Abstract
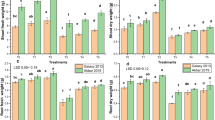
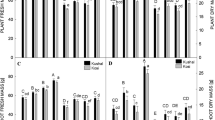
A pot experiment was conducted to examine the effect of foliar application of various levels of ZnSO4 on wheat (Triticum aestivum L.) under cadmium (Cd) stress. Seeds of two wheat varieties i.e., Ujala-2016 and Anaj-2017 were sown in sand filled plastic pots. Cadmium (CdCl2) stress i.e., 0 and 0.5 mM CdCl2 was applied in full strength Hoagland’s nutrient solution after 4 weeks of seed germination. Foliar spray of varying ZnSO4 levels i.e., 0, 2, 4, 6 and 8 mM was applied after 2 weeks of CdCl2 stress induction (of 6 week old plants). After 3 weeks of foliar treatment leaf samples of 9 week old wheat plants were collected for the determination of changes in various growth and physiobiochemical attributes. Results obtained showed that cadmium stress (0.5 mM CdCl2) significantly decreased shoot and root fresh and dry weights, shoot and root lengths, yield attributes, chlorophyll a contents and total phenolics, while increased hydrogen peroxide (H2O2), total soluble proteins, free proline, glycinebetaine (GB) contents, and activities of antioxidant enzymes i.e., catalase (CAT), ascorbate peroxidase (APX) and peroxidase (POD). Foliar application of varying ZnSO4 levels significantly increased various growth attributes, chlorophyll b contents, H2O2, free proline, GB and activities of antioxidant enzymes i.e., CAT, POD and APX, while decreased relative water contents and total phenolics under Cd stress or non stress conditions. Furthermore, both wheat varieties showed differential response under Cd stress and towards foliar application of ZnSO4 e.g., wheat var. Ujala-2016 was higher in shoot dry weight, root length, root fresh and dry weights, total leaf area per plant, 100 grains weight, number of tillers per plant, chlorophyll b, hydrogen peroxide (H2O2), activities of APX, POD, glycinebetaine and leaf free proline contents, while var. Anaj-2017 exhibited high shoot fresh weight, grain yield per plant, no. of grains per plant, chlorophyll contents, chlorophyll a/b ratio, total phenolics, MDA and total soluble protein contents under cadmium stress or non stress conditions.



Similar content being viewed by others
References
Abbas MS, Akmal M, Ullah S, Hassan MU, Farooq S (2017) Effectiveness of zinc and gypsum application against cadmium toxicity and accumulation in wheat (Triticum aestivum L.). Commun Soil Sci Plan 48(14):1659–1668
Akhtar T, Zia-ur-Rehman M, Naeem A, Nawaz R, Ali S, Murtaza G, Maqsood MA, Azhar M, Khalid H, Rizwan M (2017) Photosynthesis and growth response of maize (Zea mays L.) hybrids exposed to cadmium stress. Environ Sci Pollut Res 24(6):5521–5529
Al-Qurainy F, Khan S, Tarroum M, Nadeem M, Alansi S, Alshameri A (2017) Biochemical and genetical responses of Phoenix dactylifera L. to cadmium stress. Biomed Res Int. https://doi.org/10.1155/2017/9504057
Arnon DI (1949) Copper enzymes in isolated chloroplasts. Polyphenoloxidase in Beta vulgaris. Plant physiol 24:1–15
Ashraf MY, Roohi M, Iqbal Z, Ashraf M, Ozturk M, Gucel S (2016) Cadmium (Cd) and lead (Pb) induced changes in growth, some biochemical attributes, and mineral accumulation in two cultivars of mung bean [Vigna radiata (L.) Wilczek]. Commun Soil Sci Plant 47(4):405–413
Bates LS, Waldren RP, Teare ID (1973) Rapid determination of free proline for water-stress studies. Plant Soil 39:205–207
Bradford MM (1976) A rapid and sensitive method for the quantitation of microgram quantities of protein utilizing the principle of protein-dye binding. Anal Biochem 72:248–254
Cakmak I, Strbac D, Marschner H (1993) Activities of hydrogen peroxide scavenging enzymes in germinated wheat seeds. J Exp Bot 44:127–132
Carmak I, Horst JH (1991) Effects of aluminum on lipid peroxidation, superoxide dismutase, catalase, and peroxidase activities in root tips of soybean (Glycine max). Plant Physiol 83:463–468
Chance B, Maehly AC (1955) Assay of catalases and peroxidases. Meth Enzymol 2:764–775
Fasahat P (2015) Recent progress in understanding cadmium toxicity and tolerance in rice. Emir J Food Agr 94–105
