Abstract
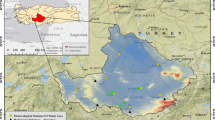
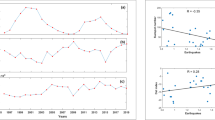
We analyzed the co-seismic responses of groundwater level and temperature in the Tayuan Well, Beijing, China, induced by 85 distant earthquakes over the period from January 2004 to July 2009. The results show that the Tayuan Well records earthquakes worldwide and that the co-seismic response shows the following pattern: water-level oscillation, temperature decrease, oscillations stop, return to normal temperature. The amplitudes of changes in water level and temperature are related to the earthquake magnitude and the distance to the epicenter. We discuss the mechanisms of the decrease in water temperature during the period of oscillations in water level, and the mechanisms of the temperature increase subsequent to the cessation of oscillations. We also analyze the results of previous studies on co-seismic response mechanisms, and consider the mechanisms of gas escape, heat diffusion, and cold-water seepage. These mechanisms may have induced the decrease in water temperature recorded in the present study, and the subsequent return to normal temperatures was due to heat exchange between the well water and the surrounding wall rock.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Asteriadis, G. and Livieratos, E., 1989, Pre-seismic responses of underground water level and temperature concerning a 4.8 magnitude earthquake in Greece on October 20, 1988. Tectonophysics, 170, 165–169.
Beak, F.J., Hector, E., and Xuan, Z., 2002, Fundamentals of Physics. Science Press, Beijing, 125 p. (in Chinese)
Brodsky, E.E., Roeloffs, E.A., Woodcock, D., Gall, I., and Manga, M., 2003, A mechanism for sustained groundwater pressure changes induced by distant earthquakes. Journal of Geophysical Research, 108, doi:10.1029/2002JB002321.
Che, Y.T., Wang, T.C., and Yu, J.Z., 1989, The status and direction of hydrosonic in China. Earthquake, 9, 70–72. (in Chinese with English abstract)
Che, Y.T., Yu, J.Z., and Liu, C.G., 1996, Researches and dynamic observation of groundwater temperature in China. Hydrogeology and Engineering Geology, 4, 34–37. (in Chinese with English abstract)
Chen, D.Q., Liu, Y.W., Yang, X.H., and Liu, Y.M., 2007, Co-seismic water level, temperature responses of some wells to far-field strong earthquakes and their mechanisms. Seismology and Geology, 29, 122–132. (in Chinese with English abstract)
Cooper, H.H., Bredehoeft, J.D., Papadopulos, I.S., and Bennett, R.R., 1965, The response of well-aquifer systems to seismic waves. Journal of Geophysical Research, 70, 3915–3926.
Fu, Z.Z., 1988, Premonition and dynamic observation of terrestrial heat. Corpus of Crust Structure and Stress, 1, 1–7. (in Chinese with English abstract)
Furuya, I. and Shimamura, H., 1988, Groundwater microtemperature and strain. Geophysical Journal International, 94, 345–353.
Gu, Y.Z., Che, Y.T., Yu, J.Z., and Zhang, P.Z., 2003, The study of the micro dynamic state of water temperature of the Tayuan Well. Earthquake, 23, 102–108. (in Chinese with English abstract)
Hamza, V.M., 2001, Tectonic leakage of fault bounded aquifers subject to non-isothermal recharge: a mechanism generating thermal precursors to seismic events. Physics of the Earth and Planetary Interiors, 126, 163–177.
Iassonov, P.P. and Beresnev, I.A., 2003, A model for enhanced fluid percolation in porous media by application of low-frequency elastic waves. Journal of Geophysical Research, 108, doi: 10.1029/2001JB000683.
Liu, L.B., Zhen, X.Y., and Peng, G.R., 1986, Primary analyze of water surging induced seismic wave in Wali well. Earthquake, 5, 12–19. (in Chinese with English abstract)
Liu, Y.W., Yang, X.H., and Liu, Y.M., 2005, The characters of groundwater responses induced by Sumatra Ms 8.7 earthquake. In: Survey and Forecast Department of CEA (ed.), Effect in Chinese Mainland Induced by Sumatra 8.7 Earthquake in Indonesia, 2004. Earthquake Press, Beijing, p. 131–258. (in Chinese)
Montgomery, D.R. and Manga, M., 2003, Streamflow and water well responses to earthquakes. Science, 300, 2047–2049.
Iassonov, P.P. and Beresnev, I.A., 2003, A model for enhanced fluid percolation in porous media by application of low-frequency elastic waves. Journal of Geophysical Research, 108, 21–38, doi10.1029/2001JB000683.
Palciauskas, V.V. and Domenico, P.A., 1982, Characterization of drained and undrained response of thermally loaded repository rocks. Water Resources Research, 18, 281–290.
Roeloffs, E.A., 1998, Persistent water level changes in a well near Parkfield California, due to local and distant earthquakes. Journal of Geophysical Research, 103, 869–889.
Shi, Y.L., Cao, J.L., Ma, L., and Yin, B.J., 2007, Tele-seismic coseismic well temperature changes and their interpretation. Acta Seismologica Sinica, 29, 265–273. (in Chinese with English abstract)
Shimamura, H., Ino, M., Hikawa, H., and Iwasaki, T., 1984, Groundwater microtemperature in earthquake regions. Pure and Applied Geophysics, 122, 298–314.
Sun, R.Y. and Cheng, G.X., 2004, Effect of artificial vibration on liquids flow through porous media. Journal of Hydrodynamics, 19, 552–557. (in Chinese with English abstract)
Wang, C., Wang, C.H., and Manga, M., 2004, Coseismic release of water from mountains: Evidence from the 1999 (MW=7.5) Chi-Chi, Taiwan, earthquake. Geology, 32, 769–772.
Yang, S.M. and Tao, W.Q., 2006, Heat Transmission. In: Song, X. (ed.), Unsteady Heat Conduction. Higher Education Press, Beijing, p. 112–138. (in Chinese)
Yang, Z.Z., Deng, Z.H., Zhao, Y.X., and Zhu, P.Y., 2005, Preliminary study on coseismic steps of water-level in Dazhai well, Simao city, Yunnan province. Acta Seismologica Sinica, 27, 569–574. (in Chinese with English abstract)
Yang, Z.Z., Deng, Z.H., Tao, J.L., Gu, Y.Z., Wang, Z.M., and Liu, C.L., 2007, Coseismic effects of water temperature based on digital observation from Tayuan well, Beijing. Acta Seismologica Sinica, 29, 203–213. (in Chinese with English abstract)
Yu, J.Z., Che, Y.T., and Liu, W.Z., 1997, Preliminary study on hydrodynamic mechanism of microbehavior of water temperature in well. Earthquake, 17, 389–396. (in Chinese with English abstract)
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Sun, X., Liu, Y. Changes in groundwater level and temperature induced by distant earthquakes. Geosci J 16, 327–337 (2012). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12303-012-0022-7
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12303-012-0022-7