agreement. Radiology 228(2):303–308
Vermeulen PB, Gasparini G, Fox SB, Toi M, Martin L, McCulloch P, Pezzella F, Viale G, Weidner N, Harris AL, Dirix LY (1996) Quantification of Angiogenesis in Solid Human Tumours: An International Consensus on the Methodology and Criteria of Evaluation. Eur J Cancer 32A(14):2474–2484
Jansson A, Sun XF (1997) Ki-67 Expression in Relation to Clinicopathological Variables and Prognosis in Colorectal Adenocarcinomas. APMIS 105(9):730–734
Sun XF, Carstensen JM, Stal O, Zhang H, Nilsson E, Sjodahl R, Nordenskjold B (1993) Prognostic Significance of p53 Expression in Relation to DNA Ploidy in Colorectal Adenocarcinoma. Virchows Arch A Pathol Anat Histopathol 423(6):443–448
Mantovani A, Biswas SK, Galdiero MR, Sica A, Locati M (2013) Macrophage Plasticity and Polarization in Tissue Repair and Remodelling. J Pathol 229(2):176–185. doi:10.1002/path.4133
Riboldi E, Porta C, Morlacchi S, Viola A, Mantovani A, Sica A (2013) Hypoxia-Mediated Regulation of Macrophage Functions in Pathophysiology. Int Immunol 25(2):67–75. doi:10.1093/intimm/dxs110
Alexander P, Eccles SA, Gauci CL (1976) The Significance of Macrophages in Human and Experimental Tumors. Ann N Y Acad Sci 276:124–133
Hagemann T, Robinson SC, Schulz M, Trumper L, Balkwill FR, Binder C (2004) Enhanced Invasiveness of Breast Cancer Cell Lines Upon co-Cultivation With Macrophages is due to TNF-Alpha Dependent up-Regulation of Matrix Metalloproteases. Carcinogenesis 25(8):1543–1549. doi:10.1093/carcin/bgh146bgh146 [pii]
Leber TM, Balkwill FR (1998) Regulation of Monocyte MMP-9 Production by TNF-Alpha and a Tumour-Derived Soluble Factor (MMPSF). Br J Cancer 78(6):724–732
Augsten M, Hagglof C, Olsson E, Stolz C, Tsagozis P, Levchenko T, Frederick MJ, Borg A, Micke P, Egevad L, Ostman A (2009) CXCL14 is an Autocrine Growth Factor for Fibroblasts and Acts as a Multi-Modal Stimulator of Prostate Tumor Growth. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 106(9):3414–3419. doi:10.1073/pnas.0813144106
Shabo IOH, Sun XF, Svanvik J (2009) Expression of the Macrophage Antigen CD163 in Rectal Cancer Cells is Associated With Early Local Recurrence and Reduced Survival Time. Int J Cancer Accepted in Mars 2009
Busund LT, Killie MK, Bartnes K, Seljelid R (2003) Spontaneously Formed Tumorigenic Hybrids of Meth A Sarcoma Cells and Macrophages in Vivo. Int j of cancer J int du cancer 106(2):153–159
Rachkovsky M, Sodi S, Chakraborty A, Avissar Y, Bolognia J, McNiff JM, Platt J, Bermudes D, Pawelek J (1998) Melanoma x Macrophage Hybrids With Enhanced Metastatic Potential. Clin Exp Metastasis 16(4):299–312
Busund LT, Killie MK, Bartnes K, Seljelid R (2002) Spontaneously Formed Tumorigenic Hybrids of Meth A Sarcoma and Macrophages Grow Faster and are Better Vascularized Than the Parental Tumor. Int j of cancer J int du cancer 100(4):407–413
Nygren JM, Liuba K, Breitbach M, Stott S, Thoren L, Roell W, Geisen C, Sasse P, Kirik D, Bjorklund A, Nerlov C, Fleischmann BK, Jovinge S, Jacobsen SE (2008) Myeloid and Lymphoid Contribution to non-Haematopoietic Lineages Through Irradiation-Induced Heterotypic Cell Fusion. Nat Cell Biol 10(5):584–592
Johansson CB, Youssef S, Koleckar K, Holbrook C, Doyonnas R, Corbel SY, Steinman L, Rossi FM, Blau HM (2008) Extensive Fusion of Haematopoietic Cells With Purkinje Neurons in Response to Chronic Inflammation. Nat Cell Biol 10(5):575–583. doi:10.1038/ncb1720
Liu C, Chen Z, Zhang T, Lu Y (2006) Multiple Tumor Types may Originate from Bone Marrow-Derived Cells. Neoplasia 8(9):716–724
Powell AE, Anderson EC, Davies PS, Silk AD, Pelz C, Impey S, Wong MH Fusion between Intestinal Epithelial Cells and Macrophages in a Cancer Context Results in Nuclear Reprogramming. Cancer Res 71 (4):1497–1505. doi:10.1158/0008-5472.CAN-10-3223
Pawelek JM, Chakraborty AK (2008) The Cancer Cell--Leukocyte Fusion Theory of Metastasis. Adv Cancer Res 101:397–444. doi:10.1016/S0065-230X(08)00410-7
Houghton J, Stoicov C, Nomura S, Rogers AB, Carlson J, Li H, Cai X, Fox JG, Goldenring JR, Wang TC (2004) Gastric Cancer Originating from Bone Marrow-Derived Cells. Science 306(5701):1568–1571. doi:10.1126/science.1099513
Acknowledgements
The authors are indebted to members of the South-East Sweden Colorectal Cancer Group for providing us with clinical data. Thanks are due to Mrs. Birgitta Frånlund for valuable help with the immunohistochemistry. The work was supported by The Health Research Council in the South-East of Sweden.
Sources of support
County Council of Östergötland, Sweden.
Competing of interest
All authors have no conflicts of interest.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Shabo, I., Olsson, H., Elkarim, R. et al. Macrophage Infiltration in Tumor Stroma is Related to Tumor Cell Expression of CD163 in Colorectal Cancer. Cancer Microenvironment 7, 61–69 (2014). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12307-014-0145-7
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12307-014-0145-7