Ghosh R, Roy S (2019) Cadmium toxicity in plants: unveiling the physicochemical and molecular aspects. In: Cadmium tolerance in plants. Academic Press, pp 223–246
Gomez-Coronado F, Poblaciones MJ, Almeida AS, Cakmak I (2016) Zinc (Zn) concentration of bread wheat grown under Mediterranean conditions as affected by genotype and soil/foliar Zn application. Plant Soil 401:331–346
Grieve CM, Grattan SR (1983) Rapid assay for determination of water soluble quaternary ammonium compounds. Plant Soil 70:303–307
Guo H, Hong C, Chen X, Xu Y, Liu Y, Jiang D, Zheng B (2016) Different growth and physiological responses to cadmium of the three Miscanthus species. PLoS ONE 11(4):e0153475
Guo G, Lei M, Wang Y, Song B, Yang J (2018) Accumulation of As, Cd, and Pb in sixteen wheat cultivars grown in contaminated soils and associated health risk assessment. Int J Environ Res Public Health 15:2601
Haider MU, Farooq M, Nawaz A, Hussain M (2018) Foliage applied zinc ensures better growth, yield and grain biofortification of mungbean. Int J Agric Biol 37(2):123–128
Hashem HA (2014) Cadmium toxicity induces lipid peroxidation and alters cytokinin content and antioxidant enzyme activities in soybean. Botany 92(1):1–7
Hatamian M, Nejad AR, Kafi M, Souri MK, Shahbazi K (2020) Nitrate improves hackberry seedling growth under cadmium application. Heliyon 6(1):e03247
Hirzel J, Retamal-Salgado J, Walter I, Matus I (2017) Cadmium accumulation and distribution in plants of three durum wheat cultivars under different agricultural environments in Chile. J Soil Water Conserv 72:77–88
Hussain I, Ashraf MA, Rasheed R, Asghar A, Sajid MA, Iqbal M (2015) Exogenous application of silicon at the boot stage decreases accumulation of cadmium in wheat (Triticum aestivum L.) grains. Braz J Bot 38:223–234
Hussain A, Ali S, Rizwan M, Rehman MZU, Javed MR, Imran M, Chatha SAS, Nazir R (2018) Zinc oxide nanoparticles alter the wheat physiological response and reduce the cadmium uptake by plants. Environ Pollut 242:1518–1526
Ibrahim MH, Chee Kong Y, Zain M, Amalina N (2017) Effect of cadmium and copper exposure on growth, secondary metabolites and antioxidant activity in the medicinal plant Sambung Nyawa (Gynura procumbens (Lour.) Merr). Molecules 22(10):1623
Jiao Y, Grant CA, Bailey L (2020) Effects of phosphorus and zinc fertilizer on cadmium uptake and distribution in flax and durum wheat. J Sci Food Agric 84:777–785
Julkenen-Titto R (1985) Phenolic constituents in the leaves of northern willows: methods for the analysis of certain phenolics. J Agr Food Chem 33:213–217
Kapoor D, Bhardwaj R (2020) Cadmium stress responses in Brassica juncea L. plants through histochemical and qualitative approaches. Plant Cell Biotech Mol Biol 21(3–4):61–66
Krivosheeva A, Tao DL, Ottander C, Wingsle G, Dube SL, Quist G (1996) Cold acclimation and photoinhibition of photosynthesis in Scots pine. Planta 200:296–305
Li H, Liu X, Wassie M, Chen L (2020) Selenium supplementation alleviates cadmium-induced damages in tall fescue through modulating antioxidant system, photosynthesis efficiency, and gene expression. Environ Sci Pollut Res 1–13
Ling T, Gao Q, Du H, Zhao Q, Ren J (2017) Growing, physiological responses and Cd uptake of corn (Zea mays L.) under different Cd supply. Che Spec Bioavailab 29(1):216–221
Liu LT, Sun HC, Chen J, Zhang YJ, Wang XD, Li DX, Li CD (2016) Cotton seedling plants adapted to cadmium stress by enhanced activities of protective enzymes. Plant Soil Environ 62(2):80–85
Loi NN, Sanzharova NI, Shchagina NI, Mironova MP (2018) The effect of cadmium toxicity on the development of Lettuce plants on contaminated sod-podzolic soil. Russ Agric Sci 44(1):49–52
Lu M, Cao X, Pan J, Li T, Khan MB, Gurajala HK, He Z, Yang X (2020) Identification of wheat (Triticum aestivum L.) genotypes for food safety on two different cadmium contaminated soils. Environ Sci Pollut Res 27:7943–7956
Rabelo FHS, Lux A, Rossi ML, Martinelli AP, Cuypers A, Lavres J (2018) Adequate S supply reduces the damage of high Cd exposure in roots and increases N, S and Mn uptake by Massai grass grown in hydroponics. Environ exp 148:35–46
