Abstract
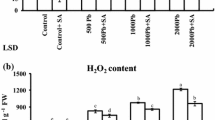
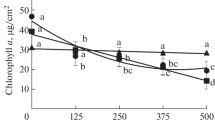
Impact of spraying 50 µM salicylic acid (SA), lead nitrate soil treatments [1 and 2 mM Pb (NO3)2] and their combinations on parsley leaves (Petroselinum crispum L.) for 3 weeks was studied to evaluate leaf symptoms, photosynthetic pigments, anthocyanin, ultrastructure, malondialdehyde (MDA), soluble proteins, phenolic compounds, and guaiacol peroxidase activity (GPOX). Under Pb effect, parsley leaves showed chlorosis and decline in the content of photosynthetic pigments chlorophyll a (Chl a), chlorophyll b (Chl b) and carotenoid (Car) with increasing Pb treatments compared to the control. SA spraying helped to reduce chlorosis and increase photosynthetic pigments of Pb-treated plants compared to that of Pb treatment alone. Leaf anthocyanin content of SA-sprayed plants significantly increased compared to the control. On contrast, the anthocyanin content of Pb-treated plants with or without SA treatment decreased compared to the control. Parsley leaf chloroplasts were characterized by many and large starch grains. Deformations of chloroplast shape, increasing formation of plastoglobules and degeneration of chloroplast grana thylakoids were observed in Pb-treated plants. MDA and total phenolic compound contents increased in Pb-treated plants compared to the control. In contrast, soluble protein content decreased in Pb-treated plants. The decrease in leaf photosynthetic pigments and increase MDA contents was Pb-concentration dependent. The results as indicated by increasing lipid peroxidation confirmed Pb treatments generated reactive oxygen species (ROS) which caused oxidative stress. In contrast, SA application declined the extent of detrimental and harmful influence of Pb toxicity as indicated by the decrease MDA content, and increase in photosynthetic pigments, anthocyanin and phenolic compound contents of parsley leaves.







Similar content being viewed by others
Abbreviations
- Car:
-
Carotenoids
- Chl:
-
Chlorophyll
- FW:
-
Fresh weight
- GPOX:
-
Guaiacol peroxidase
- MDA:
-
Malondialdehyde
- Pb:
-
Lead
- ROS:
-
Reactive oxygen species
- SA:
-
Salicylic acid
- TBARS:
-
Thiobarbituric acid reactive substance
References
Abdul Halim NI, Phang IC (2017) Salicylic acid mitigates Pb stress in Nicotiana tabacum. Sci Herit J/G War Sains (GWS) 1:16–19
Akinci IE, Akinci S, Yilmaz K (2010) Response of tomato (Solanum lycopersicum L.) to lead toxicity: growth, element uptake, chlorophyll and water content. Afr J Agric Res 5:416–423
Alberto L, Rabino MI (1975) Photocontrol of anthocyanin synthesis IV dose dependence and reciprocity relationships in anthocyanin synthesis. Plant Physiol 56:351–355
Allam AA, Maodaa SN, Abo-Eleneen R, Ajarem J (2016) Protective effect of parsley juice (Petroselinum crispum, Apiaceae) against cadmium deleterious changes in the developed albino mice newborns (Mus musculus) brain. Oxid Med Cell Longev 2016:2646840
Alves LQ, deJesus RM, deAlmeida AAF, SouzaVL Mangabeira PAO (2014) Effects of lead on anatomy, ultrastructure and concentration of nutrients in plants Oxycaryum cubense (Poep & Kunth) Palla: a species with phytoremediator potential in contaminated watersheds. Environ Sci Pollut Res 21:6558–6570
Ananieva EA, Christov KN, Popova LP (2004) Exogenous treatment with salicylic acid leads to increased antioxidant capacity in leaves of barley plants exposed to paraquat. J Plant Physiol 161:319–328
Ashraf U, Kanu AS, Deng Q, Mo Z, Pan S, Tian H, Tang X (2017) Lead (Pb) toxicity; physio-biochemical mechanisms, grain yield, quality, and Pb distribution proportions in scented rice. Front Plant Sci 8:259
