Abstract
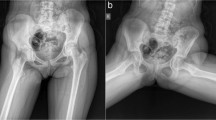
The Authors report the case of a 28-year-old patient with type 1 neurofibromatosis, who presented a pathological dislocation of the hip. This event was preceded by the development of a neurological pattern of spastic paraparesis and decreased pain sensation in both lower limbs, secondary to the progression of a dystrophic kyphoscoliosis. Pathological dislocation of the hip in neurofibromatosis has been reported in the literature as a consequence of intra-articular growth of neurofibromas. Conversely, in the case described here, clinical and radiographic features and the absence of neurofibromas in the joint, verified by means of radiographic and histological examinations, suggested the diagnosis of neuropathic arthropathy. The treatment of hip dislocation should be differentiated according to the aetiology, given the underlying articular instability in cases of neuropathic arthropathy.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Halmai V, Doman I, de Jonge T, Illes T (2002) Surgical treatment of spinal deformities associated with neurofibromatosis type 1. Report of 12 cases. J Neurosurg 97[Suppl 3]:310–316
Riccardi V (1981) Von Recklinghausen neurofibromatosis. N Engl J Med 305:1617–1627
Ruggieri M, Huson SM (1999) The neurofibromatoses. An overview. Ital J Neurol Sci 20:89–108
Feldman F (1995) Tuberous sclerosis, neurofibromatosis and fibrous dysplasia. In: Resnick D (ed) Diagnosis of bone and joint disorders, Vol. 6, 3rd Edn, WB Saunders Company, Philadelphia, pp 4353–4395
Guilleminet M, Creyssel J, de Mourgues G, Fischer L (1970) Von Recklinghausen’s neurofibromatosis. Congenital hypertrophy of the lower limb in childhood and spontaneous luxation of the homolateral hip in adult age. Presse Med 78:1269–1271
Haga N, Nakamura S, Taniguchi K, Iwaya T (1994) Pathologic dislocation of the hip in von Recklinghausen’s disease: a report of two cases. J Pediatr Orthop 14:674–676
Lachiewicz PF, Salvati EA, Hely D, Ghelman B (1983) Pathological dislocation of the hip in neufibromatosis: a case report. J Bone Joint Surg Am 65:414–415
Lucet L, Elayoubi L, Defives T et al (1993) Anterior pathologic dislocation of the hip in adulthood complicating Von Recklinghausen neurofibromatosis. Rev Rhum Ed Fr 60:79–80
Nakasone S, Norimatsu H, Hamasaki N et al (1989) A case report of recurrent dislocation of the hip joint with neurofibromatosis. Seikeigeka to Saigaigeka 38:511–514
Odent T, Ranger P, Aarabi M et al (2004) Total hip arthroplasty in a patient with neurofibromatosis type I and recurrent spontaneous hip dislocation. Can J Surg 47:219–220
Phillips JE, McMaster MJ (1987) Pathological dislocation of the hip in neurofibromatosis. J R Coll Surg Edinb 32:180–182
Johnson JT (1967) Neuropathic fractures and joint injuries. Pathogenesis and rationale of prevention and treatment. J Bone Joint Surg Am 49:1–30
Johnson JT (1973) Neuropathic injuries of the hip. Clin Orthop Relat Res 90:29–32
Jones EA, Manaster BJ, May DA, Disler DG (2000) Neuropathic osteoarthropathy: diagnostic dilemmas and differential diagnosis. Radiographics 20:S279–S293
Resnick D (1995) Neuropathic osteoarthropathy. In: Resnick D (ed) Diagnosis of bone and joint disorders, Vol. 5, 3rd Edn. WB Saunders Company, Philadelphia, pp 3413–3442
Gilman S (2002) Joint position sense and vibration sense: anatomical organisation and assessment. J Neurol Neurosurg Psychiatry 73:473–477
Ishii Y, Tojo T, Terajima K et al (1999) Intracapsular components do not change hip proprioception. J Bone Joint Surg Br 81:345–348
Lokiec F, Arbel R, Isakov J, Wientroub S (1998) Neuropathic arthropathy of the knee associated with an intra-articular neurofibroma in a child. J Bone Joint Surg Br 80:468–470
McCann PD, Herbert J, Feldman F, Kelly MA (1992) Neuropathic arthropathy associated with neurofibromatosis: a case report. J Bone Joint Surg Am 74:1411–1414
Gualtieri G, Sudanese A, Toni A, Giunti A (1991) Loosening of a hip prosthesis in a patient affected with tabetic disease. Chir Organi Mov 76:83–85
Sudanese A, Toni A, Moscato M et al (1992) Radiographic and therapeutic aspects of neurogenic arthropathy. Chir Organi Mov 77:325–333
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Lampasi, M., Greggi, T. & Sudanese, A. Pathological dislocation of the hip in neurofibromatosis: a case report. Chir Organi Mov 91, 163–166 (2008). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12306-007-0027-y
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12306-007-0027-y