Rai PK, Lee SS, Zhang M, Tsang YF, Kim KH (2019) Heavy metals in food crops: health risks, fate, mechanisms, and management. Environ Int 125:365–385
Rehman MZU, Khalid H, Akmal F, Ali S, Rizwan M, Qayyum MF, Iqbal M, Khalid MU, Azhar M (2017) Effect of limestone, lignite and biochar applied alone and combined on cadmium uptake in wheat and rice under rotation in an effluent irrigated field. Environ Pollut 227:560–568
Rehman MZU, Rizwan M, Hussain A, Saqib M, Ali S, Sohail MI, Shafiq M, Hafeez F (2018) Alleviation of cadmium (Cd) toxicity and minimizing its uptake in wheat (Triticum aestivum) by using organic carbon sources in Cd-spiked soil. Environ Pollut 241:557–565
Rehman MZU, Zafar M, Waris AA, Rizwan M, Ali S, Sabir M, Usman M, Ayub MA, Ahmad Z (2020) Residual effects of frequently available organic amendments on cadmium bioavailability and accumulation in wheat. Chemosphere 244:125548
Saifullah A, Javed H, Naeem A, Rengel Z, Dahlawi S (2016) Timing of foliar Zn application plays a vital role in minimizing Cd accumulation in wheat. Environ Sci Pollut Res Int 23:16432–16439
Sazawal S, Dhingra U, Dhingra P, Dutta A, Deb S, Kumar J, Devi P, Prakash A (2018) Efficacy of high zinc biofortified wheat in improvement of micronutrient status, and prevention of morbidity among preschool children and women—a double masked, randomized, controlled trial. Nutr J 17:86
Snedecor GW, Cochran GW (1980) Statistical methods, 7th edn. The Lowa State University Press, Ames
Sobolewska M, Wenda-Piesik A, Jaroszewska A, Stankowski S (2020) Effect of habitat and foliar fertilization with K, Zn and Mn on winter wheat grain and baking qualities. Agronomy 10:276
Sohail MI, Rehman MZU, Rizwan M, Yousaf B, Ali S, Haq MAU, Anayat A, Waris AA (2020) Efficiency of various silicon rich amendments on growth and cadmium accumulation in field grown cereals and health risk assessment. Chemosphere 244:125481
Song X, Yue X, Chen W, Jiang H, Han Y, Li X (2019) Detection of cadmium risk to the photosynthetic performance of Hybrid Pennisetum. Front Plant Sci 10:798
Ulusu Y, Ozturk L, Elmastaş M (2017) Antioxidant capacity and cadmium accumulation in parsley seedlings exposed to cadmium stress. Russ J Plant Physiol 64(6):883–888
Vatehova Z, Malovikova A, Kollarova K, Kucerova D, Liskova D (2016) Impact of cadmium stress on two maize hybrids. Plant Physiol Biochem 108:90–98
Velikova V, Yordanov I, Edreva A (2000) Oxidative stress and some antioxidant systems in acid rain-treated bean plants: protective role of exogenous polyamines. Plant Sci 151:59–66
Wang S, Zhao Y, Guo J, Zhou L (2016) Effects of Cd, Cu and Zn on Ricinus communis L. growth in single element or cocontaminated soils: pot experiments. Ecol Eng 90:347–351
Wu C, Dun Y, Zhang Z, Li M, Wu G (2020) Foliar application of selenium and zinc to alleviate wheat (Triticum aestivum L) cadmium toxicity and uptake from cadmium-contaminated soil. Ecotoxicol Environ Saf 190:110091
Xuebin Q, Yatao X, Ahmad MI, Shehzad M, Zain M (2020) Silicon and its application methods improve physiological traits and antioxidants in Triticum aestivum (L.) under cadmium stress. J Soil Sci Plant Nutr 1–12
Yang Y, Zhang L, Huang X, Zhou Y, Quan Q, Li Y, Zhu X (2020) Response of photosynthesis to different concentrations of heavy metals in Davidia involucrata. PLoS ONE 15(3):e0228563
Acknowledgements
This research article is extracted from thesis of M.Phil. study of Mr. Muhammad Tariq Javed working under the supervision of Dr. Shagufta Perveen.
Funding
All authors contributed equally in the writing of manuscript. Dr. SP designed the experiment and written the manuscript, while MTJ performed the experiment. Furthermore, Dr. MS, AP, SZ and NI did proofreading of the final manuscript.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Perveen, S., Saeed, M., Parveen, A. et al. Modulation of growth and key physiobiochemical attributes after foliar application of zinc sulphate (ZnSO4) on wheat (Triticum aestivum L.) under cadmium (Cd) stress. Physiol Mol Biol Plants 26, 1787–1797 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12298-020-00861-8
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12298-020-00861-8