Baghaie AH, Fereydoni M (2019) The potential risk of heavy metals on human health due to the daily consumption of vegetables. Environ Health Eng Manag J 6:11–16
Basile A, Sorbo S, Cardi M, Lentini M, Castiglia D, Cianciullo P, Conte B, Loppi S, Esposito S (2015) Effects of heavy metals on ultrastructure and Hsp70 induction in Lemna minor L. exposed to water along the Sarno River, Italy. Ecotoxicol Environ Saf 114:93–101
Bin Z, Chen J, Shafi M, Guo J, Wang Y, Wu J, Ye Z, He L, Liu D (2017) Effect of lead (Pb) on antioxidation system and accumulation ability of Moso bamboo (Phyllostachys pubescens). Ecotoxicol Environ Saf 138:71–77
Blokhina O, Virolainen E, Fagerstedt E (2003) Antioxidants, oxidative damage and oxygen deprivation stress: a review. Ann Bot 91:179–194
Borges KLR, Hippler FWR, Carvalho MEA, Nalin RS, Matias FI, Azevedo RA (2019) Nutritional status and root morphology of tomato under Cd-induced stress: comparing contrasting genotypes for metal-tolerance. Sci Hortic 246:518–527
Chen J, Zhu C, Li L-p, Sun Z-y, Pan X-b (2007) Effects of exogenous salicylic acid on growth and H2O2-metabolizing enzymes in rice seedlings under lead stress. J Environ Sci 19:44–49
Cho U-H, Park J-O (2000) Mercury-induced oxidative stress in tomato seedlings. Plant Sci 156:1–9
Costa RM, Magalhãs AS, Pereira JA, Andrade PB, Valentão P, Carvalho M, Silva BM (2009) Evaluation of free radical scavenging and antihemolytic activities of quince (Cydoniao blonga) leaf: a comparative study with green tea (Cammelia sinensis). Food Chem Toxicol 47:860
Dai GH, Andary C, Cosson-Monodol L, Boubals D (1994) Polyphenols and resistance of grapevines to downy mildew. Acta Hortic 381:763–766
Dao LHT, Beardall J (2016) Effects of lead on growth, photosynthetic characteristics and production of reactive oxygen species of two freshwater green algae. Chemosphere 147:420–429
Devi R, Munjral N, Gupta AK, Kaur N (2013) Effect of exogenous lead on growth and carbon metabolism of pea (Pisum sativum L.) seedlings. Physiol Mol Biol Plants 19:81–89
Díaz-Maroto MC, Vinas MAG, Cabezudo MD (2003) Evaluation of the effect of drying on aroma of parsley by free choice profiling. Eur Food Res Technol 216:227–232
Dong J, Wan G, Liang Z (2010) Accumulation of salicylic acid-induced phenolic compounds and raised activities of secondary metabolic and antioxidative enzymes in Salvia miltiorrhiza cell culture. J Biotechnol 148:99–104
Eick MJ, Peak JD, Brady PV, Pesek JD (1999) Kinetics of lead adsorption and desorption on goethite: residence time effect. J Soil Sci 164:28–39
Farmer EE, Mueller MJ (2013) ROS-mediated lipid peroxidation and RES-activated signaling. Annu Rev Plant Biol 64:429–450
Farzaei MH, Abbasabadi Z, Reza M, Ardekani S, Rahimi R (2013) Parsley: a review of ethnopharmacology, phytochemistry and biological activities. J Traditional Chin Med 33:815–826
Fayez KA (2017) Action of cadmium toxicity on growth, physiological activities and subcellular components of watercress (Eruca sativa L.) plant: the protective role of salicylic acid. Res J Pharm Biol Chem Sci 8:1853–1865
Fayez KA, Bazaid SA (2014) Improving drought and salinity tolerance in barley by application of salicylic acid and potassium nitrate. J Saudi Soc Agric Sci 13:45–55
Fayez KA, Mahmoud SY (2011) Detection and partial characterization of a putative closterovirus affecting Ficus carica: molecular, ultrastructural and physiological aspects of infected leaves. Acta Physiol Plant 33:2187–2198
Fayez KA, Radwan DEM, Mohamed AK, Abdelrahman AM (2011) Herbicides and salicylic acid applications caused alterations in total amino acids and proline contents of peanut cultivars. J Environ Stu (JES) 6:55–61
Fayez KA, Radwan DEM, Mohamed AK, Abdelrahman AM (2014) Fusilade herbicide causes alterations in chloroplast ultrastructure, pigment content and physiological activities of peanut leaves. Photosynthetica 52:548–554
Figlioli F, Sorrentino MC, Memoli V, Arena C, Maisto G, Giordano S, Capozzi F, Spagnuolo V (2019) Overall plant responses to Cd and Pb metal stress in maize: growth pattern, ultrastructure, and photosynthetic activity. Environ Sci Pollut Res 26:1781–1790
Fragnière C, Serrano M, Abou-Mansour E, Métraux J-P, L’Haridon F (2011) Salicylic acid and its location in response to biotic and abiotic stress. FEBS Lett 585:1847–1852
Gill SS, Tuteja N (2010) Reactive oxygen species and antioxidant machinery in abiotic stress tolerance in crop plants. Plant Physiol Biochem 48:909–930
Gupta DK, Nicoloso FT, Schetinger MRC, Rossato LV, Pereira LB, Castro GY, Srivastava S, Tripathi RD (2009) Antioxidant defense mechanism in hydroponically grown Zea mays seedlings under moderate lead stress. J Hazard Mater 172:479–484
Gupta DK, Huang HG, Corpas FJ (2013) Lead tolerance in plants: strategies for phytoremediation. Environ Sci Pollut Res Int 20:2150–2161
Hakmaoui A, Ater M, Boka K, Baron M (2007) Copper and cadmium tolerance, uptake and effect on chloroplast ultrastructure. Studies on Salix purpurea and Phragmitesaustralis. Z Naturforsch 62:417–426
Halliwell B, Gutteridge JMC (1999) Free radicals in biology and medicine. Oxford University Press, Oxford
Hattab S, Flores-Casseres ML, Boussetta H, Doumas P, Hernandez LE, Banni M (2016) Characterisation of lead-induced stress molecular biomarkers in Medicago sativa plants. Environ Exp Bot 123:1–12
Hayat Q, Hayat S, Irfan M, Ahmad A (2010) Effect of exogenous salicylic acid under changing environment: a review. Environ Exp Bot 68:14–25
Hernández JA, Almansa MS (2002) Short-term effects of salt stress on antioxidant systems and leaf water relations of pea leaves. Physiol Plant 115:251–257
Horváth E, Pál M, Szalai G, Páldi E, Janda T (2007a) Exogenous 4-hydroxybenzoic acid and salicylic acid modulate the effect of short-term drought and freezing stress on wheat plants. Biol Plant 51:480–487
Horváth E, Szalai G, Janda T (2007b) Induction of abiotic stress tolerance by salicylic acid signaling. J Plant Growth Regul 26:290–300
Hu ZR, Xie Y, Jin GF, Fu JM, Li HY (2015) Growth responses of two tall fescue cultivars to Pb stress and their metal accumulation characteristics. Ecotoxicology 24:563–572
Islam E, Liu D, Li T, Yang X, Jin X, Mahmood Q, Tian S, Li J (2008) Effect of Pb toxicity on leaf growth, physiology and ultrastructure in the two ecotypes of Elsholtzia argyi. J Hazard Mater 154:914–926
Jaishankar M, Tseten T, Anbalagan N, Mathew BB, Beeregowda KN (2014) Toxicity, mechanism and health effects of some heavy metals. Interdiscip Toxicol 7:60–72
Kaur G, Singh HP, Batish DR, Kohli RK (2012) A time course assessment of changes in reactive oxygen species generation and antioxidant defense in hydroponically grown wheat in response to lead ions (Pb2+). Protoplasma 249:1091–1100
Khan MIR, Fatma M, Per TS, Anjum NA, Khan NA (2015) Salicylic acid-induced abiotic stress tolerance and underlying mechanisms in plants. Front Plant Sci 6:462
Khan A, Khan S, Alam M, Khan MA, Aamir M, Qamar Z, Rehman ZU, Perveen S (2016) Toxic metal interactions affect the bioaccumulation and dietary intake of macro- and micro-nutrients. Chemosphere 146:121–128
Khan MS, Akther T, Mubarak Ali D, Hemalatha S (2019) An investigation on the role of salicylic acid alleviate the saline stress in rice crop (Oryza sativa (L). Biocat Agric Biotechnol 18:101027
Kumar A, Prasad MNV, Sytar O (2012) Lead toxicity, defense strategies and associated indicative biomarkers in Talinum triangulare grown hydroponically. Chemosphere 89:1056–1065
Lamhamdi M, Bakrim A, Aarab A, Lafont R, Sayah F (2011) Lead phytotoxicity on wheat (Triticum aestivum L.) seed germination and seedlings growth. CR Biol 334:118–126
Lamhamdi M, El Galiou O, Bakrim A, Nóvoa-Muñoz JC, Arias-Estévez M, Aarab A, Lafont R (2013) Effect of lead stress on mineral content and growth of wheat (Triticum aestivum) and spinach (Spinacia oleracea) seedlings. Saudi J Biol Sci 20:29–36
Legocka J, Sobieszczuk-Nowicka E, Wojtyla Ł, Samardakiewicz S (2015) Lead-stress induced changes in the content of free, thylakoid- and chromatin- bound polyamines, photosynthetic parameters and ultrastructure in greening barley leaves. J Plant Physiol 186–187:15–24
Li X, Bu N, Li Y, Ma L, Xin S, Zhang L (2012) Growth, photosynthesis and antioxidant responses of endophyte infected and non-infected rice under lead stress conditions. J Hazard Mater 213–214:55–61
Li N, Kang Y, Pan W, Zeng L, Zhang Q, Luo J (2015) Concentration and transportation of heavy metals in vegetables and risk assessment of human exposure to bioaccessible heavy metals in soil near a waste-incinerator site, South China. Sci Total Environ 521–522:144–151
López-Orenes A, Martínez-Pérez A, Calderón AA, Ferrer MA (2014) Pb-induced responses in Zygophyllum fabago plants are organ-dependent and modulated by salicylic acid. Plant Physiol Biochem 84:57–66
Lowry OH, Rosebrough NJ, Farr AI, Randall RJ (1951) Protein measurement with the folin phenol reagent. J Biol Chem 193:291–297
Luft JH (1961) Improvements in epoxy embedding methods. J Biophys Biochem Cytol 9:409–414
Mahmood A, Malik RN (2014) Human health risk assessment of heavy metals via consumption of contaminated vegetables collected from different irrigation sources in Lahore. Pak Arab J Chem 7:91–99
Malar S, Shivendra Vikram S, JC Favas P, Perumal V (2014) Lead heavy metal toxicity induced changes on growth and antioxidative enzymes level in water hyacinths [Eichhornia crassipes (Mart.)]. Bot Stud 55:54
Malecka A, Jarmuszkiewicz W, Tomaszewska B (2001) Antioxidative defense to lead stress in subcellular compartments of pea root cells. Acta Biochim Polon 48:687–698
Malenčić DJ, Kiprovski B, Popović M, Prvulović D, Miladinović J, Djordjević V (2010) Changes in antioxidant systems in soybean as affected by Sclerotinia sclerotiorum (Lib.) de Bary. Plant Physiol Biochem 48:903–908
Metzner H, Rau H, Senger H (1965) Untersuchungen zur Synchronisierbakeit einzelner Pigmentmangel-Mutanten von Chlorella. Planta 65:186–194
Michalak A (2006) Phenolic compounds and their antioxidant activity in plants growing under heavy metal stress. Polish J Environ Stud 15:523–530
Mihailovic N, Andrejić G, Dželetović Ž (2015) Tolerance of Portulaca grandiflora to individual and combined application of Ni, Pb and Zn. Bull Environ Contam Toxicol 194:103–107
Minkina T, Fedorenko G, Nevidomskaya D, Fedorenko A, Chaplygin V, Mandzhieva S (2018) Morphological and anatomical changes of Phragmites australis Cav. due to the uptake and accumulation of heavy metals from polluted soils. Sci Total Environ 636:392–401
Miteva E, Hristova D, Nenova V, Maneva S (2005) Arsenic as a factor affecting virus infection in tomato plants: changes in plant growth, peroxidase activity and chloroplast pigments. Sci Hortic 105:343–358
Mittler R (2002) Oxidative stress, antioxidants and stress tolerance. Trends Plant Sci 7:405–410
Mittler R (2017) ROS are good. Trends Plant Sci 22:11–19
Mohan BS, Hosetti BB (1997) Potential phytotoxicity of leaf and cadmium to Lemna minor grown in sewage stabilization ponds. Environ Pollut 98:233–238
Noctor G, Lelarge-Trouverie C, Mhamdi A (2015) The metabolic of oxidative stress. Phytochemistry 112:33–53
Oliveira AP, Valenao P, Pereira JA, Silva BM, Tavares F, Andrade PB (2009) Ficus carica L.: metabolic and biological screening. Food Chem Toxicol 47:2841–2846
Polle A, Otter T, Seifert F (1994) Apoplastic peroxidases and lignification in needles of Norway spruce (Picea abies L.). Plant Physiol 106:53–60
Rahmat A, Ahmad NSS, Ramli NS (2019) Parsley (Petroselinum crispum) supplementation attenuates serum uric acid level and improves liver and kidney structures in oxonate-induced hyperuricemic rats. Orien Pharm Exp Med 19:393–401
Reddy AM, Kumar SG, Jyonthsnakumari G, Thimmanaik S, Sudhakar C (2005) Lead induced changes in antioxidant metabolism of horsegram (Macrotyloma uniflorum (Lam.) Verdc.) and bengalgram (Cicer arietinum L.). Chemosphere 60:97–104
Salazar MJ, Pignata ML (2014) Lead accumulation in plants grown in polluted soils. Screening of native species for phytoremediation. J Geochem Explor 137:29–36
Sapkota B, Cioppa MT (2012) Using magnetic and chemical measurements to detect atmospherically-derived metal pollution in artificial soils and metal uptake in plants. Environ Pollut 170:131–144
Schrech E, Foucault Y, Sarret G, Sobanska S, Cécillon L, Castrec-Rouelle M, Uzu G, Dumat C (2012) Metal and metalloid foliar uptake by various plant species exposed to atmospheric industrial fallout: mechanisms involved for lead. Sci Tot Environ 427–428:253–262
Schreck E, Laplanche C, Le Guédard M, Bessoule J-J, Austruy A, Xiong T, Foucault Y, Dumat C (2013) Influence of fine process particles enriched with metals and metalloids on Lactuca sativa L. leaf fatty acid composition following air and/or soil-plant field exposure. Environ Pollut 179:242–249
Sęczyk Ł, Świeca M, Gawlik-Dziki U, Luty M, Czyż J (2016) Effect of fortification with parsley (Petroselinum crispum Mill.) leaves on the nutraceutical and nutritional quality of wheat pasta. Food Chem 190:419–428
Sengar RS, Pandey M (1996) Inhibition of chlorophyll biosynthesis by lead in greening Pisum sativum leaf segment. Biol Plant 38:459–462
Shah K, Kumar RG, Verma S, Dubey RS (2001) Effect of cadmium on lipid peroxidation, superoxide anion generation and activities of antioxidant enzymes in growing rice seedlings. Plant Sci 161:1135–1144
Shahid M, Dumat C, Pourrut B, Silvestre J, Laplanche C, Pinelli E (2014) Influence of EDTA and citric acid on lead-induced oxidative stress to Vicia faba roots. J Soils Sediments 14:835–843
Sharma P, Dubey RS (2005) Lead toxicity in plants. Braz J Plant Physiol 17:35–52
Sharma P, Jha AB, Dubey RS, Pessarakli M (2012) Reactive oxygen species, oxidative damage and antioxidative defense mechanism in plants under stressful conditions. J Bot 2012:217037
Sidhu GPS, Singh HP, Batish DR, Kohli RK (2016) Effect of lead on oxidative status, antioxidative response and metal accumulation in Coronopus didymus. Plant Physiol Biochem 105:290–296
Sidhu GPS, Singh HP, Batish DR, Kohli RK (2017) Alterations in photosynthetic pigments, protein, and carbohydrate metabolism in a wild plant Coronopus didymus L. (Brassicaceae) under lead stress. Acta Physiol Plant 39:176
Singh R, Tripathi RD, Dwivedi S, Kumar A, Trivedi PK, Chakrabarty D (2010) Lead bioaccumulation potential of an aquatic macrophyte Najas indica are related to antioxidant system. Bioresour Technol 101:3025–3032
Soares C, Carvalho MEA, Azevedo RA, Fidalgo F (2019) Plants facing oxidative challenges—a little help from the antioxidant networks. Environ Exp Bot 161:4–25
Song W, Zheng A, Shao H, Chu L, Brestic M, Zhang Z (2012) The alleviative effect of salicylic acid on the physiological indices of the seedling leaves in six different wheat genotypes under lead stress. Plant Omics 5:486–493
Soysal Y (2004) Microwave drying characteristics of parsley. Biosyst Eng 89:167–173
Srivastava M, Ma LQ, Singh N, Singh S (2005) Antioxidant responses of hyper-accumulator and sensitive fern species to arsenic. J Exp Bot 56:1335–1342
Tauqeer HM, Ali S, Rizwan M, Ali Q, Saeed R, Iftikhar U, Ahmad R, Farid M, Abbasi GH (2016) Phytoremediation of heavy metals by Alternanthera bettzickiana: growth and physiological response. Ecotoxicol Environ Saf 126:138–146
Tolrá R, Barcelo J, Poschenrieder CH (2009) Constitutive and aluminium-induced patterns of phenolic compounds in two maize varieties differing in aluminium tolerance. J Inorg Biochem 103:1486–1490
Uzu G, Sobanska S, Sarret G, Munoz M, Dumat C (2010) Foliar lead uptake by lettuce exposed to atmospheric fallouts. Environ Sci Technol 44:1036–1042
Verma S, Dubey RS (2003) Lead toxicity induces lipid peroxidation and alters the activities of antioxidant enzymes in growing rice plants. Plant Sci 164:645–655
Wang C, Zhang S, Wang P, Hou J, Qian J, Ao Y, Lu J, Li L (2011) Salicylic acid involved in the regulation of nutrient elements uptake and oxidative stress in Vallisneria natans (Lour.) Hara under Pb stress. Chemosphere 84:136–142
Wassie M, Zhang W, Zhang Q, Ji K, Cao L, Chen L (2020) Exogenous salicylic acid ameliorates heat stress-induced damages and improves growth and photosynthetic efficiency in alfalfa (Medicago sativa L.). Ecotoxicol Environ Saf 191:110206
Wong PYY, Kitts DD (2006) Studies on the dual antioxidant and antibacterial properties of parsley (Petroselinum crispum) and cilantro (Coriandrum sativum) extracts. Food Chem 97:505–515
Yadav SK (2010) Heavy metals toxicity in plants: an overview on the role of glutathione and phytochelatins in heavy metal stress tolerance of plants. South Afri J Bot 76:167–179
Yan Y, Pan C, Du Y, Li D, Liu W (2018) Exogenous salicylic acid regulates reactive oxygen species metabolism and ascorbate-glutathione cycle in Nitraria tangutorum bobr under salinity stress. Physiol Mol Biol Plants 24:577–589
Yang J, Ye Z (2015) Antioxidant enzymes and proteins of wetland plants: their relation to Pb tolerance and accumulation. Environ Sci Pollu Res 22:1931–1939
Yüzbaşıoğlu E, Dalyan E (2019) Salicylic acid alleviates thiram toxicity by modulating antioxidant enzyme capacity and pesticide detoxification systems in the tomato (Solanum lycopersicum Mill.). Plant Physiol Biochem 135:322–330
Zanganeh R, Jamei R, Rahmani F (2019) Role of salicylic acid and hydrogen sulfide in promoting lead stress tolerance and regulating free amino acid composition in Zea mays L. Acta Physiol Plant 41:94
Zhou ZS, Guo K, Elbaz AA, Yang ZM (2009) Salicylic acid alleviates mercury toxicity by preventing oxidative stress in roots of Medicago sativa. Environ Exp Bot 65:27–34
Zhou J, Zhang Z, Zhang Y, Wei Y, Jiang Z (2018) Effects of lead stress on the growth, physiology, and cellular structure of privet seedlings. PLoS ONE 13:e0191139
Acknowledgements
The research was financially supported by Taif University (Project number: 1-438-5902), Taif University, Saudi Arabia.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Alamer, K.H., Fayez, K.A. Impact of salicylic acid on the growth and physiological activities of parsley plants under lead toxicity. Physiol Mol Biol Plants 26, 1361–1373 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12298-020-00830-1
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12298-020-00830-1